Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to offer financial services without intermediaries, enhancing transparency and accessibility. Investment banking focuses on advisory, underwriting, and capital raising for corporations through centralized institutions. Explore how DeFi challenges traditional investment banking models and reshapes the financial landscape.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between decentralized finance (DeFi) and investment banking is crucial for making informed financial decisions and managing risks effectively. DeFi offers peer-to-peer financial services using blockchain technology, providing transparency and reduced intermediaries. Investment banking involves traditional financial institutions facilitating capital raising, mergers, and advisory services within regulated markets. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors identify suitable opportunities and navigate evolving financial landscapes.
Comparison Table
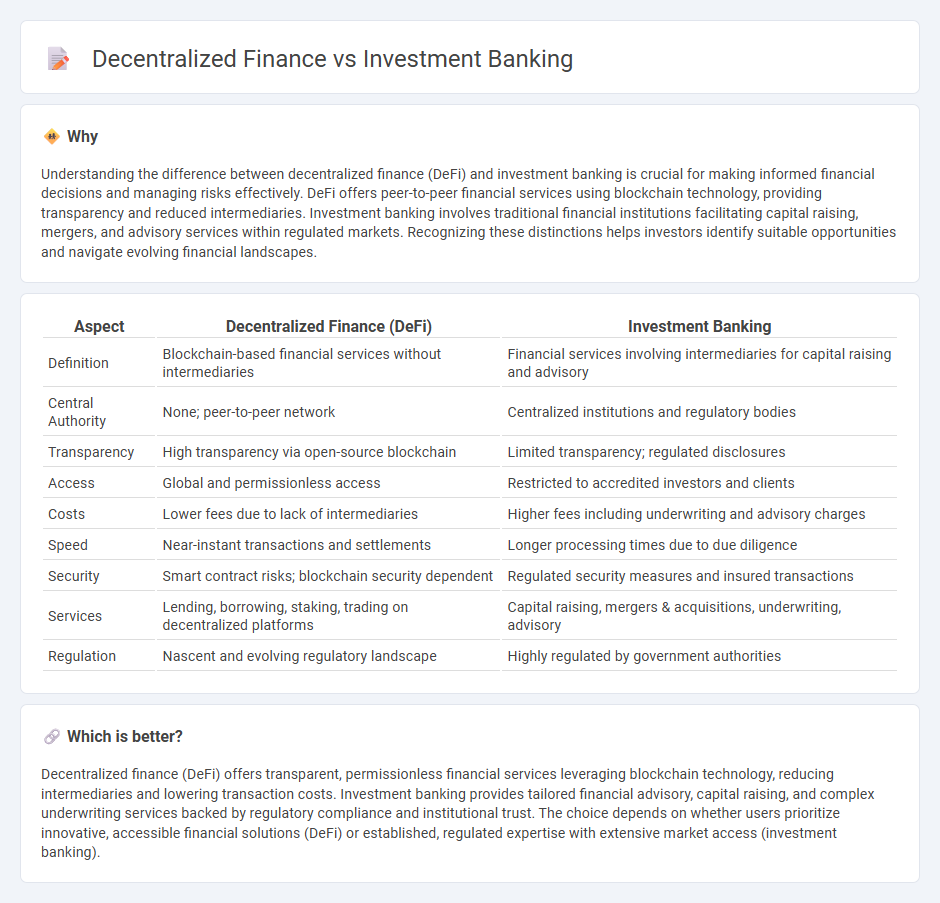
| Aspect | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) | Investment Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Blockchain-based financial services without intermediaries | Financial services involving intermediaries for capital raising and advisory |
| Central Authority | None; peer-to-peer network | Centralized institutions and regulatory bodies |
| Transparency | High transparency via open-source blockchain | Limited transparency; regulated disclosures |
| Access | Global and permissionless access | Restricted to accredited investors and clients |
| Costs | Lower fees due to lack of intermediaries | Higher fees including underwriting and advisory charges |
| Speed | Near-instant transactions and settlements | Longer processing times due to due diligence |
| Security | Smart contract risks; blockchain security dependent | Regulated security measures and insured transactions |
| Services | Lending, borrowing, staking, trading on decentralized platforms | Capital raising, mergers & acquisitions, underwriting, advisory |
| Regulation | Nascent and evolving regulatory landscape | Highly regulated by government authorities |
Which is better?
Decentralized finance (DeFi) offers transparent, permissionless financial services leveraging blockchain technology, reducing intermediaries and lowering transaction costs. Investment banking provides tailored financial advisory, capital raising, and complex underwriting services backed by regulatory compliance and institutional trust. The choice depends on whether users prioritize innovative, accessible financial solutions (DeFi) or established, regulated expertise with extensive market access (investment banking).
Connection
Decentralized finance (DeFi) disrupts traditional investment banking by enabling peer-to-peer financial transactions through blockchain technology, eliminating intermediaries and reducing costs. Investment banks are increasingly exploring partnerships with DeFi platforms to leverage smart contracts for automated asset management and enhanced liquidity solutions. This integration fosters innovation in capital markets, blending decentralized protocols with established financial infrastructures to optimize investment strategies and client services.
Key Terms
**Investment Banking:**
Investment banking centers on facilitating large-scale capital raising, mergers, and acquisitions, leveraging extensive regulatory frameworks and established financial intermediaries to provide tailored advisory and underwriting services. It plays a critical role in market liquidity and price discovery, supported by sophisticated risk management and compliance systems. Discover how investment banking shapes global financial markets and drives corporate growth strategies.
Underwriting
Investment banking underwriting involves financial institutions guaranteeing the sale of securities by purchasing them from issuers and reselling to investors, providing capital market efficiency and risk management. Decentralized finance (DeFi) underwriting leverages blockchain technology and smart contracts to automate risk assessment and capital allocation without intermediaries, potentially reducing costs and increasing transparency. Explore how these contrasting models reshape the future of capital raising and investment risk.
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)
Traditional investment banking plays a critical role in mergers and acquisitions (M&A) by offering advisory services, facilitating due diligence, and structuring complex financial transactions with regulatory oversight. Decentralized finance (DeFi) introduces blockchain-based smart contracts that enable automated, transparent, and potentially lower-cost M&A activities, though regulatory and scalability challenges remain. Explore the evolving landscape to understand how DeFi may redefine M&A processes alongside established investment banking models.
Source and External Links
What is an Investment Banker? | CFA Institute - Investment Bankers provide financial expertise, analytical skills, and persuasive communication to support clients with capital raising, mergers and acquisitions, and other corporate finance services, often working in demanding and fast-paced roles.
Investment Banking Overview - Corporate Finance Institute - Investment banking involves underwriting capital and advising on mergers and acquisitions by acting as intermediaries between investors and corporations, with full-service banks offering additional services like sales and trading and equity research.
Investment banking - Wikipedia - Investment banking is an advisory financial service focused on institutional clients, generating revenue mainly from fees for advising on transactions, with activities divided into "sell side" (e.g., underwriting, trading) and "buy side" (investment advice to institutions).
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com