Altcoins staking involves locking cryptocurrencies to support network operations and earn rewards, enhancing asset utilization and passive income potential. Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) allows coin holders to vote for delegates who validate transactions, increasing transaction speed and network efficiency compared to traditional staking methods. Explore the mechanics, benefits, and risks of both systems to optimize your crypto investment strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between altcoins staking and delegated proof of stake (DPoS) is crucial for optimizing cryptocurrency investment strategies and maximizing passive income. Staking altcoins involves locking tokens to support network security and operations, while DPoS allows token holders to vote for delegates who validate transactions, influencing decentralization and governance. Knowing these mechanisms helps investors assess risk, potential rewards, and network participation dynamics. Informed decisions on staking methods can enhance portfolio diversification and yield stability in volatile markets.
Comparison Table
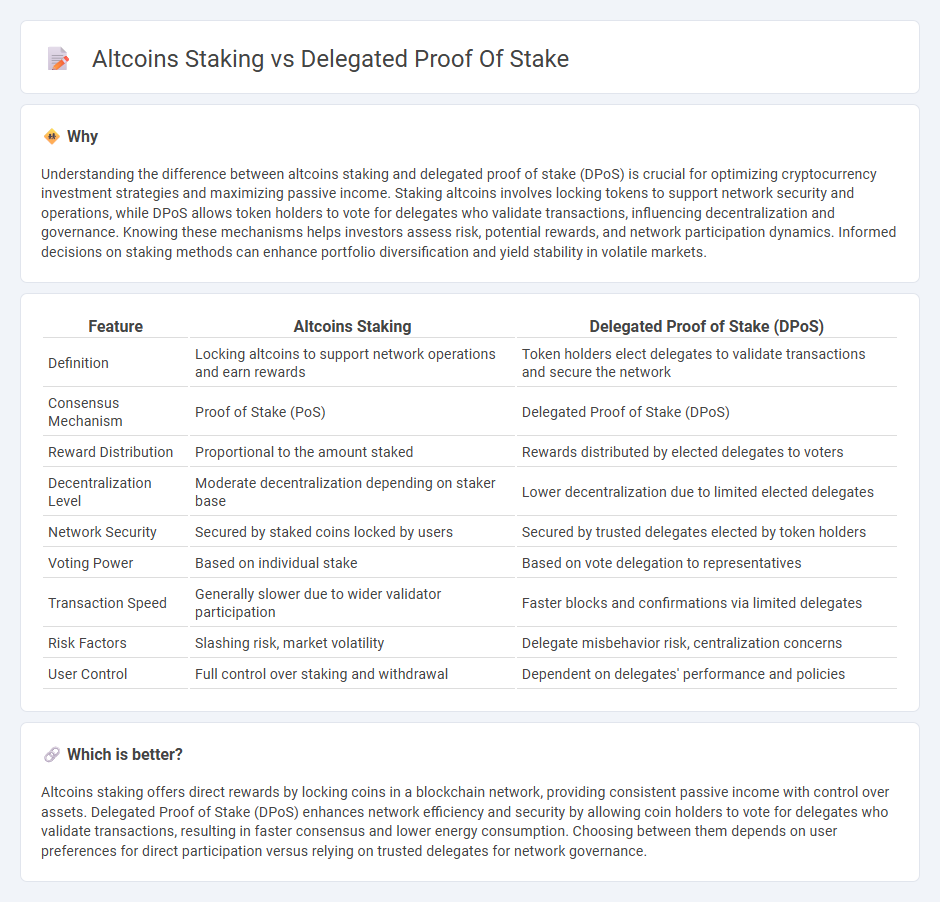
| Feature | Altcoins Staking | Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Locking altcoins to support network operations and earn rewards | Token holders elect delegates to validate transactions and secure the network |
| Consensus Mechanism | Proof of Stake (PoS) | Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) |
| Reward Distribution | Proportional to the amount staked | Rewards distributed by elected delegates to voters |
| Decentralization Level | Moderate decentralization depending on staker base | Lower decentralization due to limited elected delegates |
| Network Security | Secured by staked coins locked by users | Secured by trusted delegates elected by token holders |
| Voting Power | Based on individual stake | Based on vote delegation to representatives |
| Transaction Speed | Generally slower due to wider validator participation | Faster blocks and confirmations via limited delegates |
| Risk Factors | Slashing risk, market volatility | Delegate misbehavior risk, centralization concerns |
| User Control | Full control over staking and withdrawal | Dependent on delegates' performance and policies |
Which is better?
Altcoins staking offers direct rewards by locking coins in a blockchain network, providing consistent passive income with control over assets. Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) enhances network efficiency and security by allowing coin holders to vote for delegates who validate transactions, resulting in faster consensus and lower energy consumption. Choosing between them depends on user preferences for direct participation versus relying on trusted delegates for network governance.
Connection
Altcoins staking involves locking up cryptocurrency assets to support blockchain network operations and earn rewards, a process central to Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanisms. In DPoS, token holders delegate their staking power to trusted validators who validate transactions and maintain network security, increasing efficiency and scalability. This symbiotic relationship enhances decentralization while providing passive income opportunities for altcoin holders.
Key Terms
Validators
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) relies on a limited number of elected Validators who are responsible for validating transactions and securing the network, offering faster consensus and higher scalability compared to typical altcoins staking mechanisms where numerous individual stakers participate. Validators in DPoS systems earn rewards by maintaining network integrity and are often subject to community voting, enhancing decentralization through representative delegation. Explore how Validator roles differ across altcoins to optimize your staking strategies and maximize rewards.
Governance
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) empowers token holders to vote for a limited number of delegates who validate transactions, offering a more democratized and scalable governance model compared to traditional altcoins staking, which often grants voting power proportional to the amount staked. This distinction enhances network efficiency and responsiveness to community decisions while maintaining security through delegated consensus. Explore more about how governance structures impact blockchain ecosystems and staking benefits.
Lock-up Period
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) systems typically have shorter or flexible lock-up periods compared to traditional altcoins staking, which often requires participants to lock their tokens for fixed durations to earn rewards. The reduced or adjustable lock-up in DPoS enhances liquidity and allows users to maintain greater control over their assets while contributing to network security. Explore detailed comparisons and implications of lock-up periods in staking mechanisms to optimize your cryptocurrency investment strategy.
Source and External Links
What is Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)? - Coinbase - Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a consensus mechanism evolved from Proof of Stake that uses voting by network users to elect delegates who validate blocks, aiming to improve democratic process and efficiency in blockchain validation.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) - Bitcoinwiki - DPoS is a highly efficient and democratic consensus algorithm where users vote for delegates or witnesses to validate blocks and protect blockchain from centralization, developed by Daniel Larimer.
What Is Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS)? - Ledger - DPoS is a variation of Proof of Stake that uses a voting system to elect delegates who validate blockchain blocks, providing a scalable and democratic way to confirm transactions on-chain.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com