Greenium refers to the premium investors are willing to pay for sustainable or environmentally friendly financial assets, reflecting increased demand for green investments. In contrast, the discount rate represents the interest rate used to determine the present value of future cash flows, influencing investment decisions and asset valuations. Explore deeper insights into how greenium and discount rates impact sustainable finance strategies and portfolio management.
Why it is important
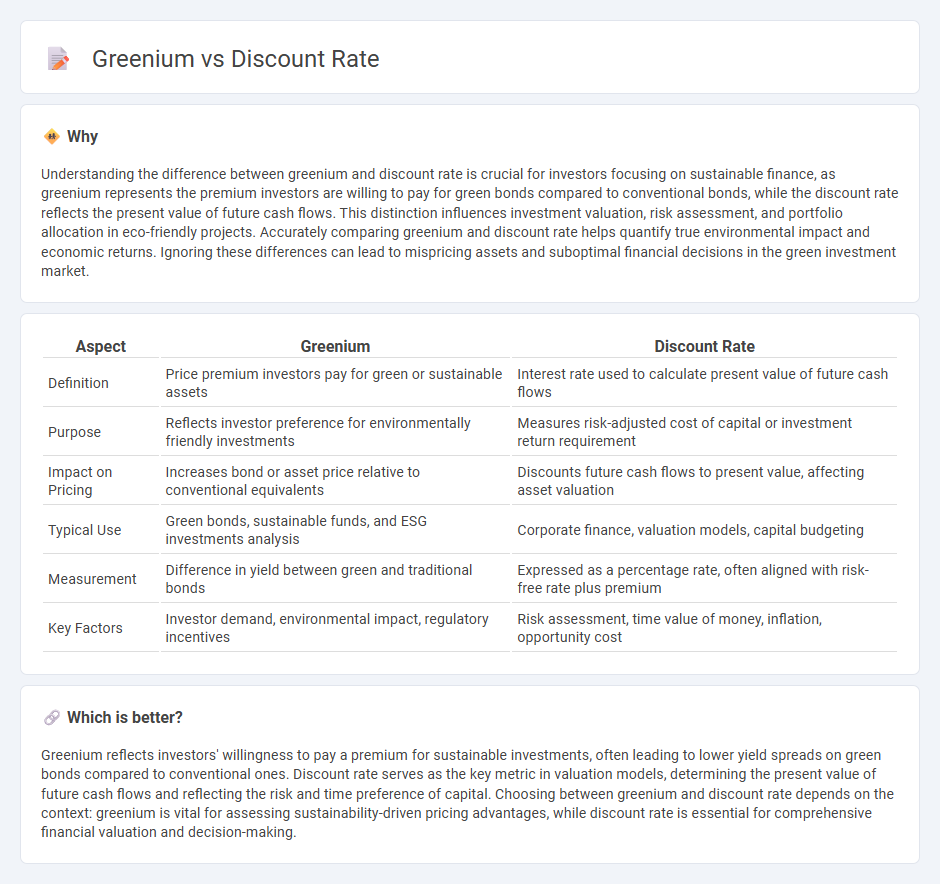
Understanding the difference between greenium and discount rate is crucial for investors focusing on sustainable finance, as greenium represents the premium investors are willing to pay for green bonds compared to conventional bonds, while the discount rate reflects the present value of future cash flows. This distinction influences investment valuation, risk assessment, and portfolio allocation in eco-friendly projects. Accurately comparing greenium and discount rate helps quantify true environmental impact and economic returns. Ignoring these differences can lead to mispricing assets and suboptimal financial decisions in the green investment market.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Greenium | Discount Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Price premium investors pay for green or sustainable assets | Interest rate used to calculate present value of future cash flows |
| Purpose | Reflects investor preference for environmentally friendly investments | Measures risk-adjusted cost of capital or investment return requirement |
| Impact on Pricing | Increases bond or asset price relative to conventional equivalents | Discounts future cash flows to present value, affecting asset valuation |
| Typical Use | Green bonds, sustainable funds, and ESG investments analysis | Corporate finance, valuation models, capital budgeting |
| Measurement | Difference in yield between green and traditional bonds | Expressed as a percentage rate, often aligned with risk-free rate plus premium |
| Key Factors | Investor demand, environmental impact, regulatory incentives | Risk assessment, time value of money, inflation, opportunity cost |
Which is better?
Greenium reflects investors' willingness to pay a premium for sustainable investments, often leading to lower yield spreads on green bonds compared to conventional ones. Discount rate serves as the key metric in valuation models, determining the present value of future cash flows and reflecting the risk and time preference of capital. Choosing between greenium and discount rate depends on the context: greenium is vital for assessing sustainability-driven pricing advantages, while discount rate is essential for comprehensive financial valuation and decision-making.
Connection
Greenium, the premium investors pay for sustainable investments, directly influences the discount rate used in financial valuations by reducing perceived risk and expected returns. A lower discount rate reflects increased confidence in green projects, enhancing their present value and attractiveness. This connection drives capital allocation towards environmentally friendly initiatives, aligning financial performance with sustainability goals.
Key Terms
Present Value
The discount rate significantly impacts the present value of future cash flows, with lower rates increasing the value of green investments by reflecting reduced risk and longer-term sustainability benefits. Greenium, the premium investors are willing to pay for environmentally friendly assets, directly influences the discount rate, often leading to a lower rate due to perceived lower risk and higher demand. Explore how variations in discount rates and greenium affect investment valuations and decision-making models.
Carbon Pricing
Carbon pricing mechanisms influence discount rates and greenium by assigning monetary value to carbon emissions, thereby affecting investment decisions in sustainable projects. The greenium reflects the premium investors pay for green bonds, driven by lower perceived risks and favorable discount rates tied to carbon pricing policies. Explore how integrating carbon pricing reshapes financial markets and investment strategies in sustainability.
Yield Spread
The discount rate represents the required return used to calculate the present value of future cash flows, directly impacting bond valuation and yield spreads. Greenium refers to the premium investors are willing to pay for green bonds, often resulting in a narrower yield spread compared to conventional bonds due to heightened demand for sustainable assets. Explore the dynamics between discount rate and greenium to understand their influence on yield spreads in sustainable finance.
Source and External Links
Discount Rate - Definition, Types and Examples, Issues - The discount rate is the rate of return used to discount future cash flows back to their present value, often represented by a company's Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) or required rate of return considering investment risk.
Discount Rate | Formula + Calculator - Wall Street Prep - The discount rate can be calculated by taking the future value divided by the present value, raised to the reciprocal of the number of periods minus one; it reflects the minimum expected return on an investment given its risk.
Discount Rate--Explanation, Definition and Examples - Valutico - Types of discount rates include the risk-free rate, cost of equity, cost of debt, WACC, and internal rate of return (IRR), each serving to evaluate the present value of future investment cash flows based on different risk and capital structure aspects.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com