Grey market imports refer to genuine products imported and sold through unauthorized channels, often bypassing official distribution networks, resulting in potential legal and warranty issues. Parallel imports involve goods brought into a country without the permission of the intellectual property owner but comply with local laws, typically offering lower prices but raising concerns about quality and after-sales service. Explore the distinctions and implications of grey market versus parallel imports to understand their impact on the economy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Grey market imports and Parallel imports is crucial for businesses to ensure compliance with international trade laws and intellectual property rights. Grey market imports often bypass authorized distribution, risking counterfeit products and violating manufacturer warranties. Parallel imports, while legally sourced, can affect pricing strategies and brand reputation across different markets. Recognizing these distinctions helps companies manage supply chains effectively and protect consumer trust.
Comparison Table
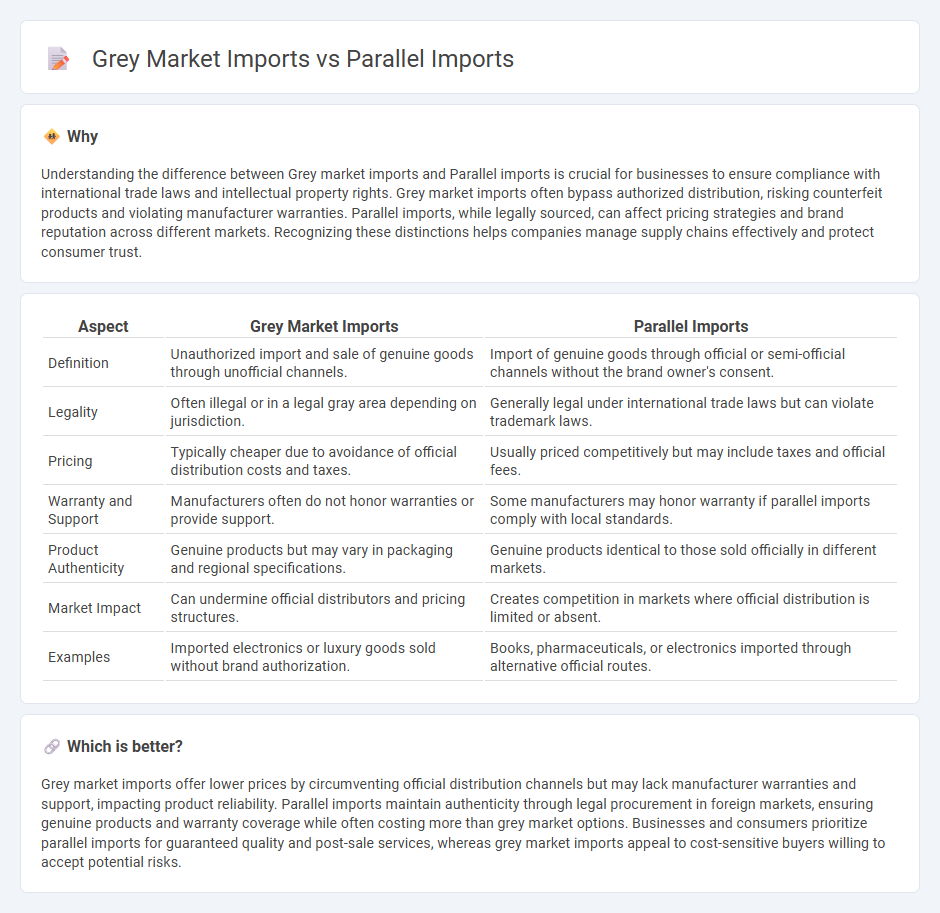
| Aspect | Grey Market Imports | Parallel Imports |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unauthorized import and sale of genuine goods through unofficial channels. | Import of genuine goods through official or semi-official channels without the brand owner's consent. |
| Legality | Often illegal or in a legal gray area depending on jurisdiction. | Generally legal under international trade laws but can violate trademark laws. |
| Pricing | Typically cheaper due to avoidance of official distribution costs and taxes. | Usually priced competitively but may include taxes and official fees. |
| Warranty and Support | Manufacturers often do not honor warranties or provide support. | Some manufacturers may honor warranty if parallel imports comply with local standards. |
| Product Authenticity | Genuine products but may vary in packaging and regional specifications. | Genuine products identical to those sold officially in different markets. |
| Market Impact | Can undermine official distributors and pricing structures. | Creates competition in markets where official distribution is limited or absent. |
| Examples | Imported electronics or luxury goods sold without brand authorization. | Books, pharmaceuticals, or electronics imported through alternative official routes. |
Which is better?
Grey market imports offer lower prices by circumventing official distribution channels but may lack manufacturer warranties and support, impacting product reliability. Parallel imports maintain authenticity through legal procurement in foreign markets, ensuring genuine products and warranty coverage while often costing more than grey market options. Businesses and consumers prioritize parallel imports for guaranteed quality and post-sale services, whereas grey market imports appeal to cost-sensitive buyers willing to accept potential risks.
Connection
Grey market imports and parallel imports both involve the entry of goods into a country without the authorization of the intellectual property owner, often bypassing official distribution channels. These imports impact the economy by affecting local businesses, disrupting pricing strategies, and reducing tax revenues due to untaxed or misdeclared goods. Understanding their connection is key to formulating policies that safeguard markets while balancing consumer access to diverse products.
Key Terms
Price discrimination
Parallel imports occur when genuine products are imported and sold without the manufacturer's authorization, often exploiting price differences between markets to offer lower prices legally. Grey market imports involve unauthorized goods that may bypass official channels, frequently impacting brand pricing strategies and consumer trust due to uncertain warranty and support. Explore the nuances of price discrimination strategies and their effects on market dynamics to understand the full implications of these import practices.
Intellectual property rights
Parallel imports refer to genuine products imported without the trademark owner's permission but legally purchased abroad, while grey market imports involve unauthorized goods that may not meet local regulations. Intellectual property rights protect the trademark owner's control over distribution, often challenged by parallel imports due to trademark exhaustion doctrines, whereas grey market goods can infringe on copyrights or patents if they violate local standards. Explore detailed legal interpretations and case studies to understand the nuances of intellectual property enforcement in these import scenarios.
Market segmentation
Parallel imports involve genuine products sourced through unauthorized channels, targeting price-sensitive segments seeking brand authenticity at lower costs. Grey market imports often include products not intended for the local market, appealing to niche consumers desiring exclusive or unavailable items. Explore deeper market segmentation strategies to optimize import channel effectiveness and consumer reach.
Source and External Links
Parallel import - Wikipedia - A parallel import is a genuine, non-counterfeit product imported from another country without the intellectual property owner's permission, often influenced by exhaustion of intellectual property rights and varying legal frameworks across countries, commonly affecting pricing and availability of goods like pharmaceuticals and electronics.
Parallel Imports are A Global Phenomenon and a Grey Area - Parallel imports are authentic goods imported without the IP owner's consent, with legality differing globally: allowed in places like the EU and Australia under exhaustion principles, but generally prohibited or restricted in the U.S., impacting intellectual property rights and market dynamics.
Are parallel imports fake? - Wiser Market - Parallel imports are genuine trademark-protected products imported through unauthorized channels; while legitimate, they may differ in packaging, support, or warranty terms, and such differences can sometimes make their sale unlawful under certain conditions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com