Nearshoring involves relocating business processes closer to the company's home country to reduce costs, improve supply chain efficiency, and enhance responsiveness to market changes. Global sourcing leverages worldwide suppliers to optimize cost advantages, access diverse resources, and scale production flexibly. Explore the strategic benefits and challenges of nearshoring versus global sourcing to make informed economic decisions.
Why it is important
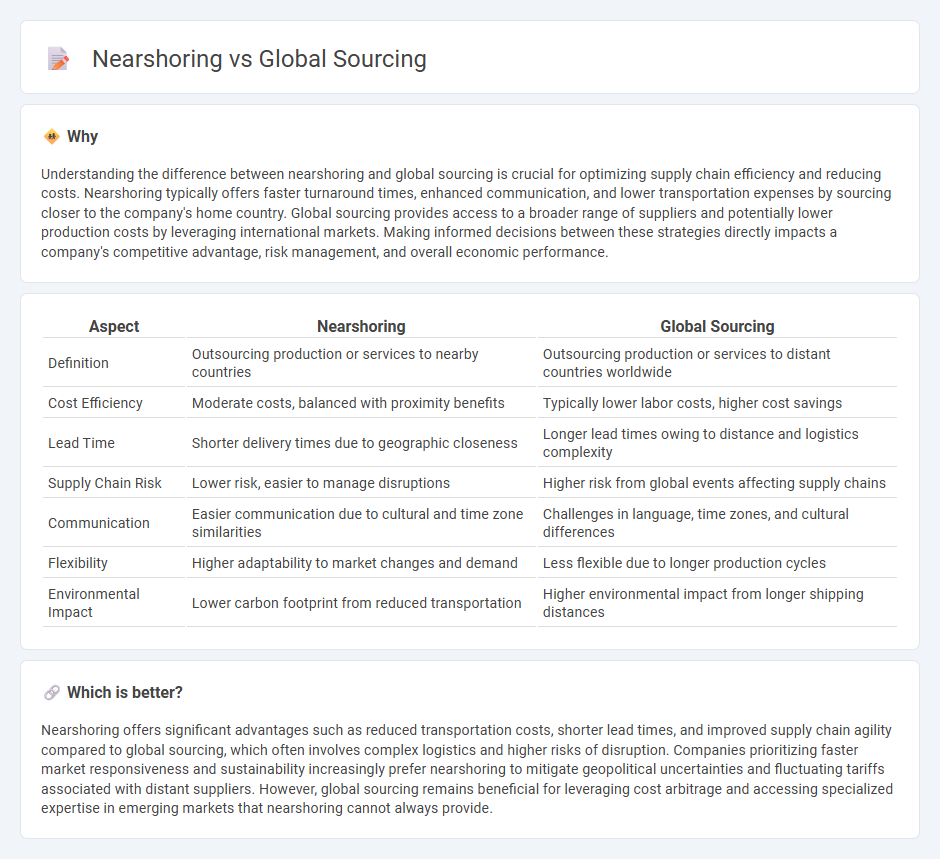
Understanding the difference between nearshoring and global sourcing is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing costs. Nearshoring typically offers faster turnaround times, enhanced communication, and lower transportation expenses by sourcing closer to the company's home country. Global sourcing provides access to a broader range of suppliers and potentially lower production costs by leveraging international markets. Making informed decisions between these strategies directly impacts a company's competitive advantage, risk management, and overall economic performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Nearshoring | Global Sourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outsourcing production or services to nearby countries | Outsourcing production or services to distant countries worldwide |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate costs, balanced with proximity benefits | Typically lower labor costs, higher cost savings |
| Lead Time | Shorter delivery times due to geographic closeness | Longer lead times owing to distance and logistics complexity |
| Supply Chain Risk | Lower risk, easier to manage disruptions | Higher risk from global events affecting supply chains |
| Communication | Easier communication due to cultural and time zone similarities | Challenges in language, time zones, and cultural differences |
| Flexibility | Higher adaptability to market changes and demand | Less flexible due to longer production cycles |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint from reduced transportation | Higher environmental impact from longer shipping distances |
Which is better?
Nearshoring offers significant advantages such as reduced transportation costs, shorter lead times, and improved supply chain agility compared to global sourcing, which often involves complex logistics and higher risks of disruption. Companies prioritizing faster market responsiveness and sustainability increasingly prefer nearshoring to mitigate geopolitical uncertainties and fluctuating tariffs associated with distant suppliers. However, global sourcing remains beneficial for leveraging cost arbitrage and accessing specialized expertise in emerging markets that nearshoring cannot always provide.
Connection
Nearshoring and global sourcing are interconnected strategies that optimize supply chain efficiency by balancing cost reduction with proximity advantages. Nearshoring relocates production closer to the target market, reducing lead times and transportation costs, while global sourcing taps into competitive international suppliers to maximize value. Together, they create a hybrid approach enabling businesses to enhance flexibility, mitigate risks, and respond swiftly to market demand fluctuations.
Key Terms
Supply Chain
Global sourcing offers access to diverse suppliers worldwide, driving cost efficiency and innovation in supply chains, while nearshoring reduces lead times and enhances supply chain agility by sourcing closer to the end market. Supply chain resilience improves with nearshoring due to lower transportation risks and quicker response to demand fluctuations. Explore the benefits of each strategy to optimize your supply chain operations effectively.
Cost Efficiency
Global sourcing leverages international suppliers to minimize production expenses by capitalizing on lower labor and material costs in distant regions, often resulting in significant savings but increased logistics and tariff complexity. Nearshoring reduces transportation expenses and lead times by relocating production closer to the target market, enhancing agility and responsiveness while maintaining moderate cost efficiency. Explore the detailed cost efficiency comparison between global sourcing and nearshoring to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Geographic Proximity
Global sourcing involves procuring goods or services from suppliers worldwide to leverage cost advantages and access specialized skills. Nearshoring prioritizes geographic proximity by sourcing from nearby countries, reducing transportation time and costs while improving supply chain agility. Explore the benefits and challenges of each strategy to determine the optimal approach for your business needs.
Source and External Links
Global Sourcing - Wikipedia - Global sourcing is the practice of sourcing goods and services across geopolitical boundaries to exploit global efficiencies.
A Complete Guide To Global Sourcing Strategies - This guide explores the strategic practice of procuring goods, materials, or services from international suppliers to meet a company's needs.
Global Sourcing: Benefits, Examples and Strategies - This resource discusses global sourcing as a procurement strategy to acquire goods and services from suppliers in other countries at the best possible price.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com