Degen boxes are decentralized finance instruments designed for leveraged trading and liquidity provision, offering high-risk, high-reward opportunities through smart contract automation on blockchain platforms. Interest rate swaps are financial derivatives used by institutions to manage exposure to fluctuations in interest rates by exchanging fixed-rate payments for floating-rate ones, optimizing debt costs and cash flow. Explore the detailed mechanisms and risk profiles of degen boxes and interest rate swaps to understand their roles in modern finance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a degen box and an interest rate swap is crucial in finance because the former involves high-risk, speculative trading strategies while the latter is a structured derivative used for hedging interest rate exposure. A degen box often implies leveraging volatile assets for potential high returns, increasing portfolio risk, whereas interest rate swaps help manage interest rate fluctuations, stabilizing cash flows. Knowing these distinctions enables investors to balance risk and optimize financial strategies effectively. Mastery of both concepts supports informed decision-making in risk management and speculative investment approaches.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Degen Box | Interest Rate Swap |
|---|---|---|
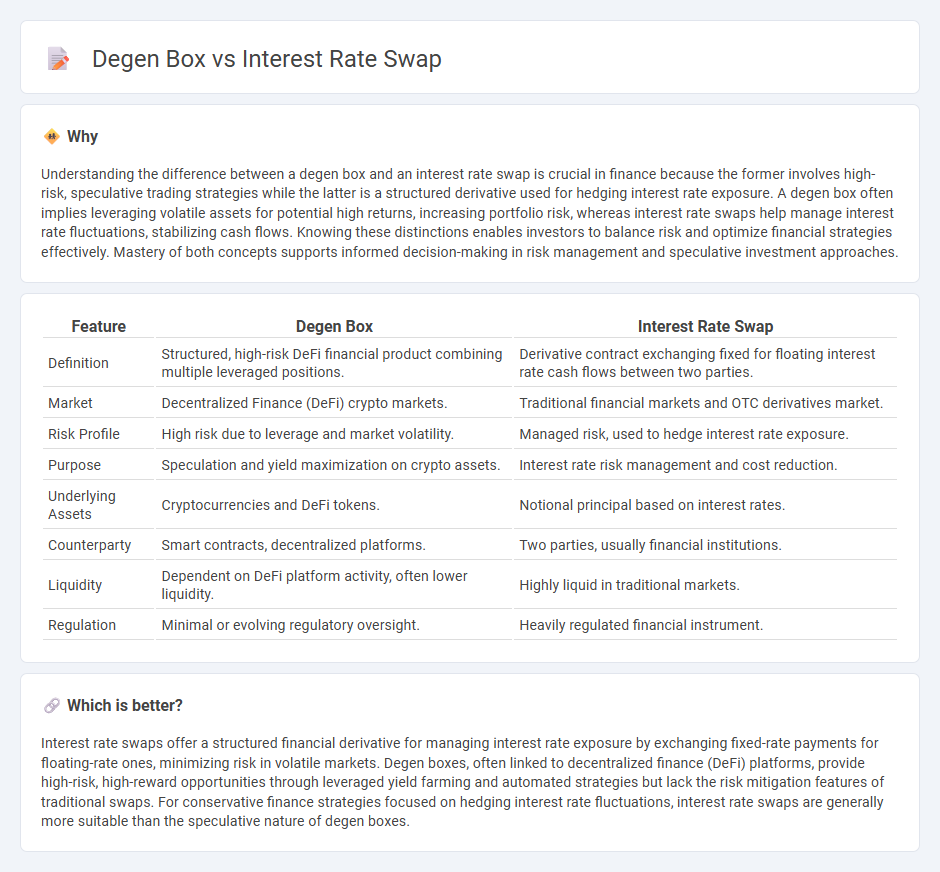
| Definition | Structured, high-risk DeFi financial product combining multiple leveraged positions. | Derivative contract exchanging fixed for floating interest rate cash flows between two parties. |
| Market | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) crypto markets. | Traditional financial markets and OTC derivatives market. |
| Risk Profile | High risk due to leverage and market volatility. | Managed risk, used to hedge interest rate exposure. |
| Purpose | Speculation and yield maximization on crypto assets. | Interest rate risk management and cost reduction. |
| Underlying Assets | Cryptocurrencies and DeFi tokens. | Notional principal based on interest rates. |
| Counterparty | Smart contracts, decentralized platforms. | Two parties, usually financial institutions. |
| Liquidity | Dependent on DeFi platform activity, often lower liquidity. | Highly liquid in traditional markets. |
| Regulation | Minimal or evolving regulatory oversight. | Heavily regulated financial instrument. |
Which is better?
Interest rate swaps offer a structured financial derivative for managing interest rate exposure by exchanging fixed-rate payments for floating-rate ones, minimizing risk in volatile markets. Degen boxes, often linked to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, provide high-risk, high-reward opportunities through leveraged yield farming and automated strategies but lack the risk mitigation features of traditional swaps. For conservative finance strategies focused on hedging interest rate fluctuations, interest rate swaps are generally more suitable than the speculative nature of degen boxes.
Connection
Degen box strategies often involve complex financial instruments like interest rate swaps to hedge risks associated with volatile asset positions. Interest rate swaps allow parties to exchange fixed and floating rate payments, enabling investors within a degen box to manage exposure to fluctuating interest rates and optimize yield. This connection enhances portfolio flexibility by mitigating interest rate risk while pursuing high-return opportunities in decentralized finance ecosystems.
Key Terms
Notional Principal
Interest rate swaps involve exchanging cash flows based on a notional principal amount that remains constant throughout the contract, serving as the foundation for calculating interest payments without any actual exchange of principal. In contrast, degen box strategies often utilize varying notional principals subject to market volatility and higher risk exposure, impacting their leverage and potential returns significantly. Explore the detailed mechanics of notional principal in both instruments to enhance your financial strategy knowledge.
Yield Farming
Interest rate swaps provide a fixed-for-floating interest exchange mechanism often used for hedging and managing risk in decentralized finance yield farming. Degen boxes, typically associated with high-risk, high-reward strategies, involve leveraging assets in protocols like Abracadabra DAO to maximize yield farming returns. Explore detailed comparisons and strategies to optimize your yield farming outcomes.
Source and External Links
Video An Overview Of Interest Rate Swaps - An interest rate swap is an agreement between two parties to exchange a floating interest rate for a fixed interest rate, helping borrowers manage interest rate risk and budget more predictably by converting variable loan payments into fixed payments.
Interest Rate Swap: Meaning, Types, Examples and How ... - Interest rate swaps are derivative contracts where two parties exchange future interest payments based on a notional amount, typically swapping fixed interest payments for floating rate payments or vice versa to hedge against interest rate fluctuations and stabilize cash flows.
Interest Rate Swap (IRS) - An interest rate swap is a derivative contract where two parties agree to exchange interest payment streams--one paying fixed and the other floating rates--without exchanging the underlying debt, allowing them to hedge interest rate exposures or speculate on interest rate movements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com