Greenium refers to the premium investors pay for green bonds compared to conventional bonds due to their environmental benefits. ESG bonds are debt securities issued by companies or governments that meet environmental, social, and governance criteria to promote sustainable projects. Explore more to understand how these financial instruments impact investment strategies and sustainability goals.
Why it is important
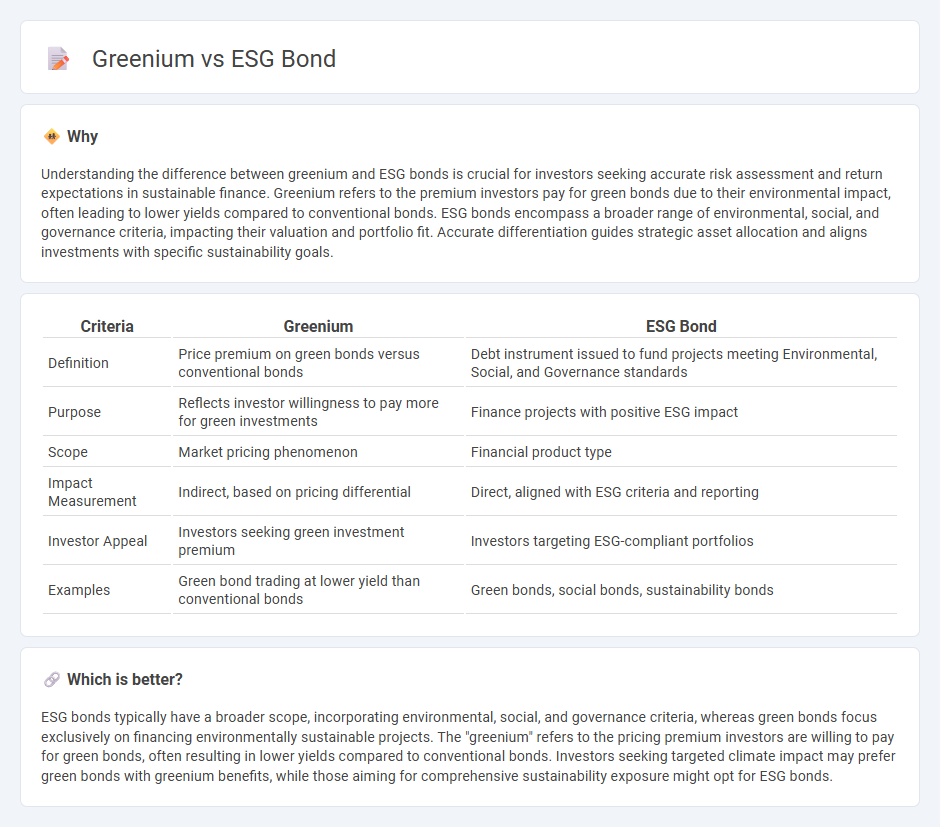
Understanding the difference between greenium and ESG bonds is crucial for investors seeking accurate risk assessment and return expectations in sustainable finance. Greenium refers to the premium investors pay for green bonds due to their environmental impact, often leading to lower yields compared to conventional bonds. ESG bonds encompass a broader range of environmental, social, and governance criteria, impacting their valuation and portfolio fit. Accurate differentiation guides strategic asset allocation and aligns investments with specific sustainability goals.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Greenium | ESG Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Price premium on green bonds versus conventional bonds | Debt instrument issued to fund projects meeting Environmental, Social, and Governance standards |
| Purpose | Reflects investor willingness to pay more for green investments | Finance projects with positive ESG impact |
| Scope | Market pricing phenomenon | Financial product type |
| Impact Measurement | Indirect, based on pricing differential | Direct, aligned with ESG criteria and reporting |
| Investor Appeal | Investors seeking green investment premium | Investors targeting ESG-compliant portfolios |
| Examples | Green bond trading at lower yield than conventional bonds | Green bonds, social bonds, sustainability bonds |
Which is better?
ESG bonds typically have a broader scope, incorporating environmental, social, and governance criteria, whereas green bonds focus exclusively on financing environmentally sustainable projects. The "greenium" refers to the pricing premium investors are willing to pay for green bonds, often resulting in lower yields compared to conventional bonds. Investors seeking targeted climate impact may prefer green bonds with greenium benefits, while those aiming for comprehensive sustainability exposure might opt for ESG bonds.
Connection
Greenium refers to the premium investors are willing to pay for green bonds, reflecting the higher demand for environmentally sustainable investments. ESG bonds, a broader category including green bonds, integrate environmental, social, and governance criteria to attract responsible investors. The connection between greenium and ESG bonds lies in the pricing advantage investors receive for supporting projects with positive environmental impacts.
Key Terms
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG)
ESG bonds are debt securities issued to finance projects with positive environmental, social, and governance impacts, attracting investors focused on sustainable outcomes. The term greenium refers to the premium investors are willing to pay for green bonds, a subset of ESG bonds specifically targeting environmental benefits, resulting in lower yields compared to conventional bonds. Explore the nuances between ESG bonds and greenium to enhance your sustainable investment strategy.
Green Bond
Green bonds are debt securities specifically issued to finance projects with positive environmental benefits, attracting investors interested in sustainable finance. The term "greenium" refers to the premium investors are willing to pay for these bonds due to their lower risk and positive impact on ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) goals. Explore how green bonds are shaping capital markets and driving sustainable investments for a deeper understanding.
Yield Spread (Greenium)
ESG bonds typically offer a yield spread known as the greenium, reflecting investors' willingness to accept lower yields for environmentally sustainable projects. This yield spread indicates the pricing premium green bonds command compared to conventional bonds, driven by growing demand for responsible investments. Explore the dynamics of greenium to better understand ESG bond performance and investment strategies.
Source and External Links
What Are ESG Bonds? - ESG bonds are fixed-income securities issued to finance projects aligned with environmental, social, and governance criteria, including green, social, and sustainability bonds, offering transparency and accountability to investors and issuers committed to sustainability and social responsibility.
Green Bonds | Definition + ESG Financing Examples - Green bonds are a type of ESG bond where the issuer commits to using proceeds exclusively for environmental and sustainability projects, serving as a key financing tool within the broader ESG investment field.
Green Bond Principles (GBP) - The Green Bond Principles provide voluntary guidelines promoting transparency, disclosure, and integrity in issuing green bonds to finance environmentally sustainable projects that support a net-zero emissions economy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com