Climate-linked derivatives enable investors to hedge risks associated with climate change impacts by tying financial returns to environmental outcomes. Green securitization involves pooling green assets, such as renewable energy projects or green loans, into tradable securities that finance sustainable initiatives. Explore how these innovative financial instruments are transforming environmental investment strategies and risk management.
Why it is important
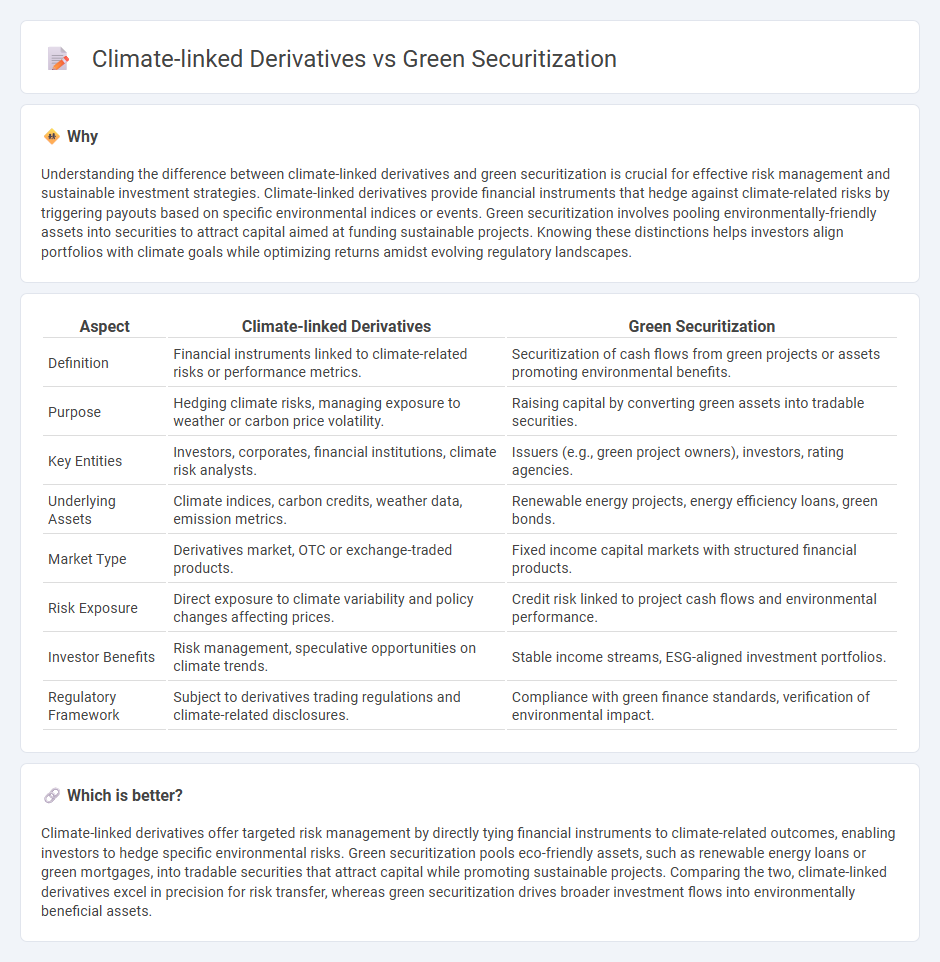
Understanding the difference between climate-linked derivatives and green securitization is crucial for effective risk management and sustainable investment strategies. Climate-linked derivatives provide financial instruments that hedge against climate-related risks by triggering payouts based on specific environmental indices or events. Green securitization involves pooling environmentally-friendly assets into securities to attract capital aimed at funding sustainable projects. Knowing these distinctions helps investors align portfolios with climate goals while optimizing returns amidst evolving regulatory landscapes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Climate-linked Derivatives | Green Securitization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial instruments linked to climate-related risks or performance metrics. | Securitization of cash flows from green projects or assets promoting environmental benefits. |
| Purpose | Hedging climate risks, managing exposure to weather or carbon price volatility. | Raising capital by converting green assets into tradable securities. |
| Key Entities | Investors, corporates, financial institutions, climate risk analysts. | Issuers (e.g., green project owners), investors, rating agencies. |
| Underlying Assets | Climate indices, carbon credits, weather data, emission metrics. | Renewable energy projects, energy efficiency loans, green bonds. |
| Market Type | Derivatives market, OTC or exchange-traded products. | Fixed income capital markets with structured financial products. |
| Risk Exposure | Direct exposure to climate variability and policy changes affecting prices. | Credit risk linked to project cash flows and environmental performance. |
| Investor Benefits | Risk management, speculative opportunities on climate trends. | Stable income streams, ESG-aligned investment portfolios. |
| Regulatory Framework | Subject to derivatives trading regulations and climate-related disclosures. | Compliance with green finance standards, verification of environmental impact. |
Which is better?
