Carbon credits represent tradable permits that allow companies to emit a specified amount of carbon dioxide, providing financial incentives for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Green bonds are debt securities issued to finance projects with environmental benefits such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, or pollution prevention. Explore the key differences between carbon credits and green bonds to understand their unique roles in sustainable finance.
Why it is important
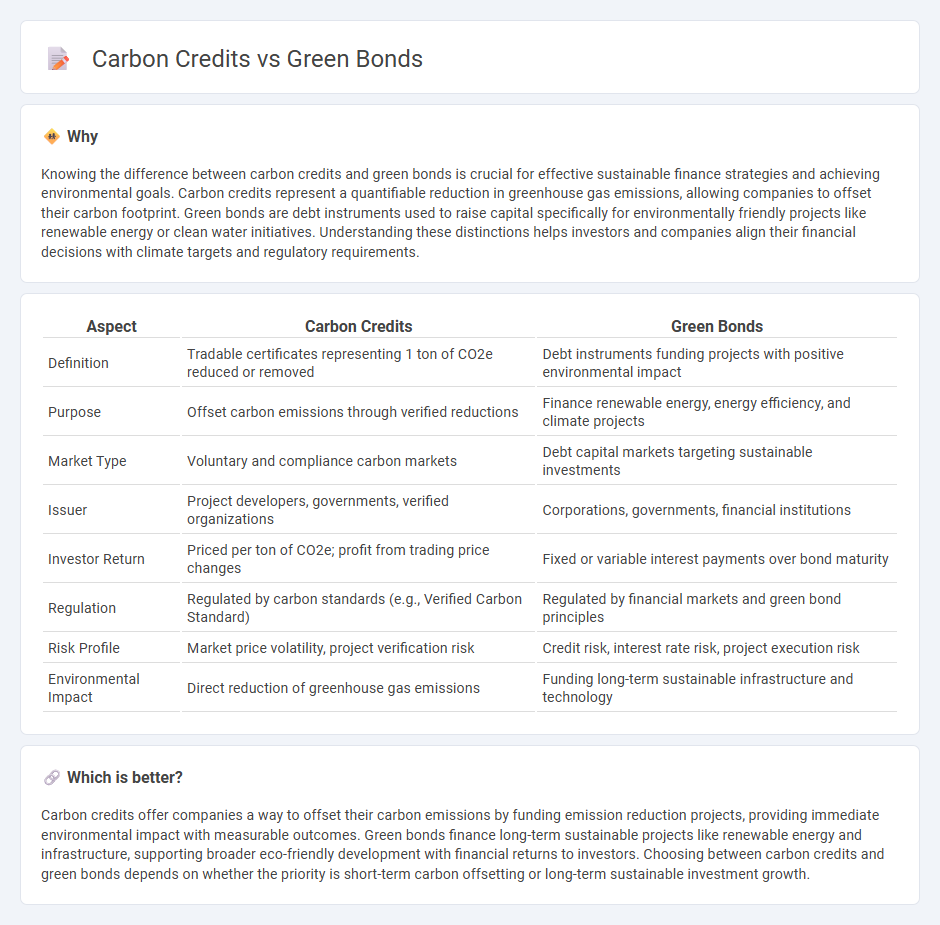
Knowing the difference between carbon credits and green bonds is crucial for effective sustainable finance strategies and achieving environmental goals. Carbon credits represent a quantifiable reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, allowing companies to offset their carbon footprint. Green bonds are debt instruments used to raise capital specifically for environmentally friendly projects like renewable energy or clean water initiatives. Understanding these distinctions helps investors and companies align their financial decisions with climate targets and regulatory requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Credits | Green Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tradable certificates representing 1 ton of CO2e reduced or removed | Debt instruments funding projects with positive environmental impact |
| Purpose | Offset carbon emissions through verified reductions | Finance renewable energy, energy efficiency, and climate projects |
| Market Type | Voluntary and compliance carbon markets | Debt capital markets targeting sustainable investments |
| Issuer | Project developers, governments, verified organizations | Corporations, governments, financial institutions |
| Investor Return | Priced per ton of CO2e; profit from trading price changes | Fixed or variable interest payments over bond maturity |
| Regulation | Regulated by carbon standards (e.g., Verified Carbon Standard) | Regulated by financial markets and green bond principles |
| Risk Profile | Market price volatility, project verification risk | Credit risk, interest rate risk, project execution risk |
| Environmental Impact | Direct reduction of greenhouse gas emissions | Funding long-term sustainable infrastructure and technology |
Which is better?
Carbon credits offer companies a way to offset their carbon emissions by funding emission reduction projects, providing immediate environmental impact with measurable outcomes. Green bonds finance long-term sustainable projects like renewable energy and infrastructure, supporting broader eco-friendly development with financial returns to investors. Choosing between carbon credits and green bonds depends on whether the priority is short-term carbon offsetting or long-term sustainable investment growth.
Connection
Carbon credits and green bonds are interconnected financial instruments that support environmental sustainability by funding projects that reduce carbon emissions. Carbon credits represent tradable certificates verifying the reduction of one metric ton of CO2 emissions, while green bonds are debt securities issued to raise capital specifically for financing eco-friendly initiatives, including renewable energy and carbon offset projects. Together, they create a market-driven mechanism incentivizing investment in low-carbon technologies and enabling companies to meet regulatory requirements or voluntary environmental goals.
Key Terms
Environmental Impact
Green bonds finance projects that deliver measurable environmental benefits, such as renewable energy installations or sustainable infrastructure, directly reducing carbon emissions. Carbon credits represent a tradeable permit allowing the holder to emit one ton of CO2 or equivalent greenhouse gases, effectively promoting emission reductions through market mechanisms. Explore how these tools uniquely contribute to climate goals and environmental sustainability.
Investment Mechanism
Green bonds and carbon credits represent distinct investment mechanisms targeting environmental sustainability; green bonds raise capital for specific eco-friendly projects through fixed-income securities, enabling investors to fund renewable energy, clean transportation, and sustainable agriculture initiatives. Carbon credits function in emission trading systems, allowing companies to buy or sell allowances that represent a ton of CO2 reduced or removed, incentivizing lower emissions by monetizing the carbon savings. Explore further to understand how these financial tools drive climate action and portfolio diversification.
Regulatory Compliance
Green bonds align with regulatory compliance by funding projects that contribute to environmental sustainability, satisfying standards set by organizations like the Climate Bonds Initiative. Carbon credits function as tradable permits that comply with emissions reduction regulations under frameworks such as the Kyoto Protocol and the EU Emissions Trading System. Explore the detailed regulatory frameworks governing green bonds and carbon credits to enhance your environmental investment strategies.
Source and External Links
Green bond - Wikipedia - A green bond is a fixed-income financial instrument used to fund projects with positive environmental benefits like renewable energy, energy efficiency, and pollution control, issued by governments or corporations and following Green Bond Principles.
What are Green Bonds and what projects do they finance? - Iberdrola - Green bonds are debt instruments issued by public or private institutions to finance environmentally sustainable projects that contribute to climate change action and Sustainable Development Goals.
Green Bond Principles (GBP) - ICMA - The Green Bond Principles provide voluntary guidelines promoting transparency, disclosure, and integrity in issuing green bonds for projects that contribute to a net-zero emissions economy and environmental protection.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com