Private credit involves direct lending from non-bank institutions to businesses, offering tailored financing solutions with potentially higher returns and stricter terms. Crowdfunding leverages online platforms to pool small investments from numerous individuals, enabling startups and projects to access capital with broader investor participation. Explore the differences and benefits of private credit versus crowdfunding to determine the best financing strategy for your needs.
Why it is important
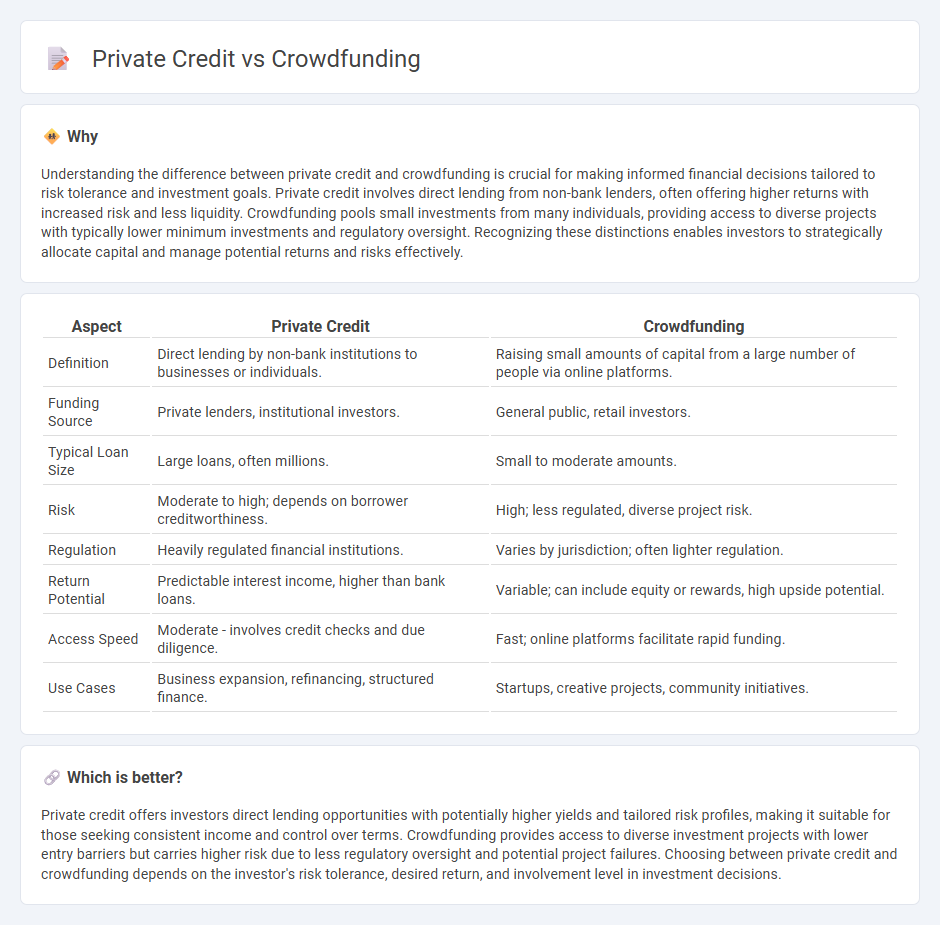
Understanding the difference between private credit and crowdfunding is crucial for making informed financial decisions tailored to risk tolerance and investment goals. Private credit involves direct lending from non-bank lenders, often offering higher returns with increased risk and less liquidity. Crowdfunding pools small investments from many individuals, providing access to diverse projects with typically lower minimum investments and regulatory oversight. Recognizing these distinctions enables investors to strategically allocate capital and manage potential returns and risks effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Private Credit | Crowdfunding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct lending by non-bank institutions to businesses or individuals. | Raising small amounts of capital from a large number of people via online platforms. |
| Funding Source | Private lenders, institutional investors. | General public, retail investors. |
| Typical Loan Size | Large loans, often millions. | Small to moderate amounts. |
| Risk | Moderate to high; depends on borrower creditworthiness. | High; less regulated, diverse project risk. |
| Regulation | Heavily regulated financial institutions. | Varies by jurisdiction; often lighter regulation. |
| Return Potential | Predictable interest income, higher than bank loans. | Variable; can include equity or rewards, high upside potential. |
| Access Speed | Moderate - involves credit checks and due diligence. | Fast; online platforms facilitate rapid funding. |
| Use Cases | Business expansion, refinancing, structured finance. | Startups, creative projects, community initiatives. |
Which is better?
Private credit offers investors direct lending opportunities with potentially higher yields and tailored risk profiles, making it suitable for those seeking consistent income and control over terms. Crowdfunding provides access to diverse investment projects with lower entry barriers but carries higher risk due to less regulatory oversight and potential project failures. Choosing between private credit and crowdfunding depends on the investor's risk tolerance, desired return, and involvement level in investment decisions.
Connection
Private credit and crowdfunding are interconnected through their roles in alternative finance, offering businesses access to capital outside traditional bank loans. Private credit involves direct lending by non-bank entities to companies, while crowdfunding enables multiple individual investors to contribute small amounts of capital via online platforms. Both methods increase funding diversity and democratize investment opportunities, supporting entrepreneurial growth and financial inclusion.
Key Terms
Investor Base
Crowdfunding platforms typically attract a diverse investor base composed of individual retail investors seeking high-growth opportunities, often with lower entry thresholds and varying risk appetites. Private credit investors are usually institutional entities or accredited individuals prioritizing steady income streams and risk mitigation through direct lending arrangements. Explore detailed insights on how investor profiles shape funding strategies in both markets.
Risk Profile
Crowdfunding typically involves diverse small investors sharing risks and potential rewards, often suited for those seeking moderate risk tolerance. Private credit features direct lending with higher risk exposure but offers potential for higher returns through structured agreements. Explore the detailed risk profiles to determine which financing option aligns best with your investment strategy.
Regulation
Crowdfunding operates under specific regulatory frameworks such as the JOBS Act in the United States, which mandates disclosure requirements and investor limits to protect the public. Private credit, often governed by less stringent regulations, focuses on institutional investors and allows for more flexible lending terms but demands rigorous due diligence. Explore detailed regulatory differences to optimize funding strategies effectively.
Source and External Links
Crowdfunding - Wikipedia - Crowdfunding is the practice of funding a project or venture by raising money from a large number of people, typically via the internet, acting as an alternative to traditional finance with over $34 billion raised worldwide in 2015.
What is crowdfunding? Here are four types for startups to know - Stripe - Crowdfunding is a funding method that uses the collective effort of friends, family, investors, and the public, predominantly online, allowing startups to bypass traditional funding avenues.
Crowdfunding - Small Business Financing: A Resource Guide - Crowdfunding comes in donation, reward, and equity-based forms, where funds are raised online from many contributors, with platforms like GoFundMe and Kickstarter serving different crowdfunding purposes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com