Impact investing targets measurable social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, focusing on direct positive change in sectors like renewable energy and affordable housing. Responsible investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to minimize risks and promote sustainable business practices within investment portfolios. Explore how each strategy aligns with your financial goals and values in greater detail.
Why it is important
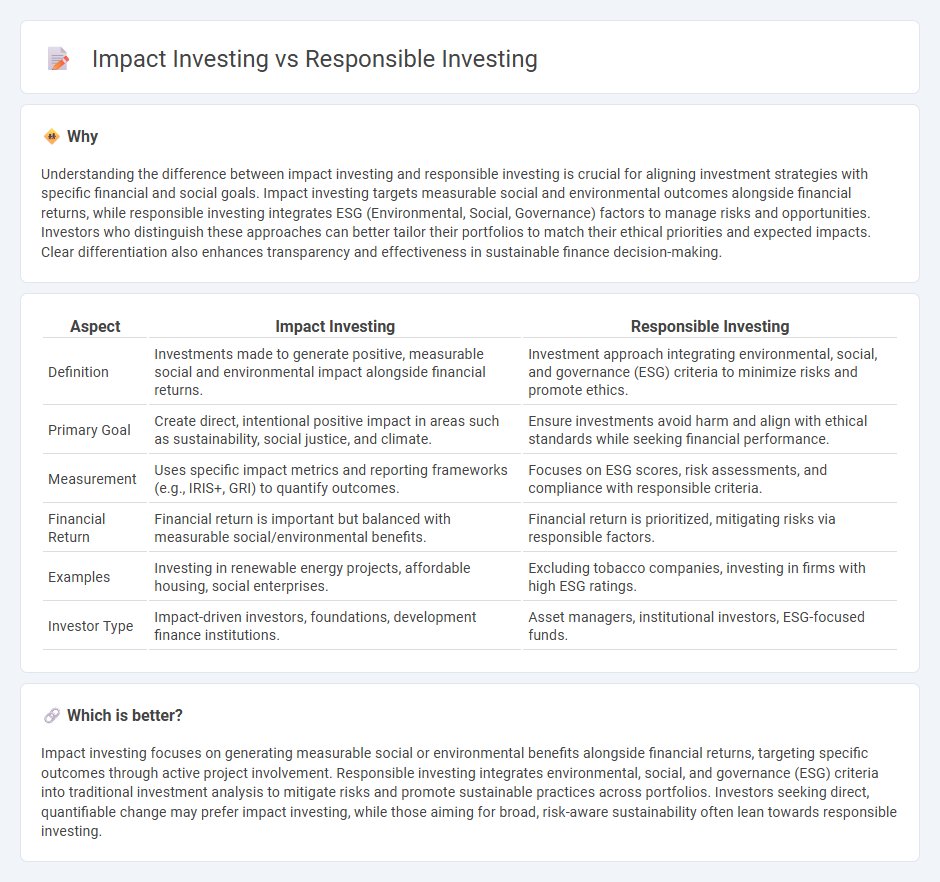
Understanding the difference between impact investing and responsible investing is crucial for aligning investment strategies with specific financial and social goals. Impact investing targets measurable social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, while responsible investing integrates ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) factors to manage risks and opportunities. Investors who distinguish these approaches can better tailor their portfolios to match their ethical priorities and expected impacts. Clear differentiation also enhances transparency and effectiveness in sustainable finance decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Impact Investing | Responsible Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investments made to generate positive, measurable social and environmental impact alongside financial returns. | Investment approach integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to minimize risks and promote ethics. |
| Primary Goal | Create direct, intentional positive impact in areas such as sustainability, social justice, and climate. | Ensure investments avoid harm and align with ethical standards while seeking financial performance. |
| Measurement | Uses specific impact metrics and reporting frameworks (e.g., IRIS+, GRI) to quantify outcomes. | Focuses on ESG scores, risk assessments, and compliance with responsible criteria. |
| Financial Return | Financial return is important but balanced with measurable social/environmental benefits. | Financial return is prioritized, mitigating risks via responsible factors. |
| Examples | Investing in renewable energy projects, affordable housing, social enterprises. | Excluding tobacco companies, investing in firms with high ESG ratings. |
| Investor Type | Impact-driven investors, foundations, development finance institutions. | Asset managers, institutional investors, ESG-focused funds. |
Which is better?
Impact investing focuses on generating measurable social or environmental benefits alongside financial returns, targeting specific outcomes through active project involvement. Responsible investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into traditional investment analysis to mitigate risks and promote sustainable practices across portfolios. Investors seeking direct, quantifiable change may prefer impact investing, while those aiming for broad, risk-aware sustainability often lean towards responsible investing.
Connection
Impact investing and responsible investing share a commitment to generating positive social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns. Both strategies prioritize Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria to guide investment decisions, ensuring sustainable and ethical business practices. Investors in these fields seek measurable impact while managing risks linked to sustainability challenges.
Key Terms
ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance)
Responsible investing integrates ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) criteria to minimize risks and ensure sustainable business practices without directly seeking measurable social or environmental impact. Impact investing prioritizes generating positive, quantifiable social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns by actively allocating capital to solutions addressing global challenges. Explore more to understand how each approach shapes investment strategies and drives corporate responsibility.
Intentionality
Responsible investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to manage risk and generate sustainable returns, emphasizing ethical considerations without necessarily aiming for direct social impact. Impact investing prioritizes intentionality by targeting measurable social and environmental outcomes alongside financial gains, often directing capital toward underserved communities or innovative solutions. Explore the distinctions and strategies for intentional capital allocation to enhance both profit and purpose.
Financial Returns
Responsible investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to minimize risks and enhance long-term financial returns while promoting sustainable business practices. Impact investing targets measurable social and environmental impact alongside competitive financial returns, balancing profit with purpose in sectors like renewable energy and affordable housing. Explore deeper insights into how these investment strategies align with financial goals and ethical considerations.
Source and External Links
Responsible investing | TIAA - Responsible investing integrates environmental, social and governance (ESG) factors with traditional financial criteria to seek long-term, resilient returns and mitigate risks while doing good for society and the planet.
What is responsible investment? - Responsible investment explicitly factors in environmental, social and governance elements to create long-term sustainable social, environmental, and economic value alongside financial returns.
Socially responsible investing - Wikipedia - Socially responsible investing (SRI) combines financial goals with ethical, social, or environmental objectives, often focusing on ESG issues and sometimes involving negative screening or proactive impact investing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com