Zombie companies, characterized by their inability to cover debt servicing costs with current earnings, drain economic resources and hinder market dynamism, while sunset industries face declining demand due to technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences. Both phenomena pose significant challenges to economic growth and require strategic interventions to reallocate capital efficiently and foster innovation. Explore the critical differences and implications of zombie companies versus sunset industries to better understand their impact on the economy.
Why it is important
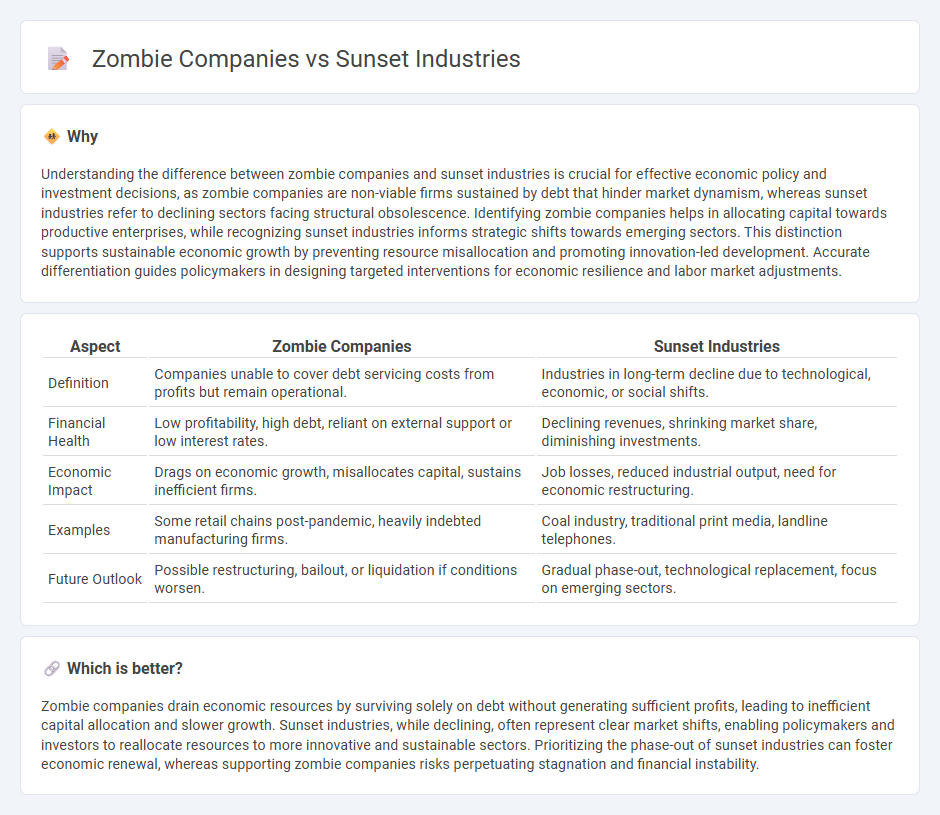
Understanding the difference between zombie companies and sunset industries is crucial for effective economic policy and investment decisions, as zombie companies are non-viable firms sustained by debt that hinder market dynamism, whereas sunset industries refer to declining sectors facing structural obsolescence. Identifying zombie companies helps in allocating capital towards productive enterprises, while recognizing sunset industries informs strategic shifts towards emerging sectors. This distinction supports sustainable economic growth by preventing resource misallocation and promoting innovation-led development. Accurate differentiation guides policymakers in designing targeted interventions for economic resilience and labor market adjustments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zombie Companies | Sunset Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Companies unable to cover debt servicing costs from profits but remain operational. | Industries in long-term decline due to technological, economic, or social shifts. |
| Financial Health | Low profitability, high debt, reliant on external support or low interest rates. | Declining revenues, shrinking market share, diminishing investments. |
| Economic Impact | Drags on economic growth, misallocates capital, sustains inefficient firms. | Job losses, reduced industrial output, need for economic restructuring. |
| Examples | Some retail chains post-pandemic, heavily indebted manufacturing firms. | Coal industry, traditional print media, landline telephones. |
| Future Outlook | Possible restructuring, bailout, or liquidation if conditions worsen. | Gradual phase-out, technological replacement, focus on emerging sectors. |
Which is better?
Zombie companies drain economic resources by surviving solely on debt without generating sufficient profits, leading to inefficient capital allocation and slower growth. Sunset industries, while declining, often represent clear market shifts, enabling policymakers and investors to reallocate resources to more innovative and sustainable sectors. Prioritizing the phase-out of sunset industries can foster economic renewal, whereas supporting zombie companies risks perpetuating stagnation and financial instability.
Connection
Zombie companies, characterized by their inability to cover debt servicing costs, rely heavily on low-interest rates and government support, inhibiting economic dynamism by diverting capital from more productive uses. Sunset industries, defined by declining demand and outdated business models, often house these struggling firms, amplifying economic stagnation within sectors such as coal mining and traditional manufacturing. This interconnection exacerbates resource misallocation and slows structural economic transformation essential for sustainable growth and innovation.
Key Terms
Structural Decline
Sunset industries face structural decline due to irreversible shifts in technology, consumer behavior, and economic trends, leading to diminished market relevance and profitability. Zombie companies survive through persistent debt and external support, despite lacking the innovation or efficiency to sustain growth in evolving markets. Explore the distinctions between these entities to understand how structural decline reshapes industries and investment strategies.
Insolvency
Sunset industries refer to sectors in economic decline due to structural changes, often facing escalating insolvency risks as businesses fail to adapt, resulting in increased bankruptcy filings and liquidation cases. Zombie companies operate within viable industries but persist primarily through continuous restructuring and debt refinancing, leading to solvency challenges that strain creditors and hinder economic growth. Explore detailed insights on insolvency patterns and financial health assessment to understand these contrasting business dynamics fully.
Market Efficiency
Sunset industries, characterized by declining demand and obsolescence, contrast sharply with zombie companies that survive solely through continuous debt refinancing despite unprofitability, both impacting market efficiency differently. Market efficiency suffers when resources remain trapped in zombie companies, preventing capital reallocation to more innovative and sustainable sectors typically found in emerging or growth industries. Explore the mechanisms by which financial markets identify and address inefficiencies caused by these two types of firms to understand their broader economic implications.
Source and External Links
SUNSET INDUSTRY definition | Cambridge English Dictionary - A sunset industry is one that has existed for a long time but is declining in success and profitability compared to the past, such as steel or shipbuilding.
Sunset industry - Wikipedia - A sunset industry is in decline, having passed its peak, and while still significant for employment, it usually faces protectionist measures to reduce decline as new industries emerge.
Home - Sunset Industrial - Sunset Industrial specializes in supplying industrial products like bearings, chains, lubrication supplies, and cylinders to keep machinery running efficiently.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com