Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) operate on blockchain technology, allowing peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries, enhancing security and control over funds. Centralized exchanges (CEXs) offer higher liquidity, faster transactions, and user-friendly interfaces but require users to trust a third party with their assets. Explore the key differences and advantages of DEXs and CEXs to determine the best fit for your trading needs.
Why it is important
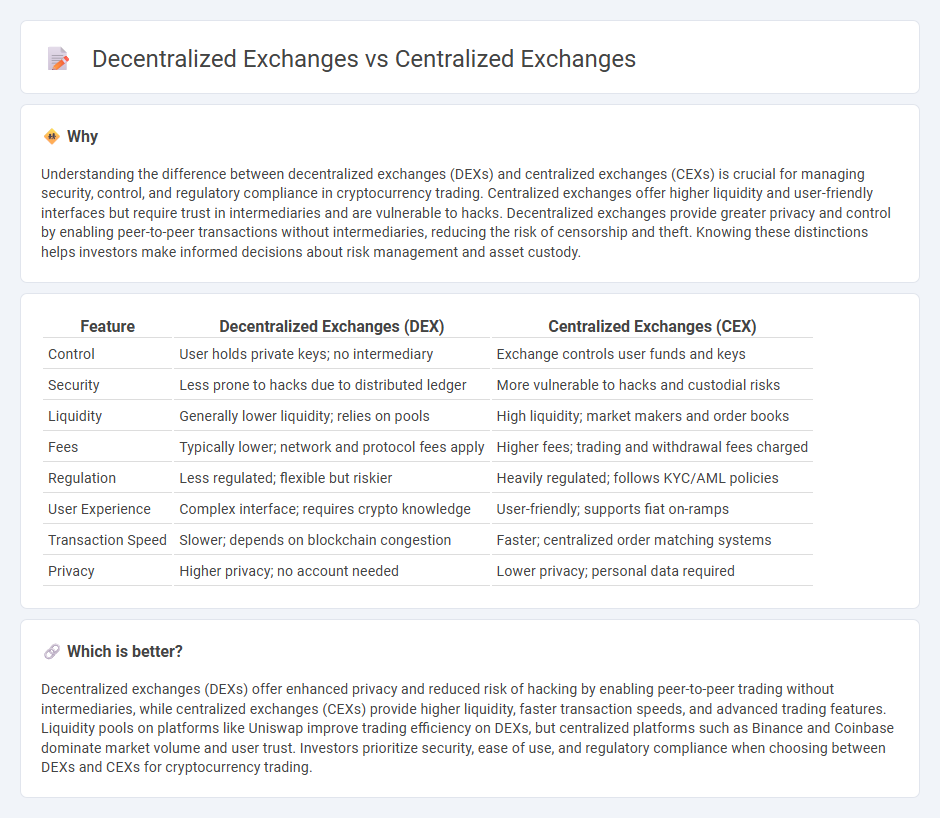
Understanding the difference between decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and centralized exchanges (CEXs) is crucial for managing security, control, and regulatory compliance in cryptocurrency trading. Centralized exchanges offer higher liquidity and user-friendly interfaces but require trust in intermediaries and are vulnerable to hacks. Decentralized exchanges provide greater privacy and control by enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, reducing the risk of censorship and theft. Knowing these distinctions helps investors make informed decisions about risk management and asset custody.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) | Centralized Exchanges (CEX) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | User holds private keys; no intermediary | Exchange controls user funds and keys |
| Security | Less prone to hacks due to distributed ledger | More vulnerable to hacks and custodial risks |
| Liquidity | Generally lower liquidity; relies on pools | High liquidity; market makers and order books |
| Fees | Typically lower; network and protocol fees apply | Higher fees; trading and withdrawal fees charged |
| Regulation | Less regulated; flexible but riskier | Heavily regulated; follows KYC/AML policies |
| User Experience | Complex interface; requires crypto knowledge | User-friendly; supports fiat on-ramps |
| Transaction Speed | Slower; depends on blockchain congestion | Faster; centralized order matching systems |
| Privacy | Higher privacy; no account needed | Lower privacy; personal data required |
Which is better?
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) offer enhanced privacy and reduced risk of hacking by enabling peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries, while centralized exchanges (CEXs) provide higher liquidity, faster transaction speeds, and advanced trading features. Liquidity pools on platforms like Uniswap improve trading efficiency on DEXs, but centralized platforms such as Binance and Coinbase dominate market volume and user trust. Investors prioritize security, ease of use, and regulatory compliance when choosing between DEXs and CEXs for cryptocurrency trading.
Connection
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and centralized exchanges (CEXs) are connected through their roles in cryptocurrency trading, providing complementary functions within the digital asset ecosystem. CEXs offer high liquidity and user-friendly interfaces, while DEXs prioritize security and privacy by enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. Integration solutions like cross-chain bridges and hybrid platforms facilitate asset transfer and interoperability between DEXs and CEXs, enhancing overall market efficiency.
Key Terms
Custodianship
Centralized exchanges (CEXs) hold users' funds and private keys, entrusting custody to the platform, which increases risks like hacking or mismanagement but simplifies user experience and regulatory compliance. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) enable users to maintain control of their private keys at all times through smart contracts, enhancing security and privacy while requiring users to manage their own custody risks. Explore the nuanced differences in custodianship models and their implications to make informed trading decisions.
Liquidity
Centralized exchanges (CEXs) provide high liquidity by aggregating order books and facilitating large-volume transactions with minimal slippage, often supported by market makers and institutional participants. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) rely on automated market makers (AMMs) and liquidity pools, which may offer lower liquidity and higher slippage but enable permissionless trading and asset control. Explore the key differences in liquidity models and trading efficiency to optimize your exchange choice.
KYC/AML
Centralized exchanges (CEXs) enforce strict KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) protocols to comply with regulatory standards and reduce fraud risks, often requiring users to submit identity documents and undergo verification processes. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) operate without intermediaries and typically do not mandate KYC/AML checks, prioritizing privacy and user control but facing regulatory challenges due to potential misuse. Explore our comprehensive guide to understand how KYC and AML impact both exchange types and user security.
Source and External Links
Cryptocurrency Exchanges - Overview, Advantages, Top 10 - Centralized exchanges (CEX) act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, operate via an order book system, and earn through commissions and transaction fees; popular examples include Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken.
Centralized Crypto Exchanges Examined - Gemini - Centralized exchanges are regulated platforms that facilitate crypto trading with custodial control of private keys and remain the easiest and safest way for many users to buy and hold cryptocurrencies despite the rise of decentralized exchanges.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Crypto Exchanges - CoinLedger - Centralized exchanges are suitable for beginners for ease of use and trusted operation, with Coinbase and Binance being leading examples of centralized platforms in the crypto space.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com