Tax loss harvesting involves selling investments at a loss to offset capital gains and reduce taxable income, while gains harvesting entails strategically selling appreciated assets to utilize lower tax brackets or capitalize on available deductions. Both strategies aim to optimize tax efficiency and improve after-tax investment returns by managing realized gains and losses. Explore these techniques further to enhance your portfolio's tax strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between tax loss harvesting and gains harvesting is crucial for optimizing investment portfolios and minimizing tax liabilities. Tax loss harvesting involves selling securities at a loss to offset capital gains, thereby reducing taxable income. Gains harvesting, on the other hand, strategically sells appreciated assets to benefit from low tax rates or reset cost bases. Mastery of both techniques enables investors to enhance after-tax returns and improve overall financial efficiency.
Comparison Table
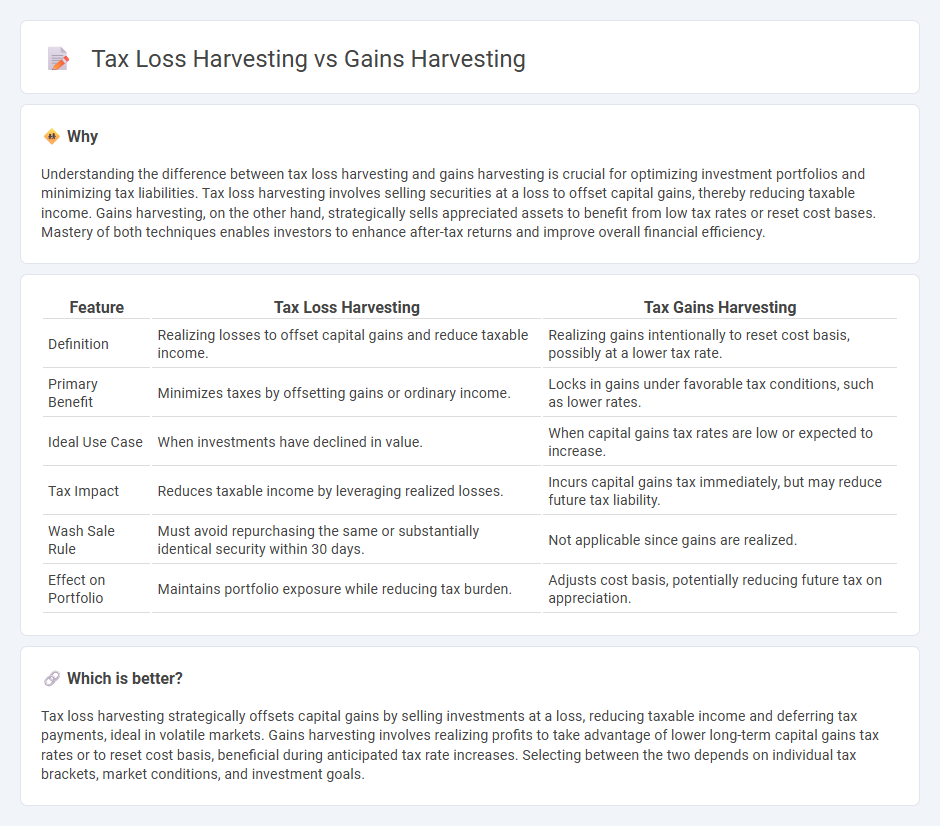
| Feature | Tax Loss Harvesting | Tax Gains Harvesting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Realizing losses to offset capital gains and reduce taxable income. | Realizing gains intentionally to reset cost basis, possibly at a lower tax rate. |
| Primary Benefit | Minimizes taxes by offsetting gains or ordinary income. | Locks in gains under favorable tax conditions, such as lower rates. |
| Ideal Use Case | When investments have declined in value. | When capital gains tax rates are low or expected to increase. |
| Tax Impact | Reduces taxable income by leveraging realized losses. | Incurs capital gains tax immediately, but may reduce future tax liability. |
| Wash Sale Rule | Must avoid repurchasing the same or substantially identical security within 30 days. | Not applicable since gains are realized. |
| Effect on Portfolio | Maintains portfolio exposure while reducing tax burden. | Adjusts cost basis, potentially reducing future tax on appreciation. |
Which is better?
Tax loss harvesting strategically offsets capital gains by selling investments at a loss, reducing taxable income and deferring tax payments, ideal in volatile markets. Gains harvesting involves realizing profits to take advantage of lower long-term capital gains tax rates or to reset cost basis, beneficial during anticipated tax rate increases. Selecting between the two depends on individual tax brackets, market conditions, and investment goals.
Connection
Tax loss harvesting and gains harvesting are connected through their strategic use in portfolio management to optimize tax liabilities. Tax loss harvesting involves selling securities at a loss to offset taxable gains, while gains harvesting entails realizing profits in a controlled manner to take advantage of lower tax rates or allowances. Both techniques work synergistically to balance realized gains and losses, ultimately reducing an investor's overall tax burden and enhancing after-tax returns.
Key Terms
Capital Gains
Capital gains harvesting maximizes profits by selling appreciated assets to realize gains strategically, aligning with favorable tax rates and investment goals. Tax loss harvesting offsets realized gains by selling underperforming assets, reducing taxable income and mitigating capital gains tax liability. Explore detailed strategies to optimize your capital gains management effectively.
Capital Losses
Capital Losses play a crucial role in both gains harvesting and tax loss harvesting strategies, as they offset taxable gains and reduce overall tax liability. Gains harvesting involves realizing gains to use up lower tax brackets or capital losses, while tax loss harvesting strategically realizes losses to offset gains and up to $3,000 of ordinary income annually. Discover how effectively managing Capital Losses can optimize your tax strategy and maximize after-tax returns.
Tax Liability
Gains harvesting involves selling appreciated assets to realize profits while potentially resetting cost basis and managing future tax liability, whereas tax loss harvesting uses the sale of assets at a loss to offset capital gains and reduce taxable income. Both strategies aim to optimize portfolio performance and minimize overall tax liability by strategically timing transactions based on individual tax brackets and market conditions. Explore more to understand which harvesting approach suits your financial goals and tax situation best.
Source and External Links
What is gain harvesting? - Moisand Fitzgerald Tamayo - Gain harvesting involves selling a holding in a taxable account to realize gains now, potentially paying lower taxes when in a low tax bracket, and then immediately repurchasing the asset to reset its cost basis for lower future taxes on subsequent gains.
Understanding How Tax Gain Harvesting Works - SmartAsset - Tax gain harvesting strategically sells appreciated assets during lower-tax years to minimize taxes, rebalance the portfolio, and avoid over-concentration that increases risk.
Tax-gain harvesting, explained | Ameriprise Financial - Tax-gain harvesting is the strategic sale of appreciated assets at potentially lower current tax rates, combined with reinvestment, aimed at saving taxes over the long term while considering goals and risk tolerance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com