Eco-anxiety reflects growing concerns about environmental degradation impacting economic stability, while the circular economy focuses on sustainable resource use by minimizing waste and maximizing reuse. Shifting from a linear economy to circular systems promotes resilience and long-term growth by creating closed-loop supply chains. Explore how balancing eco-anxiety with circular economy principles can drive innovative solutions for a sustainable future.
Why it is important
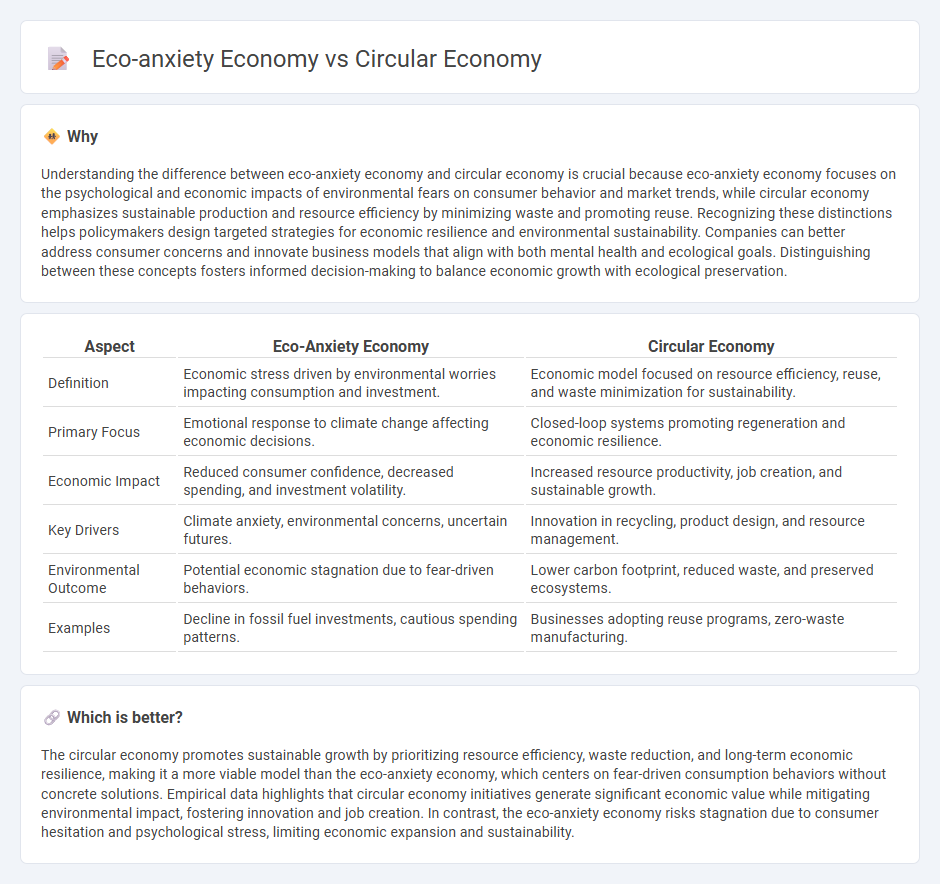
Understanding the difference between eco-anxiety economy and circular economy is crucial because eco-anxiety economy focuses on the psychological and economic impacts of environmental fears on consumer behavior and market trends, while circular economy emphasizes sustainable production and resource efficiency by minimizing waste and promoting reuse. Recognizing these distinctions helps policymakers design targeted strategies for economic resilience and environmental sustainability. Companies can better address consumer concerns and innovate business models that align with both mental health and ecological goals. Distinguishing between these concepts fosters informed decision-making to balance economic growth with ecological preservation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Eco-Anxiety Economy | Circular Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic stress driven by environmental worries impacting consumption and investment. | Economic model focused on resource efficiency, reuse, and waste minimization for sustainability. |
| Primary Focus | Emotional response to climate change affecting economic decisions. | Closed-loop systems promoting regeneration and economic resilience. |
| Economic Impact | Reduced consumer confidence, decreased spending, and investment volatility. | Increased resource productivity, job creation, and sustainable growth. |
| Key Drivers | Climate anxiety, environmental concerns, uncertain futures. | Innovation in recycling, product design, and resource management. |
| Environmental Outcome | Potential economic stagnation due to fear-driven behaviors. | Lower carbon footprint, reduced waste, and preserved ecosystems. |
| Examples | Decline in fossil fuel investments, cautious spending patterns. | Businesses adopting reuse programs, zero-waste manufacturing. |
Which is better?
The circular economy promotes sustainable growth by prioritizing resource efficiency, waste reduction, and long-term economic resilience, making it a more viable model than the eco-anxiety economy, which centers on fear-driven consumption behaviors without concrete solutions. Empirical data highlights that circular economy initiatives generate significant economic value while mitigating environmental impact, fostering innovation and job creation. In contrast, the eco-anxiety economy risks stagnation due to consumer hesitation and psychological stress, limiting economic expansion and sustainability.
Connection
Eco-anxiety drives consumer demand for sustainable products, influencing the growth of the circular economy by promoting resource efficiency and waste reduction. The circular economy addresses eco-anxiety by providing systemic solutions that minimize environmental impact through recycling, reuse, and regenerative design. This connection fosters innovation in green technologies and sustainable business models, aligning economic growth with ecological well-being.
Key Terms
**Circular Economy:**
The circular economy emphasizes sustainable resource use by designing products for reuse, repair, and recycling, minimizing waste and environmental impact. It fosters economic growth while conserving natural capital and promoting closed-loop systems that reduce dependence on finite resources. Explore how circular economy principles can drive innovation and mitigate eco-anxiety in modern society.
Resource Efficiency
The circular economy prioritizes resource efficiency by minimizing waste through reuse, recycling, and sustainable design, thereby extending product lifecycles and reducing environmental impact. In contrast, the eco-anxiety economy centers on consumer stress driven by environmental concerns, which can both hinder and motivate sustainable behaviors affecting resource use. Explore more about how these economic models shape resource efficiency and environmental resilience.
Closed-Loop Systems
Closed-loop systems form the backbone of the circular economy by minimizing waste through continuous recycling and reuse of materials, promoting sustainable resource management. In contrast, the eco-anxiety economy reflects the psychological stress caused by environmental degradation and climate change, driving demand for green solutions yet often hindering consumer confidence. Explore how closed-loop systems can alleviate eco-anxiety by fostering tangible environmental progress.
Source and External Links
Circular economy - Wikipedia - A circular economy is a model of production and consumption that prioritizes sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling materials and products to extend their lifecycle, reduce waste, and tackle climate change and resource depletion by designing out waste and pollution, keeping materials in use, and regenerating natural systems.
What is a circular economy? | Ellen MacArthur Foundation - The circular economy is a regenerative system designed to keep products and materials in use through maintenance, reuse, refurbishment, and recycling, eliminating waste and pollution, while decoupling economic activity from finite resource consumption.
What is Circular Economy & How Does It Work? : Complete Guide - Circular economy is an industrial system that intentionally loops resources back through reuse, repair, remanufacture, and disassembly, minimizing waste and emissions, and contrasting with the linear "take-make-dispose" economy to improve environmental sustainability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com