Loss harvesting involves strategically selling securities at a loss to offset capital gains taxes, enhancing after-tax returns in investment portfolios. Gain harvesting focuses on realizing capital gains intentionally to utilize lower tax rates or reset the cost basis, aiding in long-term tax planning. Explore how each strategy can optimize your investment tax outcomes and financial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between loss harvesting and gain harvesting is crucial for optimizing tax strategies in finance. Loss harvesting involves selling investments at a loss to offset taxable gains, reducing overall tax liability. Gain harvesting entails selling investments at a profit to take advantage of lower tax rates or reset the cost basis. Properly applying these techniques enhances portfolio management and maximizes after-tax returns.
Comparison Table
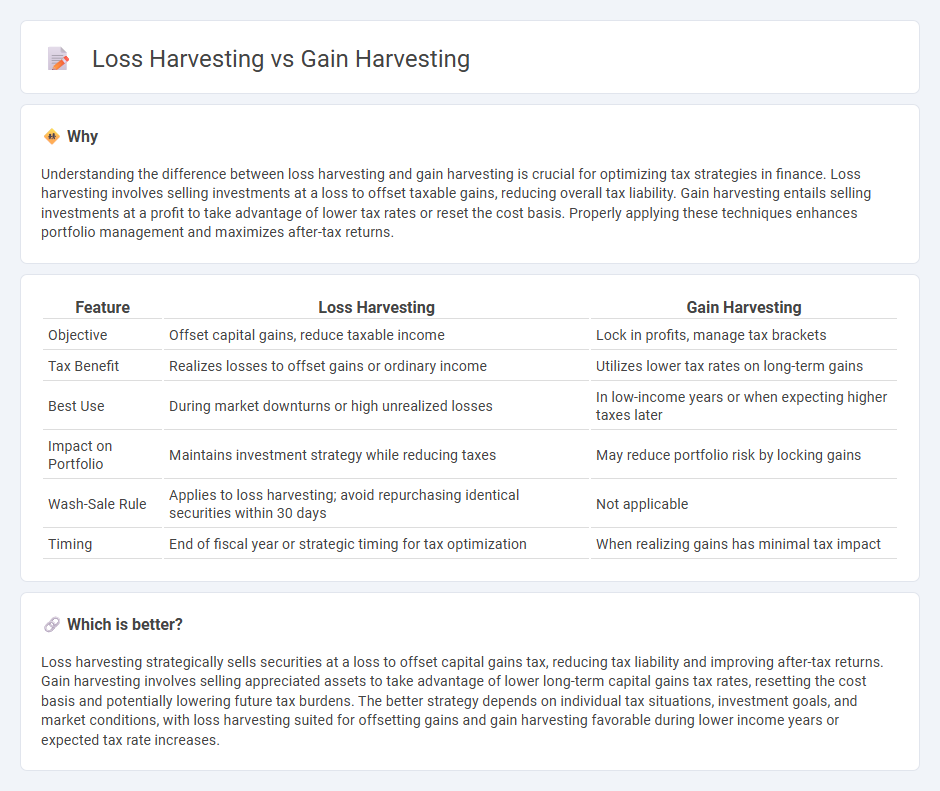
| Feature | Loss Harvesting | Gain Harvesting |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Offset capital gains, reduce taxable income | Lock in profits, manage tax brackets |
| Tax Benefit | Realizes losses to offset gains or ordinary income | Utilizes lower tax rates on long-term gains |
| Best Use | During market downturns or high unrealized losses | In low-income years or when expecting higher taxes later |
| Impact on Portfolio | Maintains investment strategy while reducing taxes | May reduce portfolio risk by locking gains |
| Wash-Sale Rule | Applies to loss harvesting; avoid repurchasing identical securities within 30 days | Not applicable |
| Timing | End of fiscal year or strategic timing for tax optimization | When realizing gains has minimal tax impact |
Which is better?
Loss harvesting strategically sells securities at a loss to offset capital gains tax, reducing tax liability and improving after-tax returns. Gain harvesting involves selling appreciated assets to take advantage of lower long-term capital gains tax rates, resetting the cost basis and potentially lowering future tax burdens. The better strategy depends on individual tax situations, investment goals, and market conditions, with loss harvesting suited for offsetting gains and gain harvesting favorable during lower income years or expected tax rate increases.
Connection
Loss harvesting and gain harvesting are connected strategies used in tax-efficient investing to optimize portfolio performance. Loss harvesting involves selling securities at a loss to offset capital gains tax liabilities, while gain harvesting entails realizing gains during periods of low tax rates or to utilize available tax credits. Together, these methods help investors manage tax exposure, improve after-tax returns, and rebalance investment portfolios effectively.
Key Terms
Capital Gains
Capital gains harvesting involves selling assets at a profit to realize gains now, potentially benefiting from lower tax rates or offsetting future losses. Loss harvesting focuses on selling investments at a loss to offset taxable gains, reducing tax liability and preserving capital. Explore strategies to optimize your portfolio's capital gains impact and tax efficiency.
Tax-Loss Harvesting
Tax-loss harvesting strategically offsets capital gains by selling securities at a loss, reducing tax liabilities and optimizing investment portfolios. In contrast, gain harvesting involves selling assets with a capital gain to reset the cost basis, potentially increasing tax obligations but also managing future gains. Explore how tax-loss harvesting can maximize your tax efficiency and enhance overall portfolio performance.
Portfolio Rebalancing
Gain harvesting involves selling appreciated assets to realize profits and reset cost bases, potentially optimizing tax efficiency within a portfolio. Loss harvesting focuses on selling underperforming investments to realize losses that offset gains, aiding in tax reduction while maintaining asset allocation. Explore strategies to balance these techniques effectively for optimal portfolio rebalancing.
Source and External Links
What is gain harvesting? - Gain harvesting is the practice of selling a holding for a gain in a taxable account to trigger a taxable event and then immediately buying it back, allowing an investor to pay tax on long-term capital gains, which are taxed at lower rates than ordinary income, and potentially benefit from favorable tax rates depending on income level.
Tax gain harvesting - Tax gain harvesting involves realizing long-term capital gains at a specific time to take advantage of lower tax brackets or avoid surtaxes, turning unrealized gains into realized gains strategically to minimize taxes over time.
Understanding How Tax Gain Harvesting Works - Tax gain harvesting strategically sells appreciated assets to minimize taxes by locking in gains during lower-income years and rebalancing one's portfolio to avoid over-concentration and reduce the risk of future losses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com