Dark pool trading involves private, off-exchange transactions that allow institutional investors to buy or sell large blocks of securities anonymously, minimizing market impact. In contrast, block trading occurs on public exchanges but focuses on executing large orders that can influence market prices due to their size. Explore the nuances and advantages of both trading methods to enhance your financial strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dark pool trading and block trading is crucial for optimizing trade execution and minimizing market impact in finance. Dark pool trading happens in private venues where large orders are executed anonymously, preventing price fluctuations. Block trading involves the public exchange of large securities, potentially affecting market prices due to visibility. Accurate knowledge helps investors and traders make informed decisions while managing risk and liquidity effectively.
Comparison Table
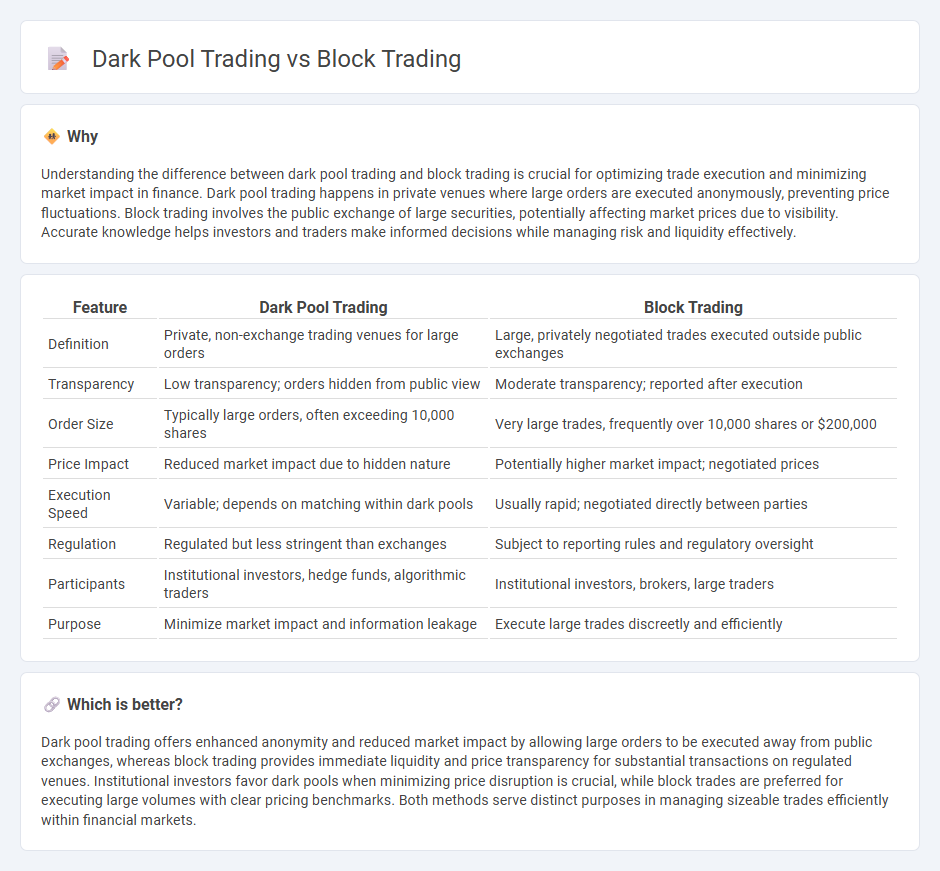
| Feature | Dark Pool Trading | Block Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private, non-exchange trading venues for large orders | Large, privately negotiated trades executed outside public exchanges |
| Transparency | Low transparency; orders hidden from public view | Moderate transparency; reported after execution |
| Order Size | Typically large orders, often exceeding 10,000 shares | Very large trades, frequently over 10,000 shares or $200,000 |
| Price Impact | Reduced market impact due to hidden nature | Potentially higher market impact; negotiated prices |
| Execution Speed | Variable; depends on matching within dark pools | Usually rapid; negotiated directly between parties |
| Regulation | Regulated but less stringent than exchanges | Subject to reporting rules and regulatory oversight |
| Participants | Institutional investors, hedge funds, algorithmic traders | Institutional investors, brokers, large traders |
| Purpose | Minimize market impact and information leakage | Execute large trades discreetly and efficiently |
Which is better?
Dark pool trading offers enhanced anonymity and reduced market impact by allowing large orders to be executed away from public exchanges, whereas block trading provides immediate liquidity and price transparency for substantial transactions on regulated venues. Institutional investors favor dark pools when minimizing price disruption is crucial, while block trades are preferred for executing large volumes with clear pricing benchmarks. Both methods serve distinct purposes in managing sizeable trades efficiently within financial markets.
Connection
Dark pool trading and block trading are interrelated as dark pools provide a private venue for executing large block trades away from public exchanges, minimizing market impact and reducing price slippage. Institutional investors frequently utilize dark pools to discreetly buy or sell substantial shares without revealing their trading intentions, which helps preserve market stability. The volume of block trades executed in dark pools significantly contributes to overall market liquidity while maintaining confidentiality.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Block trading involves the sale or purchase of large volumes of securities, directly impacting market liquidity by temporarily absorbing significant supply or demand. Dark pool trading occurs in private exchanges where large orders are matched anonymously, minimizing market impact and preserving liquidity by preventing price fluctuations. Explore the nuances of how these trading methods influence liquidity to optimize your investment strategy.
Anonymity
Block trading offers large-volume transactions executed away from public markets, enhancing anonymity by reducing market impact and price movement exposure. Dark pool trading, facilitated through private exchanges, prioritizes even greater confidentiality by concealing order details until after execution, minimizing information leakage. Explore further to understand the nuances and strategic advantages of anonymity in these trading methods.
Market Impact
Block trading involves large-volume transactions executed on public exchanges, significantly affecting market prices due to visible order sizes. Dark pool trading occurs on private platforms where large trades are concealed, minimizing market impact and price fluctuations by preventing information leakage. Explore detailed analyses to understand how these methods influence liquidity and price stability in financial markets.
Source and External Links
Understanding Block Trade in Stock Market - A block trade is a large-volume transaction privately negotiated and executed outside the open market to avoid impacting prices, typically used by institutional investors and mutual funds, with key differences from cross trades in terms of transparency and regulation.
What is Block Trade: Know its Benefits and Features - Block trades enable large buying or selling of securities in one transaction, maintaining privacy, preventing market disruption, and improving liquidity through methods like dark pools and iceberg orders facilitated by specialized brokers called block houses.
Block Trades - What is a Block Trade? - Block trades are privately negotiated futures, options, or combination transactions meeting quantity thresholds, executed apart from public auction markets according to regulatory guidelines and facilitated by brokers or direct bilateral communications.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com