Soft saving involves setting aside smaller amounts of money regularly, emphasizing liquidity and financial security, while hard investing focuses on allocating significant capital into assets for potential higher returns and long-term growth. Understanding the balance between these approaches is crucial for optimizing personal finance strategies and achieving economic stability. Explore detailed insights on how soft saving and hard investing can shape your financial future.
Why it is important
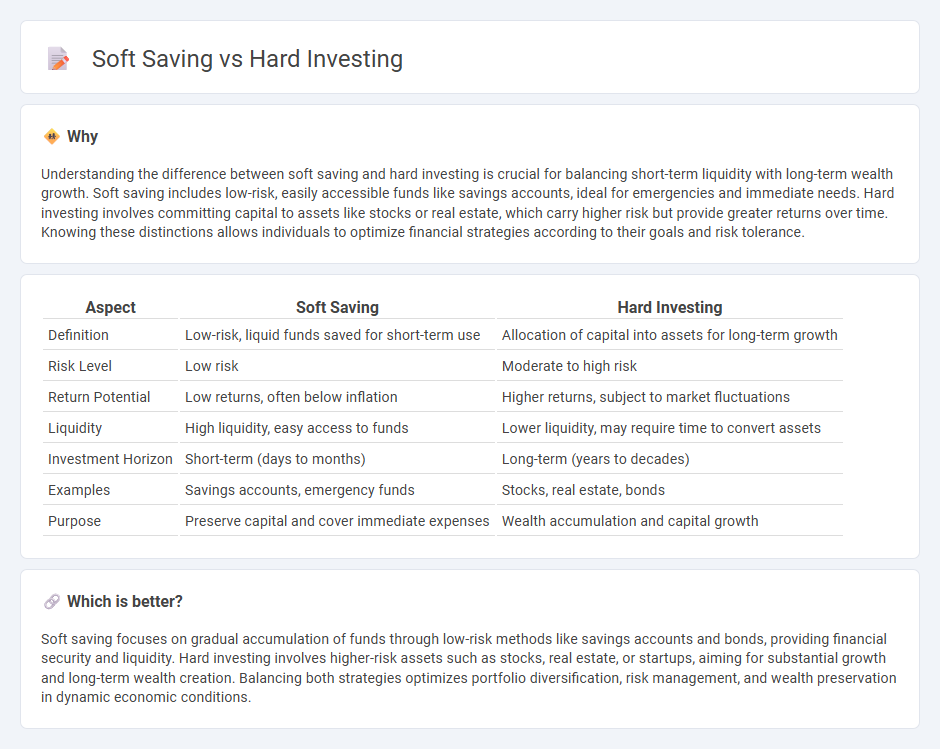
Understanding the difference between soft saving and hard investing is crucial for balancing short-term liquidity with long-term wealth growth. Soft saving includes low-risk, easily accessible funds like savings accounts, ideal for emergencies and immediate needs. Hard investing involves committing capital to assets like stocks or real estate, which carry higher risk but provide greater returns over time. Knowing these distinctions allows individuals to optimize financial strategies according to their goals and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Soft Saving | Hard Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Low-risk, liquid funds saved for short-term use | Allocation of capital into assets for long-term growth |
| Risk Level | Low risk | Moderate to high risk |
| Return Potential | Low returns, often below inflation | Higher returns, subject to market fluctuations |
| Liquidity | High liquidity, easy access to funds | Lower liquidity, may require time to convert assets |
| Investment Horizon | Short-term (days to months) | Long-term (years to decades) |
| Examples | Savings accounts, emergency funds | Stocks, real estate, bonds |
| Purpose | Preserve capital and cover immediate expenses | Wealth accumulation and capital growth |
Which is better?
Soft saving focuses on gradual accumulation of funds through low-risk methods like savings accounts and bonds, providing financial security and liquidity. Hard investing involves higher-risk assets such as stocks, real estate, or startups, aiming for substantial growth and long-term wealth creation. Balancing both strategies optimizes portfolio diversification, risk management, and wealth preservation in dynamic economic conditions.
Connection
Soft saving builds financial stability by gradually accumulating liquid assets, enabling individuals to manage risks and seize investment opportunities. Hard investing channels these accumulated savings into high-yield assets like stocks, real estate, or businesses, driving wealth growth and economic expansion. The synergy between soft saving and hard investing creates a balanced financial approach that supports long-term economic resilience and capital formation.
Key Terms
Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance plays a crucial role in differentiating hard investing from soft saving strategies, with hard investing involving higher exposure to market volatility and potential losses, while soft saving prioritizes capital preservation and liquidity. Investors with high risk tolerance typically pursue hard investing for greater returns through assets like stocks and real estate, whereas conservative savers prefer soft saving methods such as savings accounts and bonds to minimize risk. Explore risk tolerance frameworks and investment options to align your financial goals effectively.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Hard investing typically involves allocating capital to assets such as stocks, real estate, or businesses with the goal of generating substantial Return on Investment (ROI) through appreciation or income generation. Soft saving emphasizes low-risk methods like savings accounts or certificates of deposit, prioritizing capital preservation over high ROI but offering liquidity and security. Explore in-depth strategies to balance hard investing and soft saving for optimized financial growth.
Liquidity
Hard investing often involves assets like real estate or stocks, which may yield higher returns but typically lack immediate liquidity. Soft saving emphasizes cash or money market accounts, providing quick access to funds but usually offering lower interest rates. Explore the advantages and trade-offs between liquidity and growth potential to optimize your financial strategy.
Source and External Links
Hard Assets: Investment Guide - This guide provides an overview of investing in hard assets, including real estate, precious metals, and other tangible resources.
Hard Assets - This resource explains hard assets as physical investments that hold value over time, often serving as a hedge against inflation.
Why Investing is Hard but Still Worth Doing - This insight discusses the challenges and long-term benefits of investing, emphasizing perseverance through market volatility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com