Biodiversity credits represent a market-based approach to conserving ecosystems by assigning economic value to species protection, while water rights allocate legal entitlements to water usage, often influencing resource distribution and sustainability. Both instruments impact economic activities by integrating environmental stewardship into financial frameworks, driving investment in natural capital. Explore deeper to understand how biodiversity credits and water rights shape sustainable economic strategies.
Why it is important
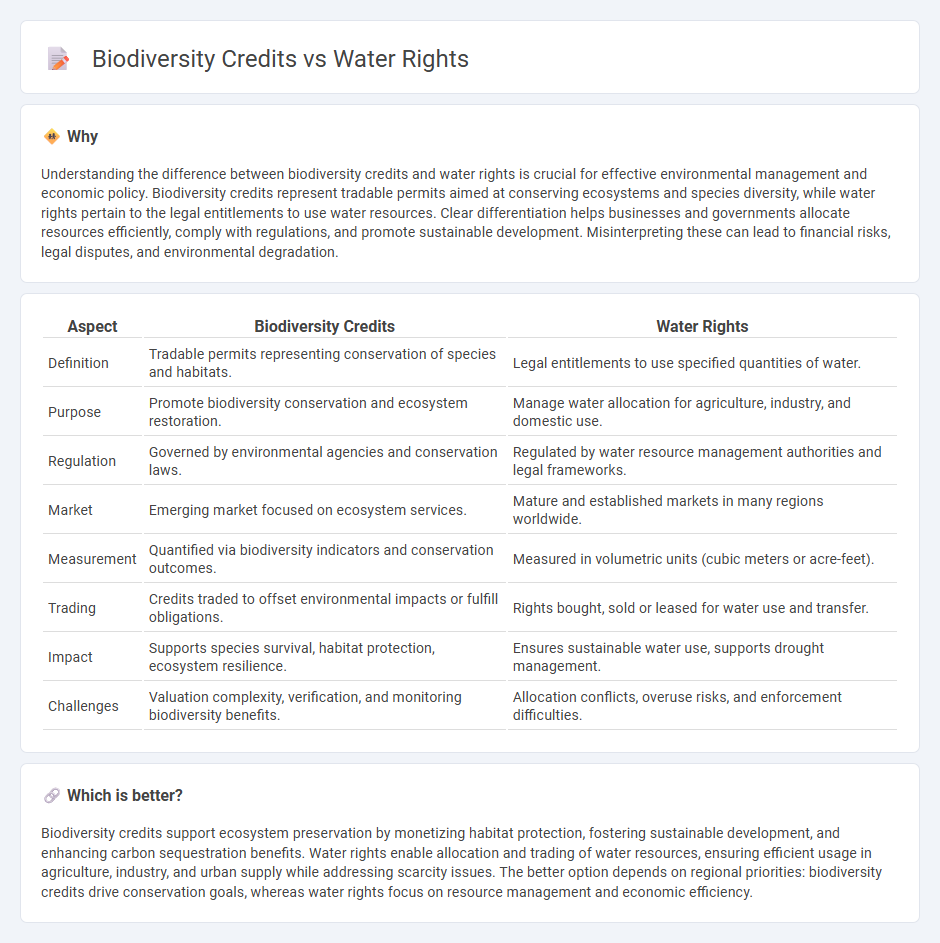
Understanding the difference between biodiversity credits and water rights is crucial for effective environmental management and economic policy. Biodiversity credits represent tradable permits aimed at conserving ecosystems and species diversity, while water rights pertain to the legal entitlements to use water resources. Clear differentiation helps businesses and governments allocate resources efficiently, comply with regulations, and promote sustainable development. Misinterpreting these can lead to financial risks, legal disputes, and environmental degradation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Biodiversity Credits | Water Rights |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tradable permits representing conservation of species and habitats. | Legal entitlements to use specified quantities of water. |
| Purpose | Promote biodiversity conservation and ecosystem restoration. | Manage water allocation for agriculture, industry, and domestic use. |
| Regulation | Governed by environmental agencies and conservation laws. | Regulated by water resource management authorities and legal frameworks. |
| Market | Emerging market focused on ecosystem services. | Mature and established markets in many regions worldwide. |
| Measurement | Quantified via biodiversity indicators and conservation outcomes. | Measured in volumetric units (cubic meters or acre-feet). |
| Trading | Credits traded to offset environmental impacts or fulfill obligations. | Rights bought, sold or leased for water use and transfer. |
| Impact | Supports species survival, habitat protection, ecosystem resilience. | Ensures sustainable water use, supports drought management. |
| Challenges | Valuation complexity, verification, and monitoring biodiversity benefits. | Allocation conflicts, overuse risks, and enforcement difficulties. |
Which is better?
Biodiversity credits support ecosystem preservation by monetizing habitat protection, fostering sustainable development, and enhancing carbon sequestration benefits. Water rights enable allocation and trading of water resources, ensuring efficient usage in agriculture, industry, and urban supply while addressing scarcity issues. The better option depends on regional priorities: biodiversity credits drive conservation goals, whereas water rights focus on resource management and economic efficiency.
Connection
Biodiversity credits and water rights are interconnected through their shared role in ecosystem services valuation and sustainable resource management. Biodiversity credits incentivize the preservation of natural habitats that regulate water quality and availability, directly influencing water rights by maintaining watershed health and ensuring water supply reliability. Integrating these mechanisms supports environmental markets and promotes balanced economic development within the circular economy framework.
Key Terms
Allocation
Water rights allocate water use among individuals or entities based on legal entitlements, prioritizing resource distribution for agriculture, industry, and domestic needs. Biodiversity credits focus on the allocation of conservation efforts by quantifying ecological benefits to support habitat protection and species survival via market-based incentives. Explore how these allocation systems balance environmental stewardship and resource management in detail.
Valuation
Water rights valuation hinges on quantifiable factors such as volume allocation, legal entitlements, and market demand in sectors like agriculture and industry. Biodiversity credits valuation involves assessing ecological services, species conservation value, and habitat preservation, often utilizing complex environmental metrics and stakeholder input. Explore the nuances of these valuation methods to understand their impact on sustainable resource management and environmental economics.
Market mechanisms
Water rights function as tradable permits that allocate water usage, enabling efficient distribution through market mechanisms and incentivizing sustainable water management practices. Biodiversity credits represent a market-based instrument allowing stakeholders to buy and sell units of conserved or restored biodiversity, promoting ecosystem preservation and restoration. Explore the evolving market solutions that balance resource allocation and environmental conservation.
Source and External Links
Water Rights Process | California State Water Resources Control Board - A water right is a legal entitlement authorizing water diversion and beneficial, nonwasteful use, considered a property right to use water but not ownership of the water itself, regulated by permits and licenses to balance orderly resource development, prevention of waste, and environmental protection.
Water Rights - Division of Water Resources, Colorado - Colorado follows the Prior Appropriation System, where water rights are allocated based on "first in time, first in right," prioritizing earlier water use claimed and certified by water courts before junior rights are satisfied.
Understanding Water Rights: 12 Types of Water Rights - MasterClass - Water rights provide legal authorization to use water from a specified source, with two main U.S. doctrines: riparian rights linked to land bordering water and prior-appropriation rights granted by the state, regulating use of surface water and groundwater to ensure reasonable, non-exhaustive usage.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com