Revenge spending reflects a surge in consumer purchases driven by pent-up demand and heightened optimism after economic disruptions. Consumer confidence indexes, such as the University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index, measure public optimism about the economy's future and directly influence spending patterns. Explore how shifts in consumer confidence empower revenge spending trends and impact overall economic recovery.
Why it is important
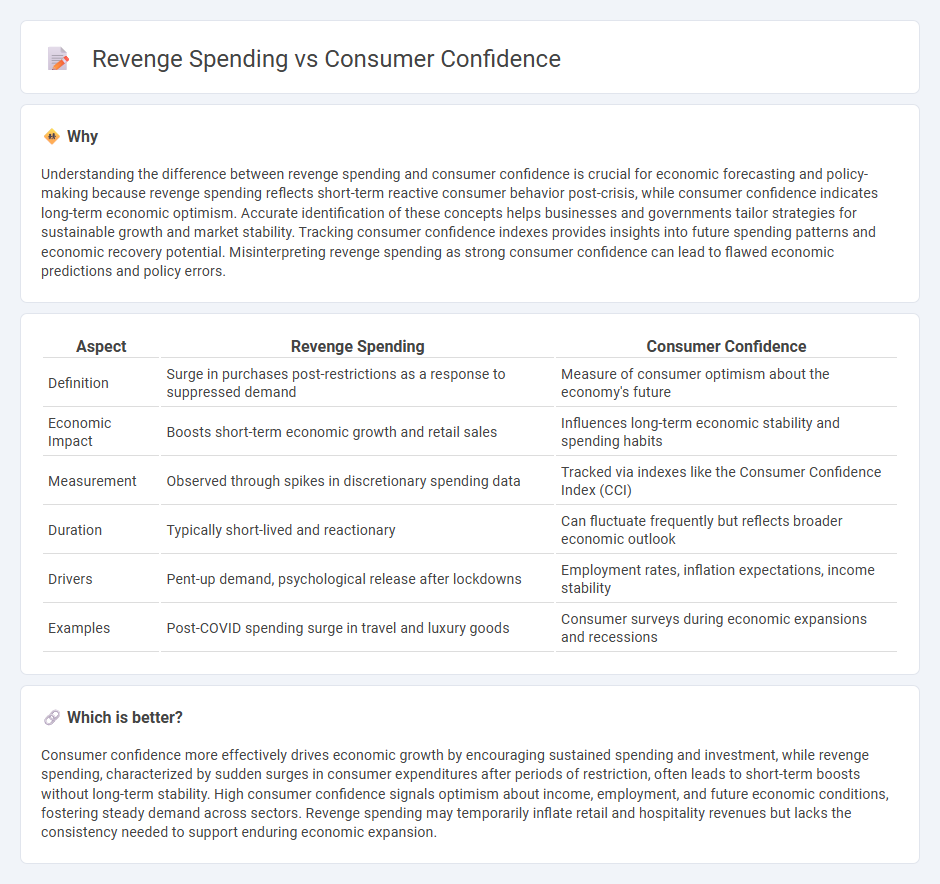
Understanding the difference between revenge spending and consumer confidence is crucial for economic forecasting and policy-making because revenge spending reflects short-term reactive consumer behavior post-crisis, while consumer confidence indicates long-term economic optimism. Accurate identification of these concepts helps businesses and governments tailor strategies for sustainable growth and market stability. Tracking consumer confidence indexes provides insights into future spending patterns and economic recovery potential. Misinterpreting revenge spending as strong consumer confidence can lead to flawed economic predictions and policy errors.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Revenge Spending | Consumer Confidence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Surge in purchases post-restrictions as a response to suppressed demand | Measure of consumer optimism about the economy's future |
| Economic Impact | Boosts short-term economic growth and retail sales | Influences long-term economic stability and spending habits |
| Measurement | Observed through spikes in discretionary spending data | Tracked via indexes like the Consumer Confidence Index (CCI) |
| Duration | Typically short-lived and reactionary | Can fluctuate frequently but reflects broader economic outlook |
| Drivers | Pent-up demand, psychological release after lockdowns | Employment rates, inflation expectations, income stability |
| Examples | Post-COVID spending surge in travel and luxury goods | Consumer surveys during economic expansions and recessions |
Which is better?
Consumer confidence more effectively drives economic growth by encouraging sustained spending and investment, while revenge spending, characterized by sudden surges in consumer expenditures after periods of restriction, often leads to short-term boosts without long-term stability. High consumer confidence signals optimism about income, employment, and future economic conditions, fostering steady demand across sectors. Revenge spending may temporarily inflate retail and hospitality revenues but lacks the consistency needed to support enduring economic expansion.
Connection
Revenge spending occurs when consumers increase their expenditures after periods of restricted consumption, reflecting a surge in consumer confidence. Elevated consumer confidence signals optimism about economic stability and future income, driving higher retail sales and service consumption. This boost in spending can stimulate economic growth, especially in sectors like travel, dining, and entertainment.
Key Terms
Economic Sentiment
Consumer confidence and economic sentiment directly influence revenge spending, as higher confidence drives increased discretionary purchases reflecting optimistic outlooks. Economic sentiment indexes measure overall public perception of economic health, which correlates with surges in spending post-economic downturns or restrictions. Explore deeper insights into how shifting sentiment impacts spending behaviors and market trends.
Disposable Income
Consumer confidence influences spending habits by affecting perceptions of economic stability and future income prospects, leading to variations in disposable income allocation. Revenge spending is characterized by a surge in consumer expenditures, often exceeding typical budgets, driven by pent-up demand and increased disposable income after periods of restriction. Explore detailed insights into how disposable income shapes consumer behavior and drives economic recovery.
Consumption Patterns
Consumer confidence strongly influences consumption patterns, with higher confidence typically driving increased spending on discretionary items and luxury goods. Revenge spending, characterized by a surge in purchases following periods of constrained consumption, often reflects pent-up demand and shifting priorities towards experiences and non-essential products. Explore deeper insights into how these dynamics shape market trends and economic recovery.
Source and External Links
Consumer Confidence Retreats in June - dshort - The Conference Board's Consumer Confidence Index dropped to 93.0 in June 2025, marking a decline driven by deteriorating views of present business conditions and future income prospects, signaling broadly weakened consumer outlooks.
United States Michigan Consumer Sentiment - Consumer confidence in the US rose to 61.8 in July 2025 from 60.7 in June, reaching a five-month high, with improved views on current business conditions and lower inflation expectations, though still below historical averages.
Consumer confidence index (CCI) - OECD - The Consumer Confidence Index measures households' sentiment on economic outlook and financial situation, where values above 100 indicate optimism and below 100 reflect pessimism affecting spending and saving behavior globally.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com