Funflation describes rising prices alongside increased spending on entertainment and leisure, reflecting consumer willingness to pay more for enjoyable experiences despite inflation. Shrinkflation occurs when product sizes or quantities decrease while prices remain the same, subtly impacting consumer value and purchasing power. Explore the detailed economic effects and examples of funflation and shrinkflation to understand their influence on market trends and consumer behavior.
Why it is important
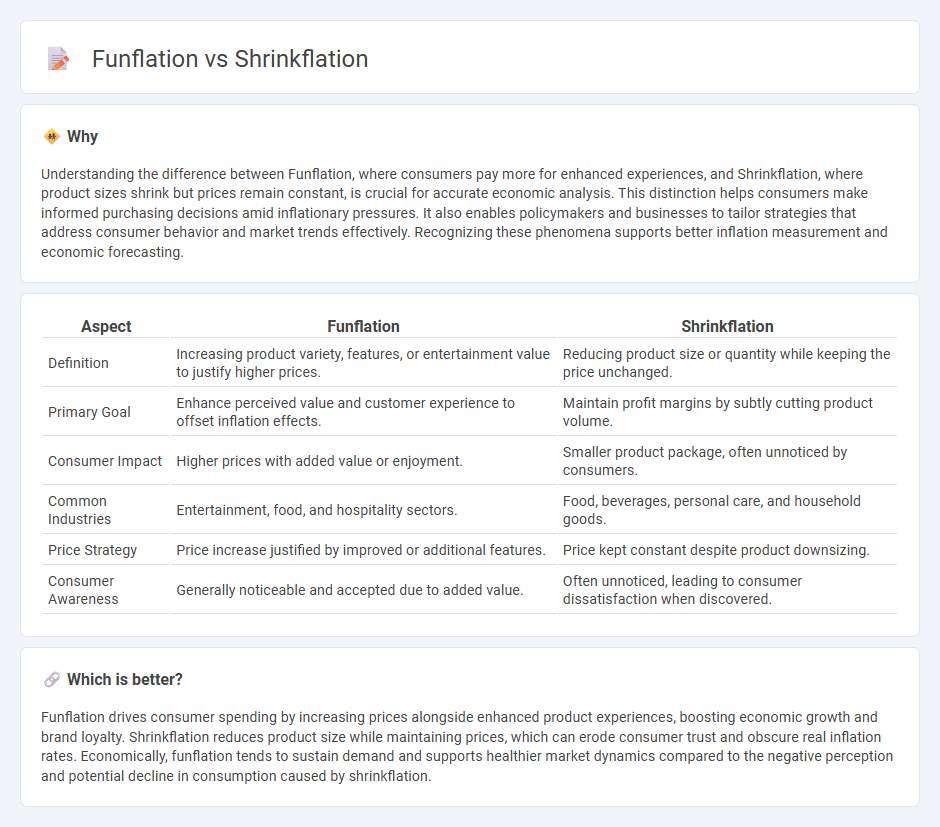
Understanding the difference between Funflation, where consumers pay more for enhanced experiences, and Shrinkflation, where product sizes shrink but prices remain constant, is crucial for accurate economic analysis. This distinction helps consumers make informed purchasing decisions amid inflationary pressures. It also enables policymakers and businesses to tailor strategies that address consumer behavior and market trends effectively. Recognizing these phenomena supports better inflation measurement and economic forecasting.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Funflation | Shrinkflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increasing product variety, features, or entertainment value to justify higher prices. | Reducing product size or quantity while keeping the price unchanged. |
| Primary Goal | Enhance perceived value and customer experience to offset inflation effects. | Maintain profit margins by subtly cutting product volume. |
| Consumer Impact | Higher prices with added value or enjoyment. | Smaller product package, often unnoticed by consumers. |
| Common Industries | Entertainment, food, and hospitality sectors. | Food, beverages, personal care, and household goods. |
| Price Strategy | Price increase justified by improved or additional features. | Price kept constant despite product downsizing. |
| Consumer Awareness | Generally noticeable and accepted due to added value. | Often unnoticed, leading to consumer dissatisfaction when discovered. |
Which is better?
Funflation drives consumer spending by increasing prices alongside enhanced product experiences, boosting economic growth and brand loyalty. Shrinkflation reduces product size while maintaining prices, which can erode consumer trust and obscure real inflation rates. Economically, funflation tends to sustain demand and supports healthier market dynamics compared to the negative perception and potential decline in consumption caused by shrinkflation.
Connection
Funflation and shrinkflation both reflect responses to inflationary pressures that impact consumer behavior and product pricing. Funflation involves businesses enhancing the entertainment or experiential value of products to justify higher prices, while shrinkflation reduces product size or quantity without changing price, effectively increasing cost per unit. Both strategies aim to maintain profit margins amid rising costs, influencing market dynamics and consumer perception.
Key Terms
Consumer Prices
Shrinkflation reflects the reduction of product sizes or quantities while maintaining prices, effectively increasing the unit cost for consumers. Funflation involves adding features or appeal to products, allowing brands to justify higher prices without altering product size. Explore our detailed analysis to understand the impact of shrinkflation and funflation on your consumer spending.
Product Value
Shrinkflation occurs when companies reduce product size or quantity while maintaining price, effectively lowering value without immediate consumer awareness. Funflation involves enhancing product packaging, features, or branding to create a perception of higher value, often justifying increased prices. Explore the nuances and consumer impacts of these pricing strategies to understand how they affect your purchasing decisions.
Experiential Spending
Shrinkflation involves reducing product size while maintaining price, subtly impacting consumer value perception, whereas funflation centers on increased spending for enhanced experiences and entertainment. Experiential spending trends emphasize customers valuing memorable moments over tangible goods, reflecting a shift in economic behavior. Explore how these contrasting inflation tactics shape consumer choices and market strategies.
Source and External Links
Shrinkflation - Definition, Causes, Effects, Examples - Shrinkflation is the practice of reducing the size or quantity of a product while keeping the price the same or slightly higher, effectively increasing the price per unit, commonly used in the food and beverage industry as a hidden way to manage rising costs without directly increasing prices.
Shrinkflation - Wikipedia - Shrinkflation, also called package downsizing, is shrinking product size or quantity while holding prices steady to deal with rising production costs, maintaining profitability without overt price hikes, often criticized as deceptive by consumer groups.
These countries are tackling the issue of shrinkflation - Shrinkflation occurs as businesses respond to inflation in raw materials and labor by reducing product sizes, prompting some governments like South Korea, France, and the US to enforce transparency laws or consider legal action against companies that do not notify consumers about size reductions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com