Deglobalization involves reducing global trade and economic interdependence, aiming to strengthen national industries while maintaining some international cooperation. Autarky pursues complete economic self-sufficiency, minimizing reliance on external trade to achieve full independence. Explore the impacts of these strategies on global markets and national economies.
Why it is important
Understanding deglobalization versus autarky is crucial for analyzing global economic trends and policy decisions. Deglobalization refers to the reduction of global interdependence through decreased international trade and investment, while autarky signifies complete economic self-sufficiency without reliance on external trade. Policymakers must distinguish these concepts to address challenges in supply chains, national security, and economic growth strategies effectively. Clear knowledge of these terms helps in forecasting economic resilience and formulating trade policies in a changing geopolitical landscape.
Comparison Table
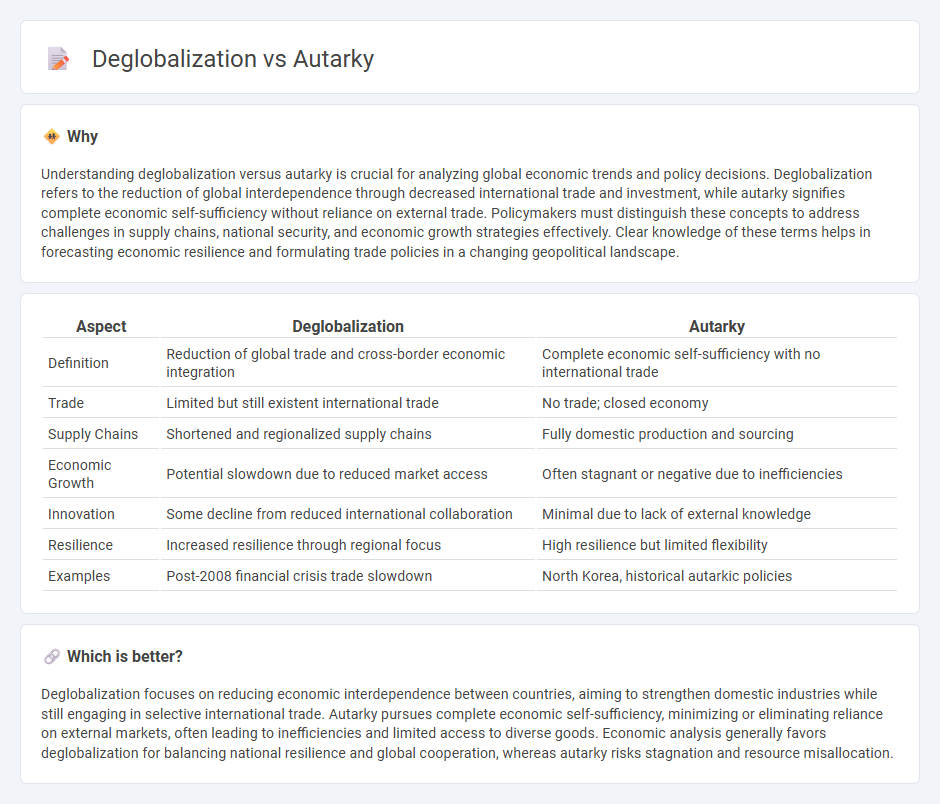
| Aspect | Deglobalization | Autarky |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduction of global trade and cross-border economic integration | Complete economic self-sufficiency with no international trade |
| Trade | Limited but still existent international trade | No trade; closed economy |
| Supply Chains | Shortened and regionalized supply chains | Fully domestic production and sourcing |
| Economic Growth | Potential slowdown due to reduced market access | Often stagnant or negative due to inefficiencies |
| Innovation | Some decline from reduced international collaboration | Minimal due to lack of external knowledge |
| Resilience | Increased resilience through regional focus | High resilience but limited flexibility |
| Examples | Post-2008 financial crisis trade slowdown | North Korea, historical autarkic policies |
Which is better?
Deglobalization focuses on reducing economic interdependence between countries, aiming to strengthen domestic industries while still engaging in selective international trade. Autarky pursues complete economic self-sufficiency, minimizing or eliminating reliance on external markets, often leading to inefficiencies and limited access to diverse goods. Economic analysis generally favors deglobalization for balancing national resilience and global cooperation, whereas autarky risks stagnation and resource misallocation.
Connection
Deglobalization and autarky are interconnected as both processes emphasize reducing dependence on global trade and promoting self-sufficiency within national economies. Deglobalization involves scaling back international supply chains and cross-border investments, while autarky seeks economic independence by minimizing imports and focusing on domestic production. These trends can lead to reshaped economic policies prioritizing local industries and national security over global market integration.
Key Terms
Self-sufficiency
Autarky refers to a nation's complete economic self-sufficiency, aiming to eliminate reliance on international trade by producing all necessary goods domestically. Deglobalization involves reducing global interdependence but does not necessarily seek full self-sufficiency, instead focusing on selective trade and regional supply chain realignments. Explore the nuances between autarky and deglobalization to understand their distinct impacts on economic strategies and global markets.
Trade barriers
Trade barriers in autarky typically manifest as strict tariffs and quotas aimed at achieving economic self-sufficiency by limiting imports and prioritizing domestic production. Deglobalization involves the reduction of global economic integration, where increased trade barriers arise from political decisions, such as sanctions or reshoring policies, but do not necessarily aim for complete self-reliance. Explore the nuanced impacts of these trade barriers on global markets and economic stability to better understand their roles.
Global supply chains
Autarky emphasizes complete economic self-sufficiency, aiming to eliminate reliance on global supply chains by producing all goods domestically. Deglobalization reduces dependence on international trade but still engages selectively with global networks to enhance supply chain resilience and diversify sourcing. Explore how these contrasting strategies reshape the future of global supply chain management and international trade dynamics.
Source and External Links
Autarky - Overview, History, and Modern World Examples - Autarky describes a country or economy that operates independently and is self-sufficient, typically avoiding reliance on outside trade or support.
Autarky - Autarky is the characteristic of self-sufficiency applied to societies, communities, or states, often pursued as a policy to reduce foreign influence and promote national independence, though it is generally seen as economically detrimental compared to free trade.
AUTARKY Definition & Meaning - Autarky refers to the condition of economic self-sufficiency, especially as a national policy aimed at achieving independence from external trade.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com