Laddered bond ETFs offer diversified fixed-income exposure by staggering maturities to reduce interest rate risk and provide predictable cash flow, whereas corporate bond funds actively manage a portfolio of corporate debt seeking higher yields. Laddered bond ETFs typically emphasize transparency and lower expenses, appealing to investors prioritizing stability and gradual income. Explore the distinct features and risk profiles of laddered bond ETFs and corporate bond funds to make informed investment decisions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Laddered Bond ETFs and Corporate Bond Funds is crucial for optimizing investment strategies in fixed income markets. Laddered Bond ETFs offer predictable maturity schedules that reduce interest rate risk, while Corporate Bond Funds provide diversified exposure to corporate credit with active management. Investors can tailor their portfolio duration and credit risk exposure more effectively by distinguishing these investment vehicles. Clear knowledge aids in aligning bond investments with specific financial goals and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
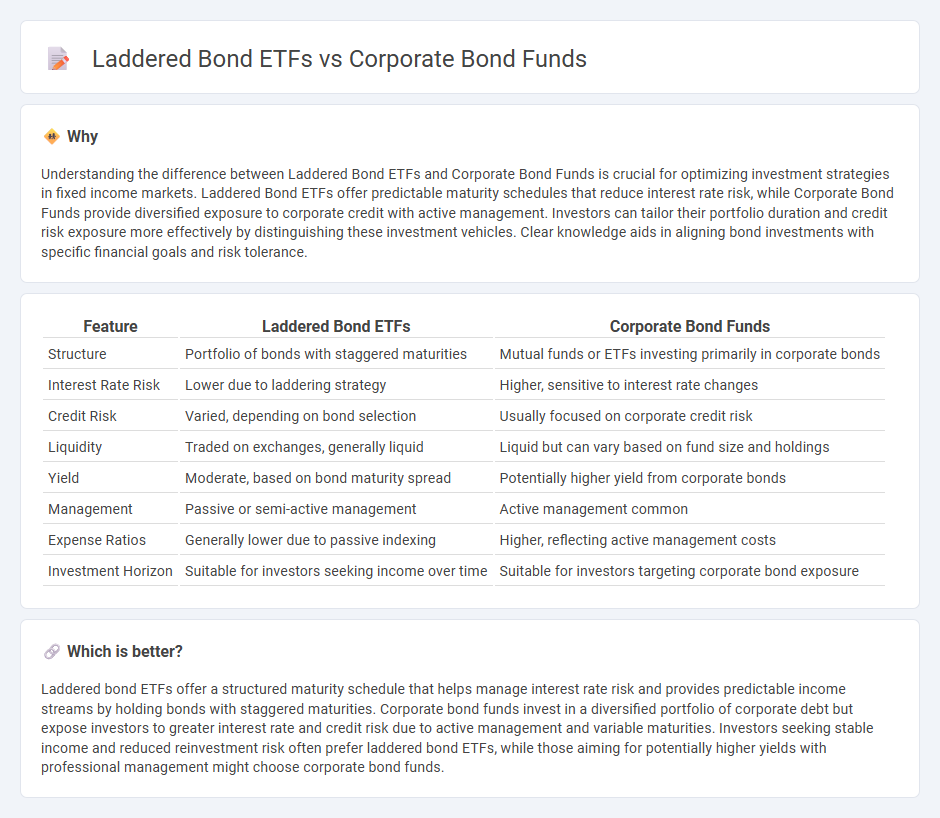
| Feature | Laddered Bond ETFs | Corporate Bond Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Portfolio of bonds with staggered maturities | Mutual funds or ETFs investing primarily in corporate bonds |
| Interest Rate Risk | Lower due to laddering strategy | Higher, sensitive to interest rate changes |
| Credit Risk | Varied, depending on bond selection | Usually focused on corporate credit risk |
| Liquidity | Traded on exchanges, generally liquid | Liquid but can vary based on fund size and holdings |
| Yield | Moderate, based on bond maturity spread | Potentially higher yield from corporate bonds |
| Management | Passive or semi-active management | Active management common |
| Expense Ratios | Generally lower due to passive indexing | Higher, reflecting active management costs |
| Investment Horizon | Suitable for investors seeking income over time | Suitable for investors targeting corporate bond exposure |
Which is better?
Laddered bond ETFs offer a structured maturity schedule that helps manage interest rate risk and provides predictable income streams by holding bonds with staggered maturities. Corporate bond funds invest in a diversified portfolio of corporate debt but expose investors to greater interest rate and credit risk due to active management and variable maturities. Investors seeking stable income and reduced reinvestment risk often prefer laddered bond ETFs, while those aiming for potentially higher yields with professional management might choose corporate bond funds.
Connection
Laddered bond ETFs strategically stagger maturity dates to mitigate interest rate risk, while corporate bond funds pool investments in diverse corporate debt for steady income. Both investment vehicles offer exposure to corporate bonds, but laddered bond ETFs provide predictable cash flows through scheduled maturities, enhancing liquidity management. Corporate bond funds complement this by actively managing credit risk and sector allocation, resulting in a balanced fixed-income portfolio.
Key Terms
Credit Risk
Corporate bond funds often carry higher credit risk due to their concentration in lower-rated corporate debt, exposing investors to potential defaults and credit downgrades. Laddered bond ETFs mitigate credit risk by diversifying bond maturities and issuers, balancing yield and risk while providing predictable income streams. Explore the detailed credit risk profiles of both options to optimize your fixed-income portfolio strategy.
Yield
Corporate bond funds typically offer higher yields due to exposure to lower-rated investment-grade or high-yield corporate debt, whereas laddered bond ETFs focus on credit quality and maturity diversification, delivering more stable but generally lower yields. Laddered bond ETFs mitigate interest rate risk through systematic maturity staggering, which helps maintain a consistent income stream amid market fluctuations. Explore detailed yield comparisons and risk profiles to determine the best fit for your income-focused investment strategy.
Duration
Corporate bond funds typically offer diversified exposure to a range of credit qualities and maturities, often resulting in variable duration profiles that adjust with market conditions. Laddered bond ETFs, structured with staggered maturities, provide more predictable duration and reduced interest rate risk by systematically spreading investments across different bond durations. Explore the nuances between these strategies to optimize duration management and enhance your fixed-income portfolio.
Source and External Links
Invesco Corporate Bond Fund - An active total return strategy focused on providing current income with capital preservation by investing primarily in corporate bonds with diversified credit quality from investment grade to high yield.
Corporate Bonds - Fidelity Overview - Corporate bonds are debt obligations issued by companies, offering fixed-rate coupons with risks including credit risk and interest rate risk, and are categorized into investment grade (lower risk) and high yield (higher risk) bonds.
MFBFX: Corporate Bond Fund - A mutual fund emphasizing current income and total return with a focus on credit quality and extensive risk management, investing in corporate bonds with solid or improving fundamentals.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com