Quantamental investing combines quantitative analysis with fundamental research to optimize stock selection and risk management, leveraging algorithms and data-driven models alongside traditional financial metrics. Growth investing focuses on companies exhibiting above-average revenue and earnings expansion, prioritizing future potential over current valuation metrics. Explore the key differences and advantages of each strategy to enhance your investment approach.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between quantamental investing and growth investing is crucial for effective portfolio diversification and risk management. Quantamental investing combines quantitative analysis with fundamental research to identify undervalued stocks using data-driven models, while growth investing focuses on companies with strong earnings growth potential. This distinction helps investors align strategies with their financial goals and market conditions. Accurate knowledge of both approaches enhances decision-making and optimizes returns in dynamic markets.
Comparison Table
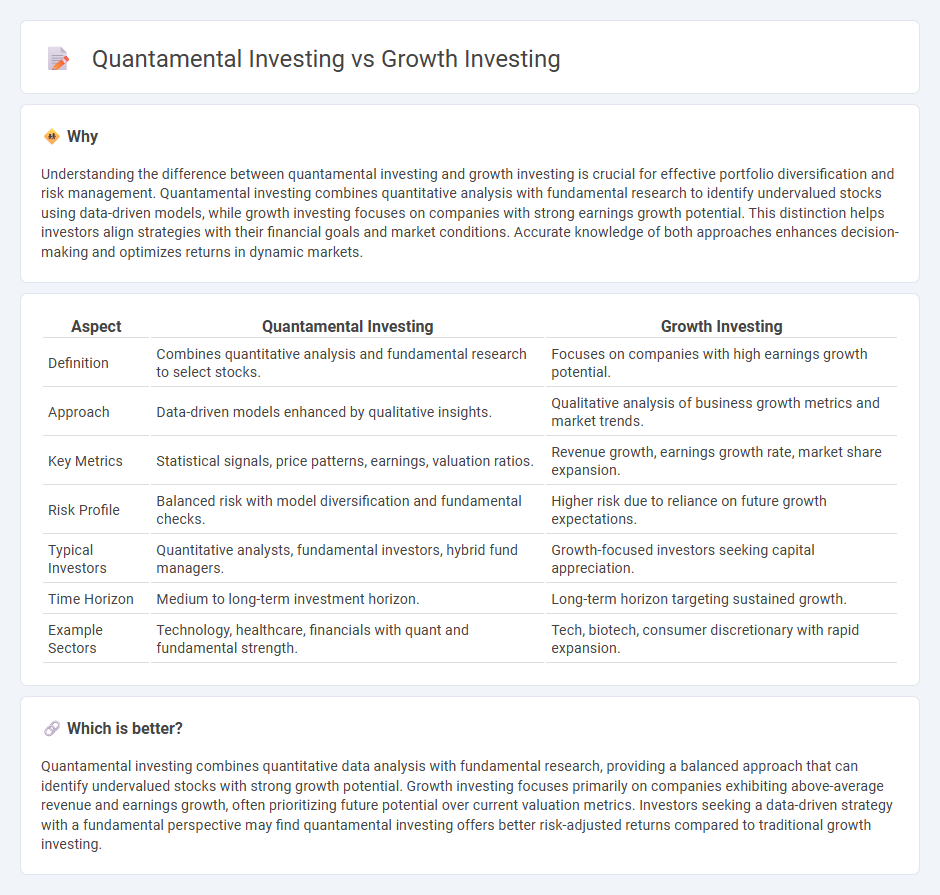
| Aspect | Quantamental Investing | Growth Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines quantitative analysis and fundamental research to select stocks. | Focuses on companies with high earnings growth potential. |
| Approach | Data-driven models enhanced by qualitative insights. | Qualitative analysis of business growth metrics and market trends. |
| Key Metrics | Statistical signals, price patterns, earnings, valuation ratios. | Revenue growth, earnings growth rate, market share expansion. |
| Risk Profile | Balanced risk with model diversification and fundamental checks. | Higher risk due to reliance on future growth expectations. |
| Typical Investors | Quantitative analysts, fundamental investors, hybrid fund managers. | Growth-focused investors seeking capital appreciation. |
| Time Horizon | Medium to long-term investment horizon. | Long-term horizon targeting sustained growth. |
| Example Sectors | Technology, healthcare, financials with quant and fundamental strength. | Tech, biotech, consumer discretionary with rapid expansion. |
Which is better?
Quantamental investing combines quantitative data analysis with fundamental research, providing a balanced approach that can identify undervalued stocks with strong growth potential. Growth investing focuses primarily on companies exhibiting above-average revenue and earnings growth, often prioritizing future potential over current valuation metrics. Investors seeking a data-driven strategy with a fundamental perspective may find quantamental investing offers better risk-adjusted returns compared to traditional growth investing.
Connection
Quantamental investing integrates quantitative analysis with fundamental research to identify high-growth companies exhibiting strong financial health, key metrics favored in growth investing. Growth investing focuses on stocks with above-average earnings expansion potential, aligning with quantamental models that leverage data-driven signals to uncover sustainable growth trends. Both strategies emphasize evaluating growth indicators such as revenue acceleration, profit margins, and market opportunity to optimize portfolio performance.
Key Terms
Growth Investing:
Growth investing targets companies with above-average earnings or revenue growth potential, emphasizing innovation, market expansion, and strong financial performance metrics like return on equity (ROE) and earnings per share (EPS). Investors prioritize high growth stocks in sectors such as technology, healthcare, and consumer discretionary, aiming for capital appreciation over dividends. Explore further to understand how growth investing strategies differ from quantamental approaches in portfolio management.
Earnings Growth
Growth investing emphasizes identifying companies with strong earnings growth rates, aiming for substantial capital appreciation through increasing revenues and profits. Quantamental investing combines quantitative analysis with fundamental insights, leveraging data-driven models to detect consistent earnings trends while incorporating qualitative factors like management quality. Explore more to understand how these strategies optimize earnings growth assessment for better investment decisions.
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
Growth investing prioritizes companies with strong earnings growth potential, often accepting higher Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratios as investors anticipate future profitability. Quantamental investing combines quantitative models with fundamental analysis, using P/E ratios alongside other metrics to identify undervalued growth opportunities. Explore how these strategies leverage P/E ratios to maximize investment returns and manage risk.
Source and External Links
Growth investing: What it is and how to build a high-growth ... - Growth investing targets companies expected to grow faster than their industry or market by focusing on strong earnings potential, compounding returns, and capitalizing on innovation and market trends.
Growth investing - Wikipedia - Growth investing is a strategy aiming for capital appreciation by investing in companies with above-average growth, often at higher valuations, with historical roots traced to Thomas Rowe Price Jr. and Phil Fisher.
Investing for growth opportunities - BlackRock - Growth investing focuses on companies with strong potential for above-average earnings growth for long-term wealth accumulation, suitable for investors with the risk appetite to pursue capital appreciation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com