Circular economy focuses on maximizing resource efficiency by designing products for reuse, repair, and recycling to minimize waste and environmental impact. Sharing economy emphasizes collaborative consumption where individuals share access to goods and services, optimizing asset utilization and reducing the need for ownership. Explore how these sustainable economic models transform industries and consumer behavior.
Why it is important
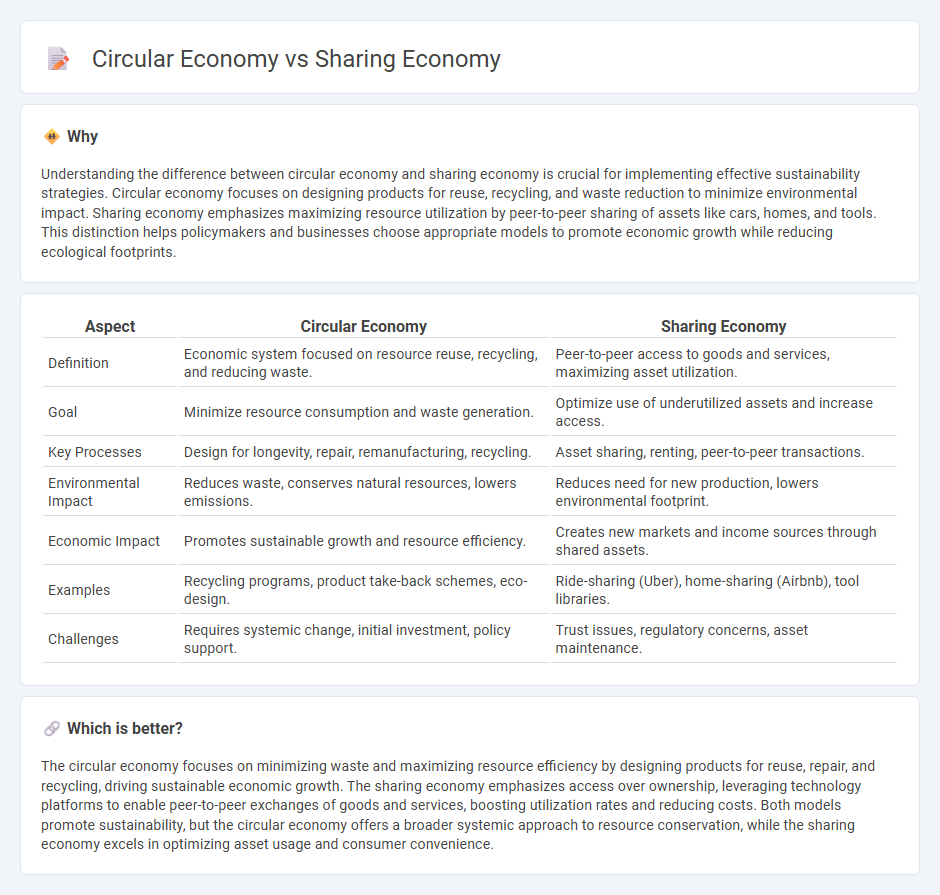
Understanding the difference between circular economy and sharing economy is crucial for implementing effective sustainability strategies. Circular economy focuses on designing products for reuse, recycling, and waste reduction to minimize environmental impact. Sharing economy emphasizes maximizing resource utilization by peer-to-peer sharing of assets like cars, homes, and tools. This distinction helps policymakers and businesses choose appropriate models to promote economic growth while reducing ecological footprints.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Economy | Sharing Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic system focused on resource reuse, recycling, and reducing waste. | Peer-to-peer access to goods and services, maximizing asset utilization. |
| Goal | Minimize resource consumption and waste generation. | Optimize use of underutilized assets and increase access. |
| Key Processes | Design for longevity, repair, remanufacturing, recycling. | Asset sharing, renting, peer-to-peer transactions. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste, conserves natural resources, lowers emissions. | Reduces need for new production, lowers environmental footprint. |
| Economic Impact | Promotes sustainable growth and resource efficiency. | Creates new markets and income sources through shared assets. |
| Examples | Recycling programs, product take-back schemes, eco-design. | Ride-sharing (Uber), home-sharing (Airbnb), tool libraries. |
| Challenges | Requires systemic change, initial investment, policy support. | Trust issues, regulatory concerns, asset maintenance. |
Which is better?
The circular economy focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency by designing products for reuse, repair, and recycling, driving sustainable economic growth. The sharing economy emphasizes access over ownership, leveraging technology platforms to enable peer-to-peer exchanges of goods and services, boosting utilization rates and reducing costs. Both models promote sustainability, but the circular economy offers a broader systemic approach to resource conservation, while the sharing economy excels in optimizing asset usage and consumer convenience.
Connection
Circular economy and sharing economy both aim to reduce resource consumption and waste by promoting the efficient use of goods and services. The circular economy focuses on designing products for longevity, reuse, and recycling, while the sharing economy facilitates access to underutilized assets through platforms that enable collaborative consumption. Together, they create sustainable economic models that minimize environmental impact and optimize resource utilization.
Key Terms
Peer-to-peer
The sharing economy emphasizes peer-to-peer access to goods and services, enabling individuals to share underutilized assets such as cars, homes, or tools directly through platforms like Airbnb and Uber. In contrast, the circular economy focuses on resource efficiency, waste reduction, and product lifecycle extension by promoting reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling practices to create closed-loop systems. Explore more about how peer-to-peer models uniquely contribute to sustainable consumption and resource optimization.
Resource efficiency
The sharing economy maximizes resource use by enabling multiple users to access products and services, reducing idle capacity and waste. Circular economy emphasizes extending the lifecycle of resources through reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling to minimize raw material extraction and environmental impact. Explore how these models enhance resource efficiency and drive sustainable business practices.
Reuse
The sharing economy emphasizes maximizing the use of assets by facilitating peer-to-peer access to goods and services, reducing the need for individual ownership and promoting reuse. The circular economy focuses on designing products and systems that enable continuous reuse, refurbishment, and recycling to minimize waste and extend product life cycles. Explore detailed strategies and examples to understand how reuse drives sustainability in both economic models.
Source and External Links
What Is the Sharing Economy - Example Companies, Definition ... - A sharing economy is a flexible network that allows people to exchange tangible and intangible assets on a large scale, increasing efficiency by enabling access without ownership, facilitated by technology like the internet.
Sharing Economy - Definition, Model, Pros and Cons - The sharing economy is an economic model where individuals share goods and resources collaboratively, turning physical assets into services, enabled by online platforms and big data to monetize underused assets like vehicles and spare rooms.
Sharing economy - Wikipedia - The sharing economy allows consumers to access goods without ownership, improves service quality through rating systems, strengthens communities, promotes flexibility, and can create new jobs while reducing costs and deadweight losses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com