Zero-day options provide traders with ultra-short-term opportunities to capitalize on immediate market movements, featuring high leverage and rapid expiration within the same trading day. Convertible bonds offer investors a hybrid approach, combining fixed income with the potential for equity conversion, thus balancing risk and return over a longer time horizon. Explore the detailed distinctions and strategic uses of zero-day options versus convertible bonds to optimize your investment portfolio.
Why it is important
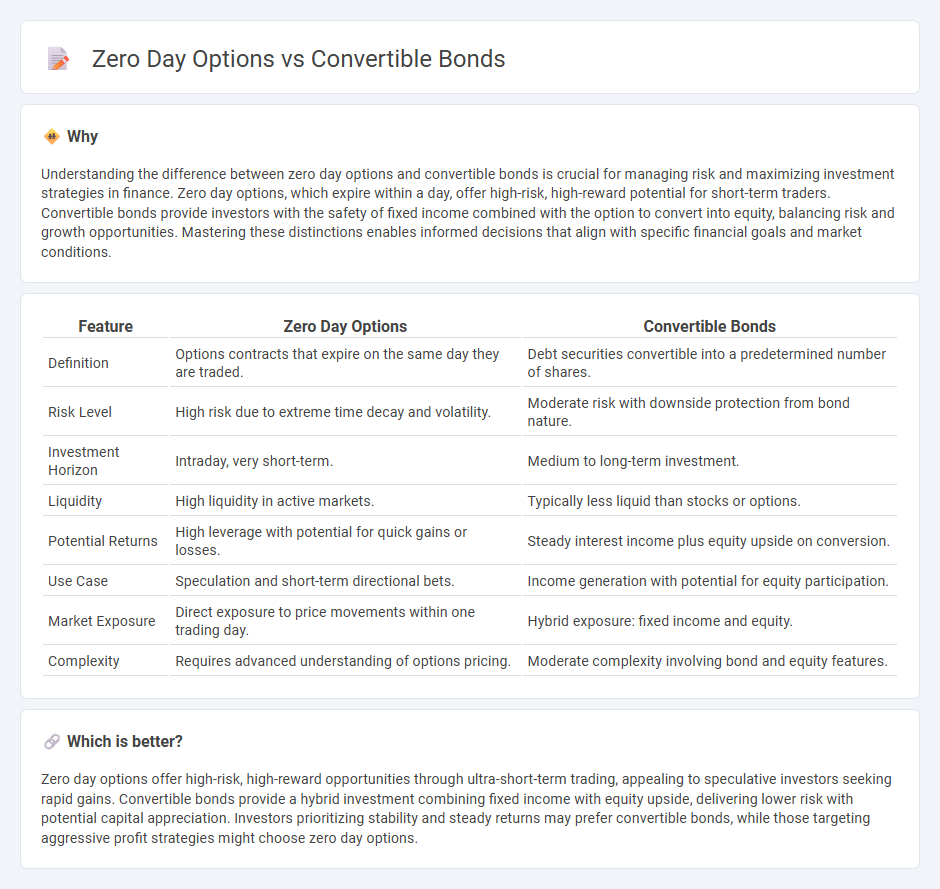
Understanding the difference between zero day options and convertible bonds is crucial for managing risk and maximizing investment strategies in finance. Zero day options, which expire within a day, offer high-risk, high-reward potential for short-term traders. Convertible bonds provide investors with the safety of fixed income combined with the option to convert into equity, balancing risk and growth opportunities. Mastering these distinctions enables informed decisions that align with specific financial goals and market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Zero Day Options | Convertible Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Options contracts that expire on the same day they are traded. | Debt securities convertible into a predetermined number of shares. |
| Risk Level | High risk due to extreme time decay and volatility. | Moderate risk with downside protection from bond nature. |
| Investment Horizon | Intraday, very short-term. | Medium to long-term investment. |
| Liquidity | High liquidity in active markets. | Typically less liquid than stocks or options. |
| Potential Returns | High leverage with potential for quick gains or losses. | Steady interest income plus equity upside on conversion. |
| Use Case | Speculation and short-term directional bets. | Income generation with potential for equity participation. |
| Market Exposure | Direct exposure to price movements within one trading day. | Hybrid exposure: fixed income and equity. |
| Complexity | Requires advanced understanding of options pricing. | Moderate complexity involving bond and equity features. |
Which is better?
Zero day options offer high-risk, high-reward opportunities through ultra-short-term trading, appealing to speculative investors seeking rapid gains. Convertible bonds provide a hybrid investment combining fixed income with equity upside, delivering lower risk with potential capital appreciation. Investors prioritizing stability and steady returns may prefer convertible bonds, while those targeting aggressive profit strategies might choose zero day options.
Connection
Zero day options and convertible bonds intersect in advanced financial strategies where investors leverage short-term options to hedge or enhance positions in convertible bonds. Convertible bonds, hybrid securities with embedded options to convert into equity, can be complemented by zero day options--options that expire the same day--to fine-tune risk exposure and capitalize on intraday market movements. This synergy allows for dynamic portfolio management blending debt instruments with rapid-option trades to optimize returns and manage volatility.
Key Terms
Conversion Ratio
Convertible bonds feature a conversion ratio that determines the number of shares an investor can receive upon conversion, directly influencing potential equity ownership and dilution. Zero-day options, expiring on the same day they are issued, do not involve conversion ratios but rather focus on immediate intrinsic value and volatility-driven pricing. Explore the detailed mechanics of conversion ratios and their impact on investment strategies to enhance your financial insights.
Maturity
Convertible bonds typically have maturities ranging from 5 to 10 years, offering investors a fixed income with potential equity conversion before maturity. Zero day options expire on the same day they are issued, providing high-risk, short-term trading opportunities without long-term commitment. Explore the strategic implications of maturity differences to optimize your investment decisions.
Time Decay (Theta)
Convertible bonds offer investors a hybrid security with equity upside and fixed income features, exhibiting minimal sensitivity to time decay (Theta) compared to zero day options, which experience rapid Theta erosion due to their imminent expiration. Zero day options lose value exponentially as expiration approaches, making them highly sensitive to time decay, whereas convertible bonds retain value through underlying stock conversion potential and coupon payments. Explore deeper insights into how Theta impacts these instruments and shapes investment strategies.
Source and External Links
Convertible bonds - What are they, definition & examples - StoneX - Convertible bonds are hybrid securities that pay interest and can be converted into a predetermined number of shares of the issuer's stock, typically offering lower interest rates in exchange for the conversion option and including features like conversion ratio, conversion price, maturity date, and call/put options.
What are convertible bonds? - RBC Global Asset Management - Convertible bonds combine features of bonds and equities by providing bond-like income and principal protection with the potential to convert to equity, offering downside protection with the "bond floor" and upside participation if share prices rise.
Convertible bond - Wikipedia - Convertible bonds allow issuers to borrow at lower fixed interest rates compared to straight bonds and can defer equity dilution by setting conversion prices typically higher than current share prices, offering benefits like lower cost borrowing and long-term fixed-rate financing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com