Carbon credits represent permits allowing the holder to emit a specific amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases, often used by companies to offset emissions and comply with environmental regulations. Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) certify that one megawatt-hour of electricity was generated from a renewable energy source, enabling businesses to support green energy production and meet sustainability goals. Explore the key distinctions and financial impacts of carbon credits and RECs to enhance your understanding of environmental investment strategies.
Why it is important
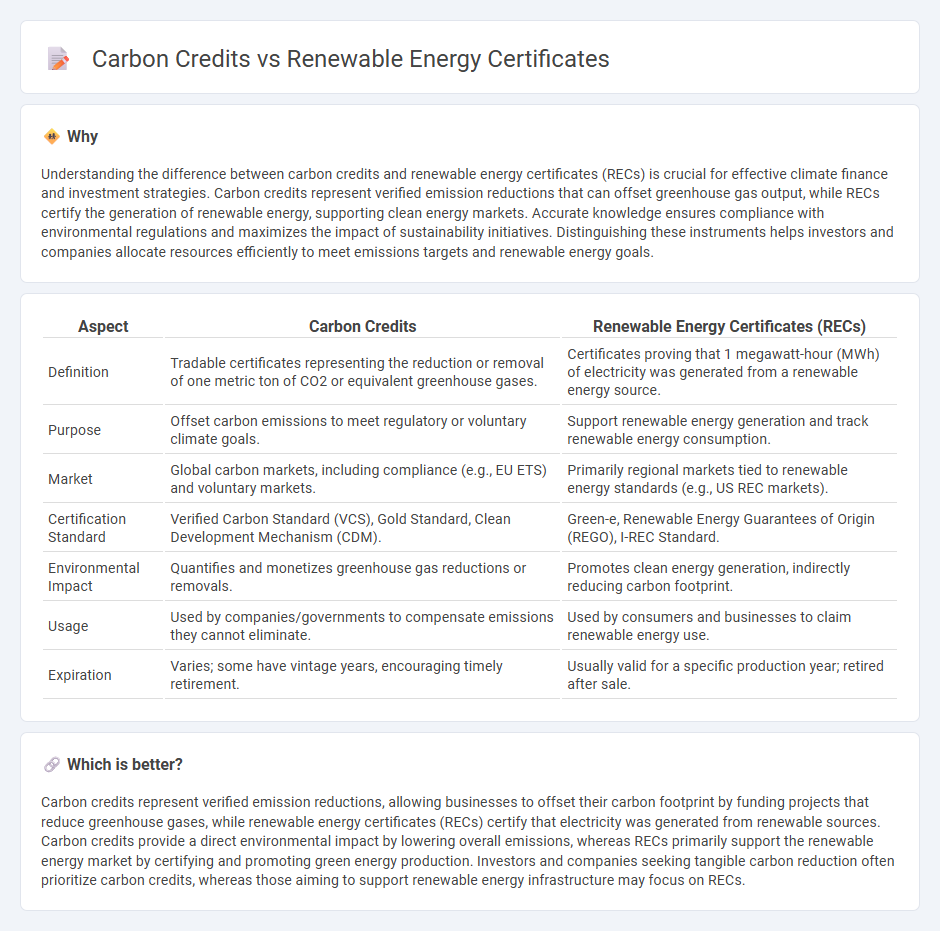
Understanding the difference between carbon credits and renewable energy certificates (RECs) is crucial for effective climate finance and investment strategies. Carbon credits represent verified emission reductions that can offset greenhouse gas output, while RECs certify the generation of renewable energy, supporting clean energy markets. Accurate knowledge ensures compliance with environmental regulations and maximizes the impact of sustainability initiatives. Distinguishing these instruments helps investors and companies allocate resources efficiently to meet emissions targets and renewable energy goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Credits | Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tradable certificates representing the reduction or removal of one metric ton of CO2 or equivalent greenhouse gases. | Certificates proving that 1 megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity was generated from a renewable energy source. |
| Purpose | Offset carbon emissions to meet regulatory or voluntary climate goals. | Support renewable energy generation and track renewable energy consumption. |
| Market | Global carbon markets, including compliance (e.g., EU ETS) and voluntary markets. | Primarily regional markets tied to renewable energy standards (e.g., US REC markets). |
| Certification Standard | Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), Gold Standard, Clean Development Mechanism (CDM). | Green-e, Renewable Energy Guarantees of Origin (REGO), I-REC Standard. |
| Environmental Impact | Quantifies and monetizes greenhouse gas reductions or removals. | Promotes clean energy generation, indirectly reducing carbon footprint. |
| Usage | Used by companies/governments to compensate emissions they cannot eliminate. | Used by consumers and businesses to claim renewable energy use. |
| Expiration | Varies; some have vintage years, encouraging timely retirement. | Usually valid for a specific production year; retired after sale. |
Which is better?
Carbon credits represent verified emission reductions, allowing businesses to offset their carbon footprint by funding projects that reduce greenhouse gases, while renewable energy certificates (RECs) certify that electricity was generated from renewable sources. Carbon credits provide a direct environmental impact by lowering overall emissions, whereas RECs primarily support the renewable energy market by certifying and promoting green energy production. Investors and companies seeking tangible carbon reduction often prioritize carbon credits, whereas those aiming to support renewable energy infrastructure may focus on RECs.
Connection
Carbon credits and renewable energy certificates (RECs) are both market-based instruments designed to promote environmental sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon credits represent a quantifiable reduction in emissions, allowing companies to offset their carbon footprint, while RECs certify that a megawatt-hour of electricity was generated from renewable sources like wind or solar. Both mechanisms enable businesses to meet regulatory requirements and demonstrate corporate social responsibility by supporting clean energy and emission reduction projects.
Key Terms
Tradable Instruments
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) represent proof that one megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity was generated from a renewable energy resource, enabling companies to meet renewable portfolio standards and support green energy production. Carbon credits quantify a reduction of one metric ton of carbon dioxide emissions, allowing entities to offset their carbon footprint by funding emission-reducing projects in sectors such as forestry and energy efficiency. Explore the distinctions between RECs and carbon credits to understand their roles in sustainability strategies and emission compliance markets.
Emissions Reduction
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) represent proof that electricity was generated from a renewable energy resource, primarily aimed at increasing renewable energy production to reduce emissions indirectly. Carbon credits directly quantify and offset greenhouse gas emissions by providing a tradable permit for a specific amount of emittted carbon dioxide or equivalent gases, playing a more direct role in emissions reduction. Explore how these mechanisms operate within environmental markets to understand their impact on meeting climate goals.
Renewable Generation
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) represent proof that one megawatt-hour of electricity was generated from a renewable energy resource, directly supporting renewable generation projects like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power. Carbon credits quantify the reduction of one metric ton of carbon dioxide or equivalent greenhouse gases, enabling entities to offset emissions through diverse projects, not limited to renewable energy. Explore the distinctions and benefits of RECs and carbon credits to enhance your sustainable energy strategies.
Source and External Links
Renewable Energy Certificate (United States) - Wikipedia - Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) are tradable certificates in the U.S. representing proof that 1 megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity was generated from a renewable source and fed into the grid, used in both compliance and voluntary markets to demonstrate renewable energy generation or consumption.
Renewable Energy Credits (RECs): What You Need To Know - RECs represent the renewable attributes of electricity generated by renewable sources like wind or solar, allowing buyers to claim the environmental benefits of clean energy generation even though the physical electrons cannot be directly traced.
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) | US EPA - RECs are market-based instruments conveying property rights to the environmental and social attributes of renewable electricity generation, issued per MWh of renewable energy fed into the grid, with detailed data for tracking and verification.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com