Shadow banking involves non-bank financial intermediaries that provide credit and other financial services outside traditional regulatory frameworks, often including entities like hedge funds and money market funds. Commercial banking encompasses regulated institutions that accept deposits, offer loans, and provide payment services under governmental oversight, ensuring depositor protection and financial stability. Explore the distinctions and implications of shadow banking versus commercial banking to understand their roles in the financial ecosystem.
Why it is important
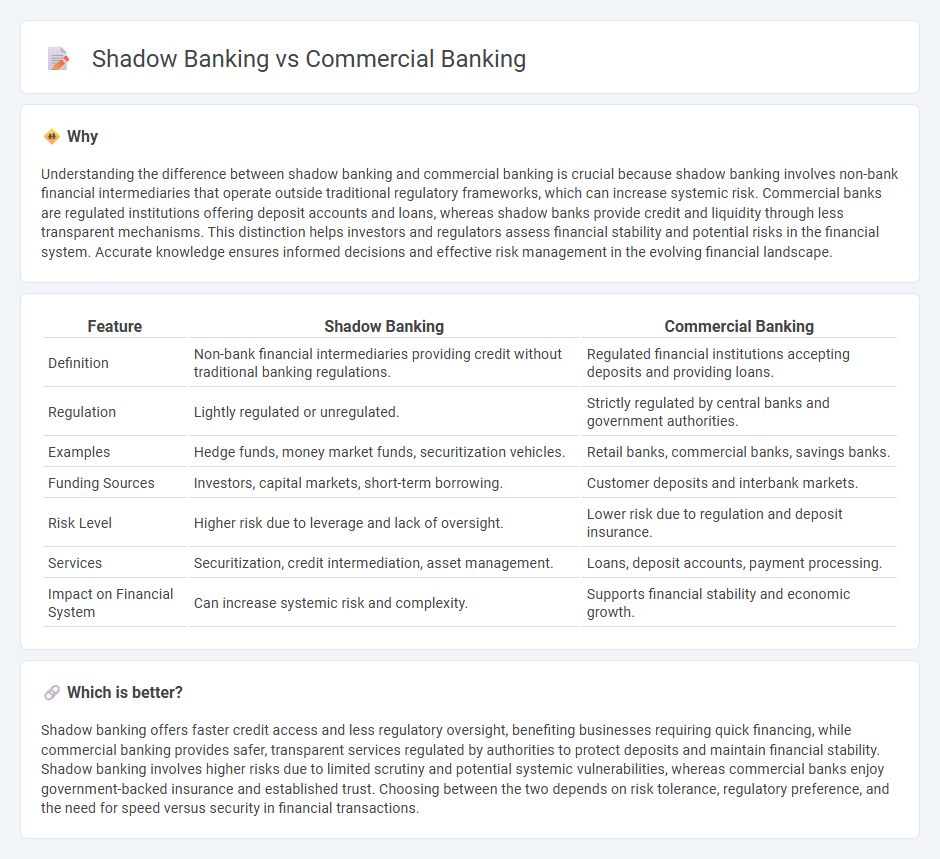
Understanding the difference between shadow banking and commercial banking is crucial because shadow banking involves non-bank financial intermediaries that operate outside traditional regulatory frameworks, which can increase systemic risk. Commercial banks are regulated institutions offering deposit accounts and loans, whereas shadow banks provide credit and liquidity through less transparent mechanisms. This distinction helps investors and regulators assess financial stability and potential risks in the financial system. Accurate knowledge ensures informed decisions and effective risk management in the evolving financial landscape.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Shadow Banking | Commercial Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-bank financial intermediaries providing credit without traditional banking regulations. | Regulated financial institutions accepting deposits and providing loans. |
| Regulation | Lightly regulated or unregulated. | Strictly regulated by central banks and government authorities. |
| Examples | Hedge funds, money market funds, securitization vehicles. | Retail banks, commercial banks, savings banks. |
| Funding Sources | Investors, capital markets, short-term borrowing. | Customer deposits and interbank markets. |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to leverage and lack of oversight. | Lower risk due to regulation and deposit insurance. |
| Services | Securitization, credit intermediation, asset management. | Loans, deposit accounts, payment processing. |
| Impact on Financial System | Can increase systemic risk and complexity. | Supports financial stability and economic growth. |
Which is better?
Shadow banking offers faster credit access and less regulatory oversight, benefiting businesses requiring quick financing, while commercial banking provides safer, transparent services regulated by authorities to protect deposits and maintain financial stability. Shadow banking involves higher risks due to limited scrutiny and potential systemic vulnerabilities, whereas commercial banks enjoy government-backed insurance and established trust. Choosing between the two depends on risk tolerance, regulatory preference, and the need for speed versus security in financial transactions.
Connection
Shadow banking and commercial banking are interconnected through their mutual involvement in credit creation and financial intermediation, with shadow banks often serving as off-balance-sheet entities that extend loans and liquidity beyond traditional regulatory frameworks. This connection influences systemic risk by amplifying credit cycles and enhancing financial leverage without the same capital and transparency requirements faced by commercial banks. Consequently, regulators monitor shadow banking activities closely to mitigate potential spillover effects on the stability of the commercial banking sector and the broader financial system.
Key Terms
Regulation
Commercial banking operates under strict regulatory frameworks such as the Dodd-Frank Act and Basel III, ensuring transparency, risk management, and depositor protection. Shadow banking involves non-bank financial intermediaries like hedge funds and money market funds that are less regulated, creating potential systemic risk due to their lack of oversight. Learn more about the regulatory distinctions and their impact on financial stability.
Funding sources
Commercial banking relies predominantly on customer deposits, including checking and savings accounts, as primary funding sources, supplemented by interbank loans and central bank borrowings. Shadow banking secures funding through non-traditional channels such as repurchase agreements, asset-backed commercial paper, and money market funds, operating largely outside the regulatory framework governing commercial banks. Learn more about how these differing funding mechanisms impact financial markets and systemic risk.
Risk profile
Commercial banking operates under strict regulatory frameworks, ensuring greater transparency and lower risk through insured deposits and capital requirements, while shadow banking involves non-bank financial intermediaries that lack direct regulation, leading to higher risk exposure and potential systemic vulnerabilities. Shadow banks often engage in activities such as securitization and leverage that amplify credit risk and liquidity risk, posing challenges for financial stability. Explore deeper insights into their risk profiles to better understand the implications for global financial markets.
Source and External Links
Commercial bank - Wikipedia - A commercial bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and provides loans for consumption and investment, playing a key role in credit creation and economic growth while being heavily regulated by central banks.
Commercial Banker Career Profile - Corporate Finance Institute - Commercial bankers serve medium-to-large businesses with financial solutions like loans, credit, cash management, and treasury services, focusing on client advisory and relationship management.
Commercial Banking and Financial Solutions | J.P. Morgan Chase - Commercial banking offers credit and financing tools, treasury and payment services, and expertise in international banking and commercial real estate to help businesses manage their financial needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com