Carbon border tax aims to reduce carbon leakage by imposing fees on imported goods based on their carbon emissions, encouraging greener production globally. Sustainability standards set environmental criteria for products and companies, promoting responsible resource use and reducing ecological impact across supply chains. Explore how these tools influence global trade and environmental policy for a sustainable economic future.
Why it is important
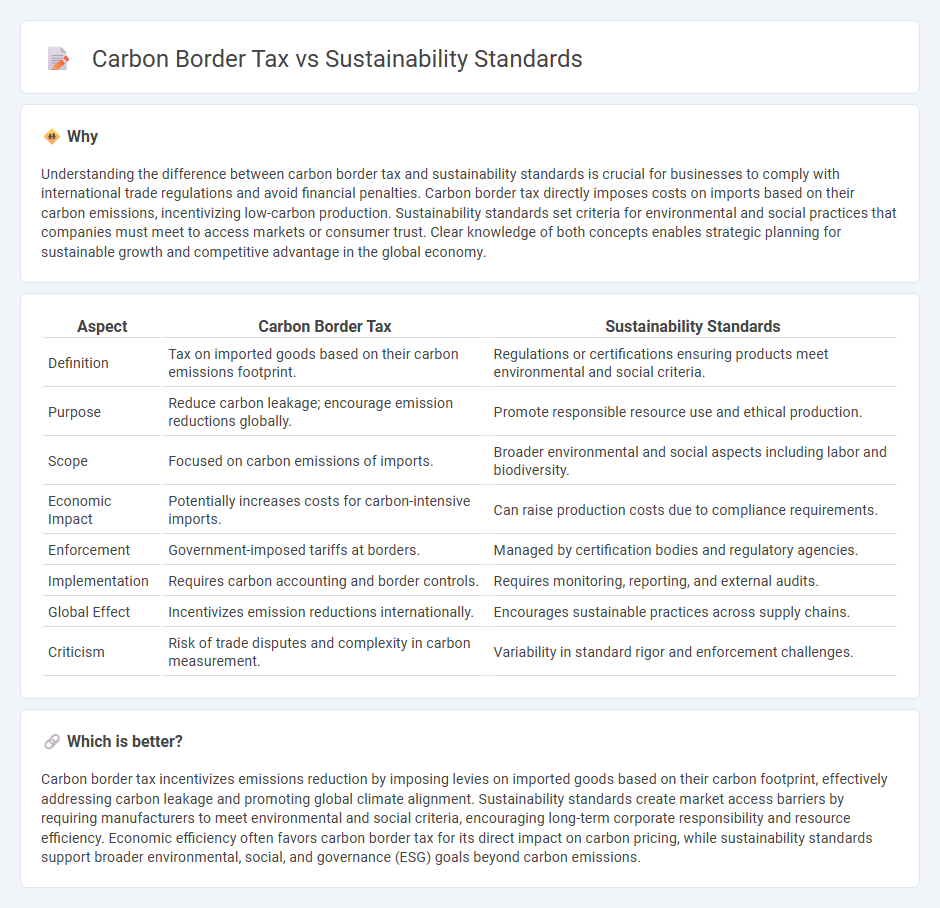
Understanding the difference between carbon border tax and sustainability standards is crucial for businesses to comply with international trade regulations and avoid financial penalties. Carbon border tax directly imposes costs on imports based on their carbon emissions, incentivizing low-carbon production. Sustainability standards set criteria for environmental and social practices that companies must meet to access markets or consumer trust. Clear knowledge of both concepts enables strategic planning for sustainable growth and competitive advantage in the global economy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Border Tax | Sustainability Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tax on imported goods based on their carbon emissions footprint. | Regulations or certifications ensuring products meet environmental and social criteria. |
| Purpose | Reduce carbon leakage; encourage emission reductions globally. | Promote responsible resource use and ethical production. |
| Scope | Focused on carbon emissions of imports. | Broader environmental and social aspects including labor and biodiversity. |
| Economic Impact | Potentially increases costs for carbon-intensive imports. | Can raise production costs due to compliance requirements. |
| Enforcement | Government-imposed tariffs at borders. | Managed by certification bodies and regulatory agencies. |
| Implementation | Requires carbon accounting and border controls. | Requires monitoring, reporting, and external audits. |
| Global Effect | Incentivizes emission reductions internationally. | Encourages sustainable practices across supply chains. |
| Criticism | Risk of trade disputes and complexity in carbon measurement. | Variability in standard rigor and enforcement challenges. |
Which is better?
Carbon border tax incentivizes emissions reduction by imposing levies on imported goods based on their carbon footprint, effectively addressing carbon leakage and promoting global climate alignment. Sustainability standards create market access barriers by requiring manufacturers to meet environmental and social criteria, encouraging long-term corporate responsibility and resource efficiency. Economic efficiency often favors carbon border tax for its direct impact on carbon pricing, while sustainability standards support broader environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals beyond carbon emissions.
Connection
Carbon border tax and sustainability standards are interconnected mechanisms designed to reduce global carbon emissions by promoting environmentally responsible trade practices. The carbon border tax imposes fees on imported goods based on their carbon footprint, incentivizing producers to adhere to sustainability standards that limit emissions throughout the supply chain. This alignment encourages international compliance with climate policies, fosters greener production methods, and helps mitigate carbon leakage across borders.
Key Terms
Environmental Regulation
Sustainability standards establish specific environmental criteria for products and services to minimize ecological impact, promoting responsible resource use and carbon footprint reduction. Carbon border tax, or carbon border adjustment mechanism, imposes tariffs on imported goods based on their carbon emissions to prevent carbon leakage and ensure fair competition for domestic producers. Explore further insights on how these environmental regulations shape global trade and climate policy frameworks.
Trade Policy
Sustainability standards regulate environmental practices to reduce carbon footprints in international trade, promoting eco-friendly production methods and ensuring compliance with global climate goals. Carbon border tax imposes tariffs on imported goods based on their carbon emissions, aiming to prevent carbon leakage and create a level playing field for domestic industries facing stringent climate regulations. Explore the impact of these mechanisms on trade policy and global market dynamics to understand their role in advancing sustainable commerce.
Carbon Leakage
Sustainability standards aim to reduce environmental impact through stringent regulations on production processes, whereas a carbon border tax specifically targets carbon leakage by imposing tariffs on imports from countries with lax emission controls. Carbon leakage occurs when companies relocate production to countries with weaker environmental regulations, undermining global emission reduction efforts. Discover how these mechanisms interplay to drive greener international trade policies.
Source and External Links
Sustainability standards and certification - Voluntary guidelines and certifications demonstrating commitment to environmental, social, ethical, and food safety practices across supply chains.
International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) - Develops global standards for sustainability disclosures tailored to investors and financial markets, aiming to create a comprehensive, comparable baseline.
The Top 7 Sustainability Reporting Standards in 2024 - Highlights leading frameworks like GRI, SASB (now integrated into ISSB), B Corp certification, and the EU's CSRD, each with distinct approaches to ESG reporting.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com