Carbon border adjustment mechanisms impose tariffs on imported goods based on their carbon emissions, promoting climate-friendly trade practices and leveling the playing field for domestic producers. Trade embargoes restrict the flow of goods, services, or investments from specific countries, primarily for political or security reasons, often causing broader economic disruptions. Explore the differences between these approaches to understand their impacts on global trade and environmental policy.
Why it is important
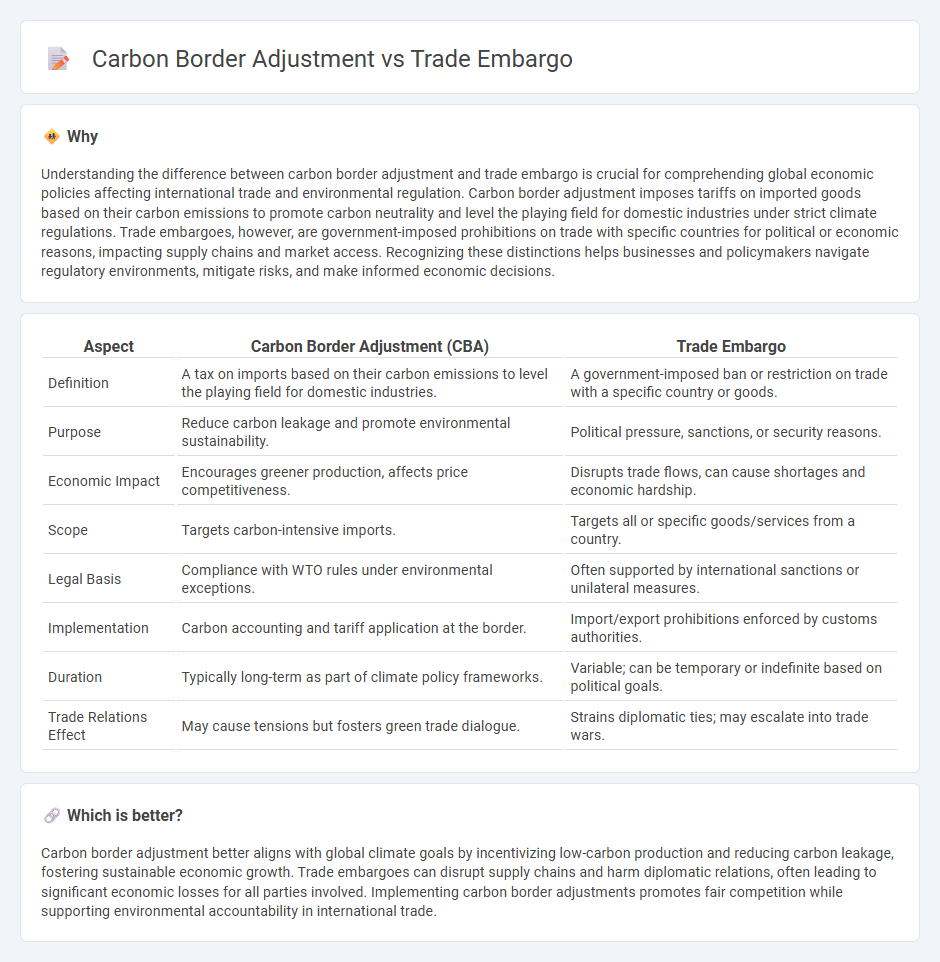
Understanding the difference between carbon border adjustment and trade embargo is crucial for comprehending global economic policies affecting international trade and environmental regulation. Carbon border adjustment imposes tariffs on imported goods based on their carbon emissions to promote carbon neutrality and level the playing field for domestic industries under strict climate regulations. Trade embargoes, however, are government-imposed prohibitions on trade with specific countries for political or economic reasons, impacting supply chains and market access. Recognizing these distinctions helps businesses and policymakers navigate regulatory environments, mitigate risks, and make informed economic decisions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Border Adjustment (CBA) | Trade Embargo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A tax on imports based on their carbon emissions to level the playing field for domestic industries. | A government-imposed ban or restriction on trade with a specific country or goods. |
| Purpose | Reduce carbon leakage and promote environmental sustainability. | Political pressure, sanctions, or security reasons. |
| Economic Impact | Encourages greener production, affects price competitiveness. | Disrupts trade flows, can cause shortages and economic hardship. |
| Scope | Targets carbon-intensive imports. | Targets all or specific goods/services from a country. |
| Legal Basis | Compliance with WTO rules under environmental exceptions. | Often supported by international sanctions or unilateral measures. |
| Implementation | Carbon accounting and tariff application at the border. | Import/export prohibitions enforced by customs authorities. |
| Duration | Typically long-term as part of climate policy frameworks. | Variable; can be temporary or indefinite based on political goals. |
| Trade Relations Effect | May cause tensions but fosters green trade dialogue. | Strains diplomatic ties; may escalate into trade wars. |
Which is better?
Carbon border adjustment better aligns with global climate goals by incentivizing low-carbon production and reducing carbon leakage, fostering sustainable economic growth. Trade embargoes can disrupt supply chains and harm diplomatic relations, often leading to significant economic losses for all parties involved. Implementing carbon border adjustments promotes fair competition while supporting environmental accountability in international trade.
Connection
Carbon border adjustment mechanisms impose tariffs on imported goods based on their carbon emissions, aiming to prevent carbon leakage and protect domestic industries implementing strict climate policies. Trade embargoes restrict or ban trade with specific countries, often for political or environmental reasons, which can overlap with carbon border adjustments when emissions-intensive goods from embargoed nations face additional barriers. Both tools influence international trade dynamics by integrating environmental considerations into economic and political strategies.
Key Terms
**Trade Embargo:**
Trade embargoes are government-imposed restrictions that prohibit trade with specific countries or entities to achieve political or economic objectives, often affecting imports, exports, or both. These sanctions may target entire sectors or specific goods, aiming to pressure governments to change policies or to punish violations of international law. Discover how trade embargoes influence global commerce and geopolitical relations.
Sanctions
Trade embargoes are comprehensive restrictions imposed by countries or international bodies to prohibit trade with specific nations, often for political or security reasons, whereas carbon border adjustments are tariffs on imports based on their carbon footprint to address climate change. Sanctions in trade embargoes aim to pressure governments by limiting economic interaction, while carbon border adjustments intend to level the playing field by deterring carbon leakage and encouraging cleaner production. Explore more to understand how these mechanisms impact global trade and environmental policy.
Import/Export Restrictions
Trade embargoes impose strict import/export restrictions by prohibiting trade with specific countries to achieve political or economic objectives. Carbon border adjustments levy tariffs on imported goods based on their carbon emissions to level the playing field for domestic industries and reduce global carbon footprints. Explore how these mechanisms impact international trade and environmental policies.
Source and External Links
What Are Trade Sanctions? A Complete Overview - A trade embargo is the most severe form of trade sanction, involving a comprehensive ban on most or all trade with a targeted country, often used to isolate that nation economically and politically, with examples including the U.S. embargoes against Cuba and North Korea.
Understanding the Impact of Trade Embargoes - Shapiro - Trade embargoes are imposed for political pressure, economic sanctions, or security concerns by restricting or halting trade to influence another country's policies or prevent the spread of dangerous materials, but they also disrupt global trade and have complex economic effects.
Understanding Trade Embargos: Why Nations Impose Them - A trade embargo is a government-imposed restriction on trading certain goods or services usually to compel policy changes in a targeted nation, with the longstanding US embargo on Cuba being a notable example causing significant economic hardship and political tension.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com