Green bond laddering enhances portfolio sustainability by staggered investment in environmentally-focused bonds, optimizing cash flow and risk management. ESG integration embeds environmental, social, and governance criteria into traditional investment analysis, promoting long-term value and responsible finance. Discover how these strategies can transform your investment approach.
Why it is important
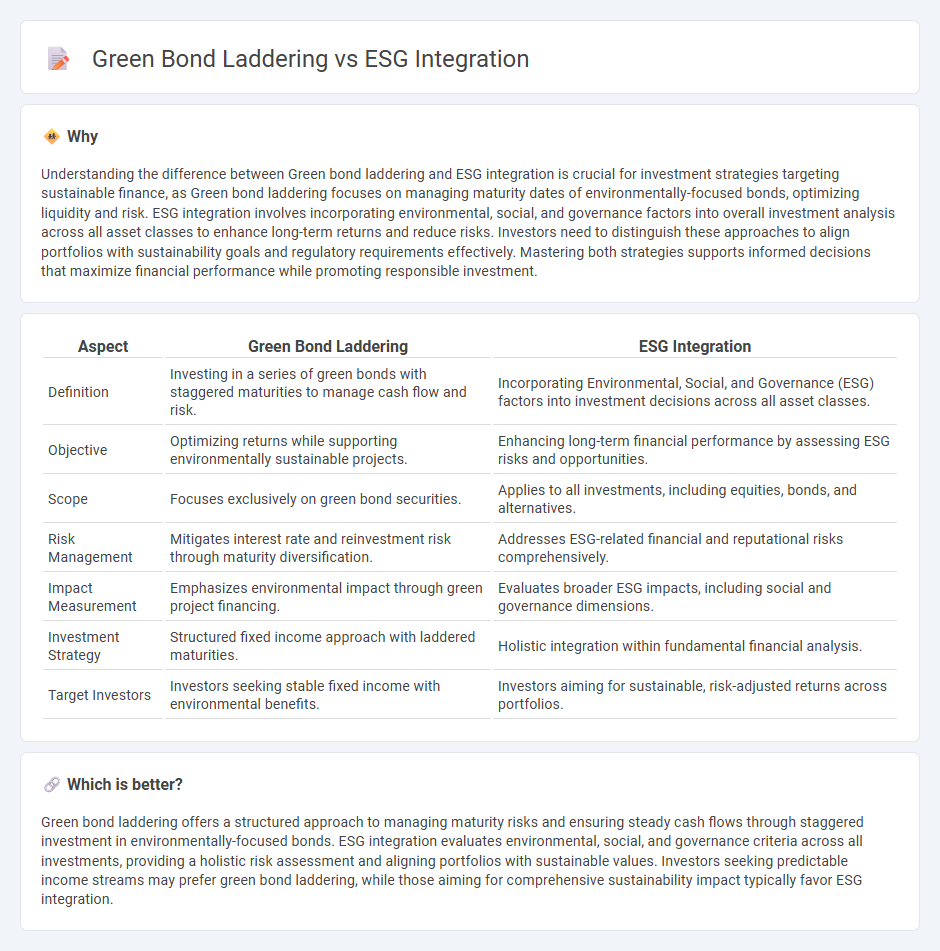
Understanding the difference between Green bond laddering and ESG integration is crucial for investment strategies targeting sustainable finance, as Green bond laddering focuses on managing maturity dates of environmentally-focused bonds, optimizing liquidity and risk. ESG integration involves incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors into overall investment analysis across all asset classes to enhance long-term returns and reduce risks. Investors need to distinguish these approaches to align portfolios with sustainability goals and regulatory requirements effectively. Mastering both strategies supports informed decisions that maximize financial performance while promoting responsible investment.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Bond Laddering | ESG Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investing in a series of green bonds with staggered maturities to manage cash flow and risk. | Incorporating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into investment decisions across all asset classes. |
| Objective | Optimizing returns while supporting environmentally sustainable projects. | Enhancing long-term financial performance by assessing ESG risks and opportunities. |
| Scope | Focuses exclusively on green bond securities. | Applies to all investments, including equities, bonds, and alternatives. |
| Risk Management | Mitigates interest rate and reinvestment risk through maturity diversification. | Addresses ESG-related financial and reputational risks comprehensively. |
| Impact Measurement | Emphasizes environmental impact through green project financing. | Evaluates broader ESG impacts, including social and governance dimensions. |
| Investment Strategy | Structured fixed income approach with laddered maturities. | Holistic integration within fundamental financial analysis. |
| Target Investors | Investors seeking stable fixed income with environmental benefits. | Investors aiming for sustainable, risk-adjusted returns across portfolios. |
Which is better?
Green bond laddering offers a structured approach to managing maturity risks and ensuring steady cash flows through staggered investment in environmentally-focused bonds. ESG integration evaluates environmental, social, and governance criteria across all investments, providing a holistic risk assessment and aligning portfolios with sustainable values. Investors seeking predictable income streams may prefer green bond laddering, while those aiming for comprehensive sustainability impact typically favor ESG integration.
Connection
Green bond laddering strategically staggers investments across various maturities, optimizing cash flow and risk management in sustainable finance portfolios. ESG integration evaluates environmental, social, and governance criteria to ensure investments support sustainable practices, directly enhancing the impact of green bond allocations. Combining these approaches enables investors to align financial returns with sustainability goals while managing liquidity and environmental risks effectively.
Key Terms
Materiality
ESG integration emphasizes the incorporation of material environmental, social, and governance factors into investment analysis to enhance long-term value and risk management. Green bond laddering involves structuring a portfolio with green bonds of varying maturities to manage liquidity and support sustainable projects, prioritizing green-certified assets. Explore how materiality drives the effectiveness of these strategies in sustainable investing.
Use of Proceeds
ESG integration involves incorporating environmental, social, and governance criteria across an investment portfolio to drive sustainable outcomes, whereas green bond laddering specifically focuses on sequencing green bonds based on their maturity to optimize cash flow and impact. The Use of Proceeds in green bond laddering is explicitly tied to financing environmental projects, ensuring targeted capital allocation, while ESG integration evaluates broader sustainability factors beyond just financing purposes. Discover how these approaches differ and complement each other in driving sustainable finance strategies.
Risk Diversification
ESG integration involves incorporating environmental, social, and governance criteria throughout the investment analysis process to identify and mitigate risks, enhancing portfolio resilience. Green bond laddering structures bond maturities at staggered intervals, ensuring steady income while reducing exposure to interest rate volatility and sector-specific risks. Explore in-depth strategies to optimize risk diversification through ESG integration and green bond laddering.
Source and External Links
The board's guide to ESG integration - Diligent - ESG integration is the process of using environmental, social, and governance data to inform investment decisions and embed ESG into corporate strategy, requiring a company-wide approach rather than siloed initiatives for effective results.
ESG integration | Zurich Insurance - Zurich defines ESG integration through four pillars--training, data, investment process, and active ownership--viewing sustainability risks and opportunities as integral to long-term risk-adjusted financial returns alongside traditional metrics.
ESG integration in listed equity: A technical guide - PRI - ESG integration involves a five-part process for equity investors including policy setting, organizational governance with accountability, staff training, and embedding ESG considerations throughout the investment cycle to better manage risks and improve returns.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com