Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) enable peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trading without intermediaries, offering enhanced security and user control. Liquidity pools, integral to DEXs, provide the necessary assets by incentivizing users to supply funds, ensuring continuous market liquidity and reducing slippage. Explore how these components transform the landscape of decentralized finance and empower traders globally.
Why it is important
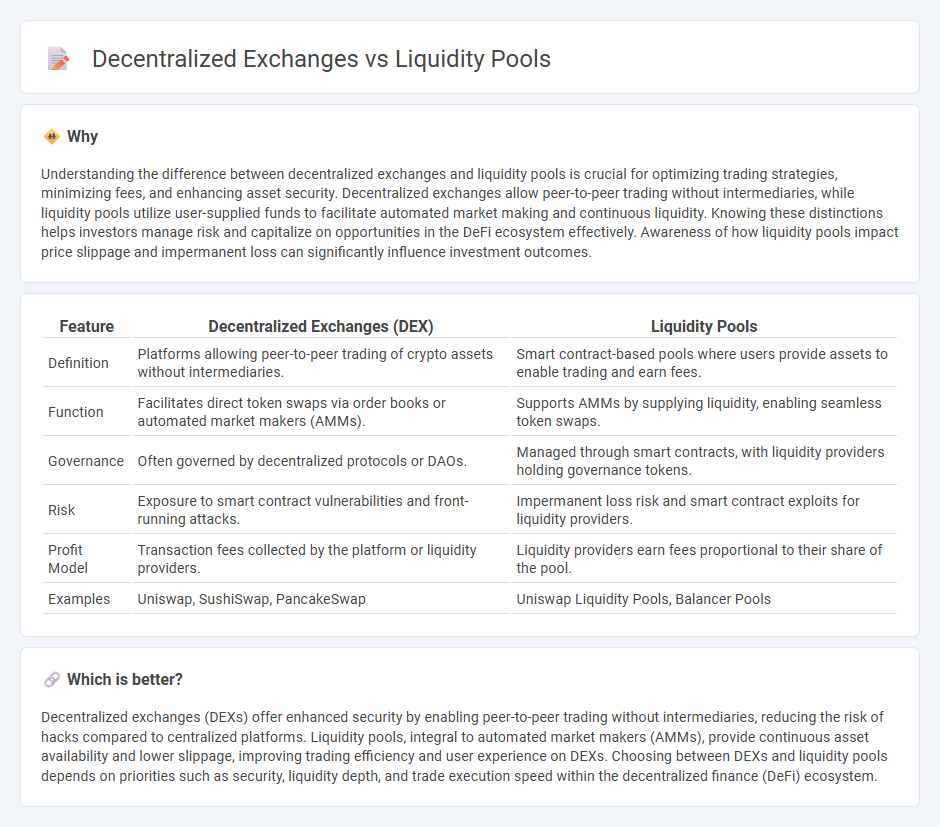
Understanding the difference between decentralized exchanges and liquidity pools is crucial for optimizing trading strategies, minimizing fees, and enhancing asset security. Decentralized exchanges allow peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries, while liquidity pools utilize user-supplied funds to facilitate automated market making and continuous liquidity. Knowing these distinctions helps investors manage risk and capitalize on opportunities in the DeFi ecosystem effectively. Awareness of how liquidity pools impact price slippage and impermanent loss can significantly influence investment outcomes.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) | Liquidity Pools |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Platforms allowing peer-to-peer trading of crypto assets without intermediaries. | Smart contract-based pools where users provide assets to enable trading and earn fees. |
| Function | Facilitates direct token swaps via order books or automated market makers (AMMs). | Supports AMMs by supplying liquidity, enabling seamless token swaps. |
| Governance | Often governed by decentralized protocols or DAOs. | Managed through smart contracts, with liquidity providers holding governance tokens. |
| Risk | Exposure to smart contract vulnerabilities and front-running attacks. | Impermanent loss risk and smart contract exploits for liquidity providers. |
| Profit Model | Transaction fees collected by the platform or liquidity providers. | Liquidity providers earn fees proportional to their share of the pool. |
| Examples | Uniswap, SushiSwap, PancakeSwap | Uniswap Liquidity Pools, Balancer Pools |
Which is better?
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) offer enhanced security by enabling peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries, reducing the risk of hacks compared to centralized platforms. Liquidity pools, integral to automated market makers (AMMs), provide continuous asset availability and lower slippage, improving trading efficiency and user experience on DEXs. Choosing between DEXs and liquidity pools depends on priorities such as security, liquidity depth, and trade execution speed within the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem.
Connection
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) utilize liquidity pools to enable peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries, allowing users to trade cryptocurrencies directly from their wallets. Liquidity pools consist of pooled tokens funded by users that facilitate asset swaps by providing the required liquidity and minimizing slippage. This connection empowers automated market making (AMM) protocols, which rely on liquidity pools to maintain continuous, efficient trading on decentralized platforms.
Key Terms
Automated Market Maker (AMM)
Liquidity pools form the backbone of Automated Market Makers (AMMs) by providing the capital necessary for seamless, permissionless trading without relying on traditional order books. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) leverage AMMs to facilitate continuous asset swaps, ensuring price determination through algorithmic formulas based on pool token ratios. Discover how liquidity pools and AMMs drive innovation in decentralized trading ecosystems.
Token Swap
Liquidity pools enable seamless token swaps by aggregating user funds into smart contracts, providing the necessary liquidity for decentralized exchanges (DEXs) to operate without order books. Decentralized exchanges utilize these pools to facilitate direct peer-to-peer token swaps with minimal slippage and lower fees compared to centralized platforms. Explore how liquidity pools power efficient token swaps on DEXs and revolutionize decentralized trading.
Liquidity Provider
Liquidity providers play a crucial role in both liquidity pools and decentralized exchanges (DEXs) by supplying assets that enable seamless trading and ensure market depth. In liquidity pools, providers deposit token pairs into smart contracts to facilitate automated market making, earning fees proportional to their share of the pool. Explore how liquidity providers optimize returns and mitigate risks within these DeFi frameworks to enhance your understanding.
Source and External Links
Liquidity Pools Explained: How They Work, Key Risks & ... - A liquidity pool is a set of cryptocurrency tokens locked in a smart contract, enabling decentralized trading by anyone providing liquidity, offering benefits like continuous trading, efficient price discovery, and opportunities for yield farming with various pool types such as traditional two-token pools, stablecoin pools, and concentrated liquidity pools.
Liquidity Pools for Beginners: DeFi 101 - Liquidity pools facilitate decentralized trading by allowing users to deposit assets for specific pairs, earn fees from trades, and participate in yield farming, thus supporting the backbone of DeFi by enabling direct wallet trading and broad inclusion for liquidity providers.
The role of liquidity pools in cryptocurrency markets - Liquidity pools enable decentralized exchanges to operate without intermediaries by using smart contracts to hold pooled assets against which trades are made, rewarding liquidity providers with transaction fees, while carrying risks such as impermanent loss and smart contract vulnerabilities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com