Climate-linked derivatives offer targeted risk management by directly tying financial instruments to climate-related outcomes, enabling investors to hedge specific environmental risks. Green securitization pools eco-friendly assets, such as renewable energy loans or green mortgages, into tradable securities that attract capital while promoting sustainable projects. Comparing the two, climate-linked derivatives excel in precision for risk transfer, whereas green securitization drives broader investment flows into environmentally beneficial assets.
Connection
Climate-linked derivatives provide financial instruments that hedge risks associated with environmental variables, directly complementing green securitization, which pools climate-friendly assets into tradable securities. Both mechanisms channel investment toward sustainable projects by quantifying and transferring climate-related risks, enhancing market liquidity and attracting capital to renewable energy and green infrastructure ventures. Integrating climate data within derivatives pricing enables more accurate risk assessment, thereby increasing investor confidence in green securitized products.
Key Terms
Asset-backed securities (ABS)
Green securitization involves pooling environmentally friendly assets such as green loans or renewable energy projects into asset-backed securities (ABS), enabling investors to fund sustainable initiatives while reducing carbon footprints. Climate-linked derivatives differ by providing financial instruments that hedge or speculate on climate-related risks, but they are not typically structured as ABS. Explore further to understand how green securitization transforms sustainability finance through tangible asset-backed collateral.
Environmental performance triggers
Green securitization structures asset-backed securities with cash flows tied to environmentally sustainable projects, using performance metrics like carbon emission reductions or renewable energy generation as triggers for payouts. Climate-linked derivatives are financial instruments whose payoffs depend on environmental indices such as temperature changes or precipitation levels, enabling risk management related to climate variability. Discover more about how these innovative financial tools integrate environmental performance triggers to drive sustainable investing.
Sustainability-linked swaps
Green securitization packages environmentally sustainable assets into tradable securities, promoting investment in renewable energy and green infrastructure, while climate-linked derivatives, particularly sustainability-linked swaps, offer risk management tools tied to specific environmental performance indicators such as carbon emission reductions. Sustainability-linked swaps provide financial incentives for companies to meet climate targets by adjusting cash flows based on sustainability metrics, enhancing alignment with ESG goals and regulatory frameworks. Explore the evolving role of sustainability-linked swaps in advancing corporate climate commitments and financial innovation.
Source and External Links
Green Securitization - NAP Global Network - Green securitization is a financial instrument where cash flows come from loans funding low-carbon assets, enabling companies to pool and sell such assets to investors, with common applications in renewable energy, water, transport, and urban development sectors.
Revamping Green Securitization Frameworks in the EU - The EU is developing regulatory frameworks to govern green securitization, using standards like the EU Green Bond Standard to promote sustainable investments while protecting investors in securitized green products.
Green Securisation - EBF - European Banking Federation - Green securitization aggregates small-scale green loans (e.g., green mortgages, rooftop solar) into larger investable products for institutional investors, with proposals for a European securitisation mechanism to boost the market and free capital for new green financing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com