The global economy faces divergent risks, with polycrisis referring to interconnected crises across sectors such as finance, climate, and geopolitics, while a bubble burst involves sudden market corrections driven by asset overvaluation. Understanding the nuanced impacts of polycrisis versus bubble bursts helps anticipate shifts in inflation, unemployment, and investment trends. Explore detailed analyses to grasp how these phenomena shape future economic stability.
Why it is important
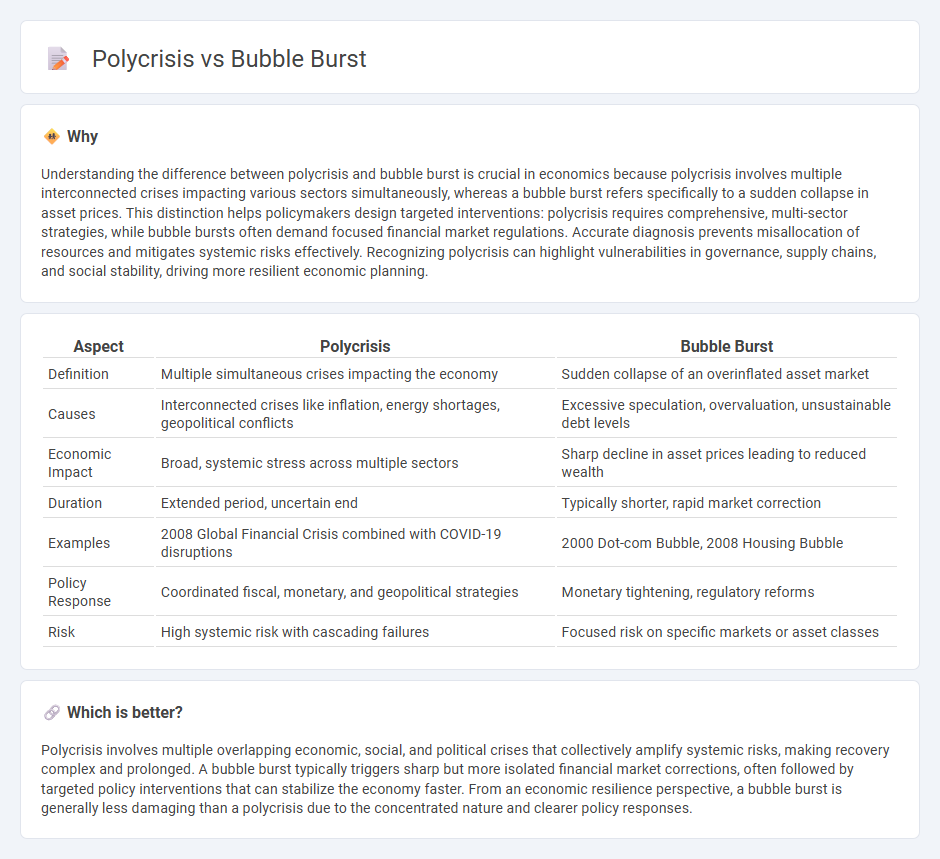
Understanding the difference between polycrisis and bubble burst is crucial in economics because polycrisis involves multiple interconnected crises impacting various sectors simultaneously, whereas a bubble burst refers specifically to a sudden collapse in asset prices. This distinction helps policymakers design targeted interventions: polycrisis requires comprehensive, multi-sector strategies, while bubble bursts often demand focused financial market regulations. Accurate diagnosis prevents misallocation of resources and mitigates systemic risks effectively. Recognizing polycrisis can highlight vulnerabilities in governance, supply chains, and social stability, driving more resilient economic planning.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Polycrisis | Bubble Burst |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple simultaneous crises impacting the economy | Sudden collapse of an overinflated asset market |
| Causes | Interconnected crises like inflation, energy shortages, geopolitical conflicts | Excessive speculation, overvaluation, unsustainable debt levels |
| Economic Impact | Broad, systemic stress across multiple sectors | Sharp decline in asset prices leading to reduced wealth |
| Duration | Extended period, uncertain end | Typically shorter, rapid market correction |
| Examples | 2008 Global Financial Crisis combined with COVID-19 disruptions | 2000 Dot-com Bubble, 2008 Housing Bubble |
| Policy Response | Coordinated fiscal, monetary, and geopolitical strategies | Monetary tightening, regulatory reforms |
| Risk | High systemic risk with cascading failures | Focused risk on specific markets or asset classes |
Which is better?
Polycrisis involves multiple overlapping economic, social, and political crises that collectively amplify systemic risks, making recovery complex and prolonged. A bubble burst typically triggers sharp but more isolated financial market corrections, often followed by targeted policy interventions that can stabilize the economy faster. From an economic resilience perspective, a bubble burst is generally less damaging than a polycrisis due to the concentrated nature and clearer policy responses.
Connection
Polycrisis, characterized by multiple interconnected global challenges such as economic instability, climate change, and geopolitical tensions, amplifies the risk and impact of financial bubbles bursting. The interconnected nature of these crises weakens economic resilience, causing asset bubbles--such as in real estate or stock markets--to collapse more abruptly and with wider systemic consequences. This dynamic disrupts market confidence, leading to reduced investment, heightened volatility, and prolonged economic downturns.
Key Terms
**Bubble Burst:**
A bubble burst refers to a rapid decrease in asset prices following a period of inflated market values, often causing significant economic disruption in sectors like housing, technology stocks, or commodities. Key examples include the 2008 financial crisis triggered by the U.S. housing bubble collapse, demonstrating how excessive speculation and leverage amplify financial instability. Explore further to understand the mechanics and impacts of financial bubbles in global markets.
Asset Prices
A bubble burst refers to the rapid collapse of inflated asset prices, typically after reaching unsustainable levels, resulting in significant market corrections. Polycrisis involves multiple, interconnected crises impacting asset prices across various sectors, leading to prolonged volatility and systemic risks. Explore further to understand the nuanced impacts of bubble bursts versus polycrisis on asset valuation and market stability.
Speculation
A bubble burst refers to the sudden collapse of asset prices following a speculative surge, often driven by excessive investor optimism and leverage in markets such as real estate or stocks. Polycrisis involves multiple interconnected crises occurring simultaneously, amplifying the overall economic instability and making recovery more complex due to overlapping factors like geopolitical tensions, financial speculation, and systemic risks. Explore further to understand how speculative behavior influences both scenarios and shapes economic outcomes.
Source and External Links
Bubble Burst - Play for free - Online Games - Bubble Burst is a space-themed bubble shooter game with 50 levels, featuring gameplay where players shoot bubbles to fill a burst meter that, when full, fires bursts to remove bubbles, including challenging boss levels with rotating bubbles and black holes.
Bubble Burst for Android - Uptodown - Bubble Burst is a fun game that offers a unique Free-2-Win model, allowing users to play for free and have a chance to earn real cash rewards without in-app purchases or pay-to-win features, accessible anytime and anywhere.
Bubble Burst App on the App Store - Bubble Burst is an addictive bubble shooter game with hundreds of exciting levels, power-ups, vibrant graphics, and social features allowing players to compete with friends and enjoy daily rewards and special events.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com