Deinfluencing challenges traditional consumer culture by promoting mindful purchasing decisions and reducing impulsive buying driven by social media trends. Ethical purchasing prioritizes products that align with sustainability, fair labor practices, and corporate accountability, fostering a responsible economy. Explore how deinfluencing and ethical purchasing reshape modern economic behaviors for a more conscious marketplace.
Why it is important
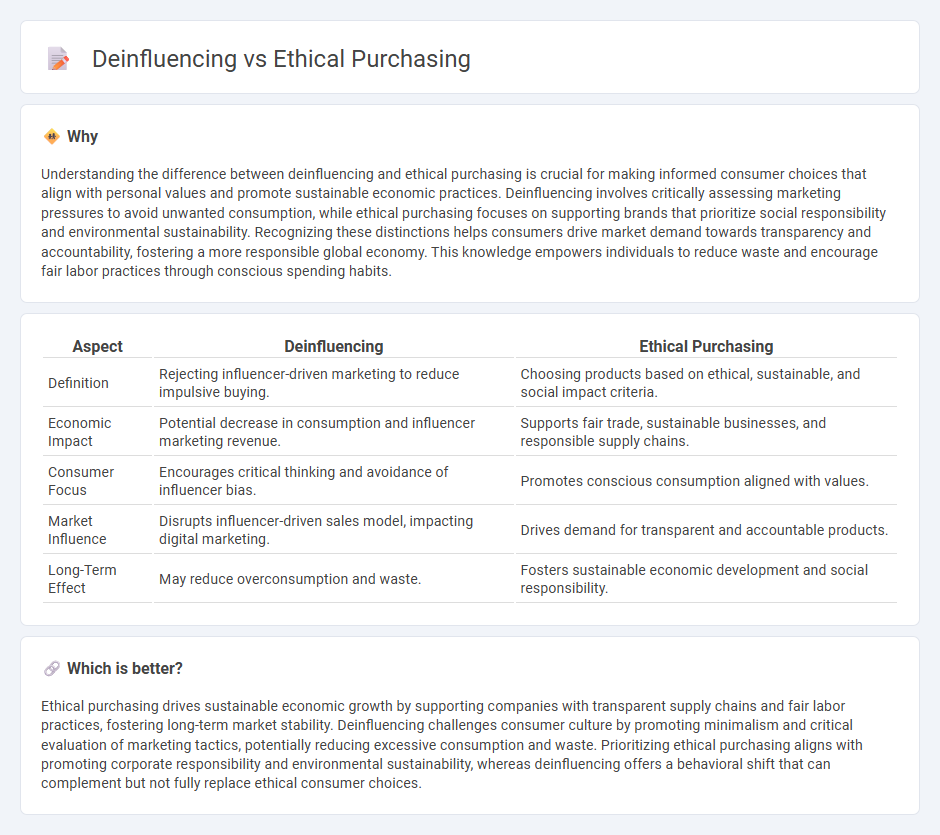
Understanding the difference between deinfluencing and ethical purchasing is crucial for making informed consumer choices that align with personal values and promote sustainable economic practices. Deinfluencing involves critically assessing marketing pressures to avoid unwanted consumption, while ethical purchasing focuses on supporting brands that prioritize social responsibility and environmental sustainability. Recognizing these distinctions helps consumers drive market demand towards transparency and accountability, fostering a more responsible global economy. This knowledge empowers individuals to reduce waste and encourage fair labor practices through conscious spending habits.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Deinfluencing | Ethical Purchasing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rejecting influencer-driven marketing to reduce impulsive buying. | Choosing products based on ethical, sustainable, and social impact criteria. |
| Economic Impact | Potential decrease in consumption and influencer marketing revenue. | Supports fair trade, sustainable businesses, and responsible supply chains. |
| Consumer Focus | Encourages critical thinking and avoidance of influencer bias. | Promotes conscious consumption aligned with values. |
| Market Influence | Disrupts influencer-driven sales model, impacting digital marketing. | Drives demand for transparent and accountable products. |
| Long-Term Effect | May reduce overconsumption and waste. | Fosters sustainable economic development and social responsibility. |
Which is better?
Ethical purchasing drives sustainable economic growth by supporting companies with transparent supply chains and fair labor practices, fostering long-term market stability. Deinfluencing challenges consumer culture by promoting minimalism and critical evaluation of marketing tactics, potentially reducing excessive consumption and waste. Prioritizing ethical purchasing aligns with promoting corporate responsibility and environmental sustainability, whereas deinfluencing offers a behavioral shift that can complement but not fully replace ethical consumer choices.
Connection
Deinfluencing reshapes consumer behavior by encouraging critical evaluation of marketing tactics, which fosters ethical purchasing decisions focused on sustainability and social responsibility. This shift reduces impulsive buying and supports companies committed to fair trade, environmental protection, and transparent supply chains. Ethical purchasing driven by deinfluencing ultimately promotes a more conscious economy prioritizing long-term societal and ecological benefits.
Key Terms
Consumer Responsibility
Ethical purchasing emphasizes consumer responsibility by encouraging buyers to choose products that support fair labor, environmental sustainability, and social justice, thereby fostering a market that values transparency and accountability. Deinfluencing challenges traditional consumerism by urging individuals to critically assess marketing tactics and reduce impulsive or unnecessary purchases, promoting mindful consumption patterns. Explore more on how ethical purchasing and deinfluencing reshape consumer responsibility in today's market.
Sustainable Consumption
Ethical purchasing emphasizes choosing products made with fair labor practices and environmentally friendly materials, promoting sustainable consumption by reducing harm to people and the planet. Deinfluencing actively discourages impulsive buying and overconsumption through transparency and critical evaluation of marketing tactics, aligning consumer behavior with sustainability goals. Discover more about how these approaches transform consumer habits and contribute to a greener economy.
Social Influence
Ethical purchasing emphasizes consumer choices that prioritize sustainability, fair trade, and social responsibility, often influenced by social norms and ethical endorsements from trusted figures. Deinfluencing challenges traditional marketing by encouraging consumers to critically evaluate trends and avoid impulsive or environmentally harmful purchases driven by social pressure. Explore how social influence shapes these consumer behaviors to make more informed, conscientious buying decisions.
Source and External Links
What is Ethical Purchasing - Ethical purchasing involves aligning procurement decisions with ethical considerations, such as social responsibility and environmental sustainability.
Ethical Purchasing - Ethical purchasing is a process that ensures goods and services are acquired without exploiting humans, animals, or the environment, promoting social equity and environmental sustainability.
Ethically Sourced Products - Ethically sourced products are obtained from supply chains that uphold ethical standards, including labor rights and environmental practices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com