The gig economy thrives on short-term, flexible jobs facilitated by digital platforms, promoting independent work and rapid service access. In contrast, the circular economy focuses on sustainable resource use by minimizing waste through recycling, reuse, and regenerating natural systems. Explore how these distinct economic models impact global markets, labor trends, and environmental sustainability.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between the gig economy, characterized by short-term, freelance jobs, and the circular economy, focused on sustainable resource use and waste reduction, is crucial for policymakers and businesses to develop targeted economic strategies. The gig economy drives flexibility and innovation in labor markets, while the circular economy promotes environmental sustainability and long-term resource efficiency. This knowledge enables effective decision-making that balances economic growth with ecological preservation. Clear differentiation helps investors and workers align with emerging market trends and sustainability goals.
Comparison Table
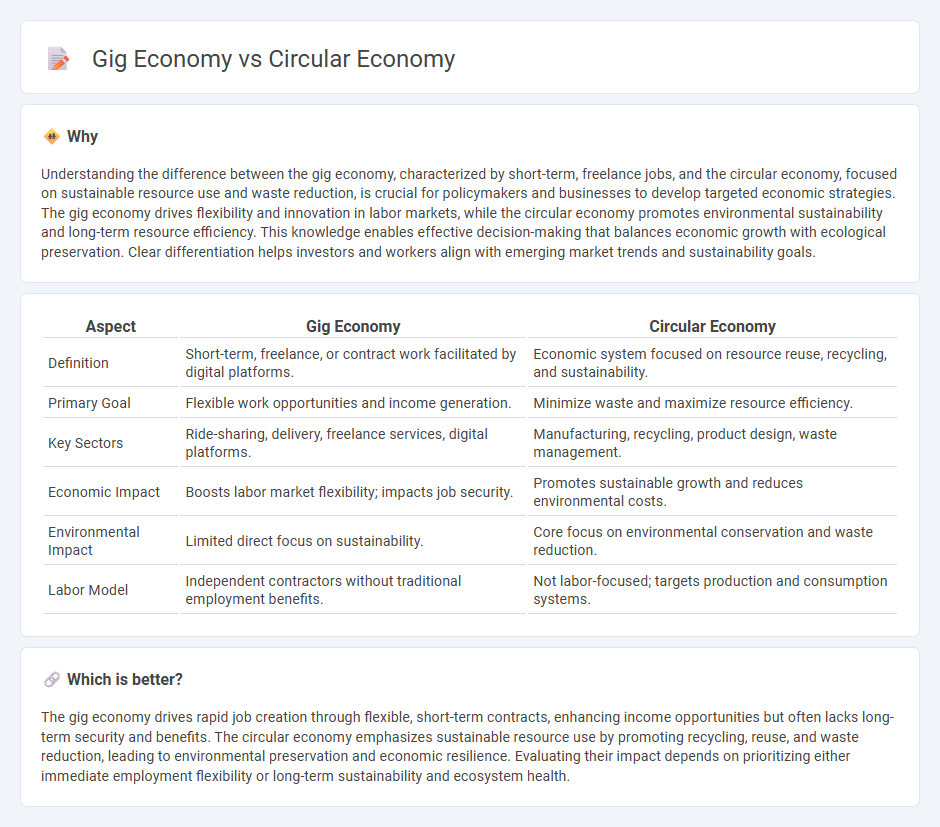
| Aspect | Gig Economy | Circular Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short-term, freelance, or contract work facilitated by digital platforms. | Economic system focused on resource reuse, recycling, and sustainability. |
| Primary Goal | Flexible work opportunities and income generation. | Minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency. |
| Key Sectors | Ride-sharing, delivery, freelance services, digital platforms. | Manufacturing, recycling, product design, waste management. |
| Economic Impact | Boosts labor market flexibility; impacts job security. | Promotes sustainable growth and reduces environmental costs. |
| Environmental Impact | Limited direct focus on sustainability. | Core focus on environmental conservation and waste reduction. |
| Labor Model | Independent contractors without traditional employment benefits. | Not labor-focused; targets production and consumption systems. |
Which is better?
The gig economy drives rapid job creation through flexible, short-term contracts, enhancing income opportunities but often lacks long-term security and benefits. The circular economy emphasizes sustainable resource use by promoting recycling, reuse, and waste reduction, leading to environmental preservation and economic resilience. Evaluating their impact depends on prioritizing either immediate employment flexibility or long-term sustainability and ecosystem health.
Connection
The gig economy promotes flexible, on-demand work that supports resource efficiency, aligning with circular economy principles of minimizing waste through shared services. Circular economy models benefit from gig platforms by enabling the redistribution, repair, and reuse of goods, creating sustainable economic loops. Both economies rely on digital technology to optimize resource utilization and reduce environmental impact.
Key Terms
**Circular economy:**
The circular economy prioritizes sustainable resource management by promoting reuse, recycling, and reducing waste to create closed-loop systems that minimize environmental impact and enhance economic resilience. Businesses adopting circular economy principles focus on product lifecycle extension, resource efficiency, and innovative design to foster long-term value creation. Explore how circular economy strategies drive sustainable growth and transform industries for a greener future.
Resource efficiency
Circular economy maximizes resource efficiency by designing products for reuse, recycling, and minimal waste, significantly reducing environmental impact. Gig economy emphasizes flexible labor models but often leads to increased resource consumption and limited sustainability practices. Explore how integrating circular strategies in gig platforms can enhance overall resource efficiency.
Waste minimization
Circular economy emphasizes waste minimization through resource reuse, recycling, and sustainable design, aiming to create closed-loop systems that reduce environmental impact. Gig economy often faces challenges in waste management due to its reliance on disposable goods and short-term service models. Explore how both economic models address sustainability and identify opportunities for integrating waste reduction strategies.
Source and External Links
Circular economy - Wikipedia - A circular economy is a model of production and consumption emphasizing sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling materials and products to extend their lifecycle, aiming to reduce waste, pollution, and carbon emissions by designing out waste and regenerative natural systems.
What is Circular Economy & How Does It Work? : Complete Guide - The circular economy is an industrial system designed to be restorative and regenerative by recapturing the value of materials through reuse, repair, disassembly, and remanufacture, contrasting the linear "take-make-dispose" economy by eliminating waste and reducing resource extraction.
What is a circular economy? | Ellen MacArthur Foundation - The circular economy is a system where materials never become waste and nature is regenerated, based on three principles: eliminating waste and pollution, circulating products and materials at their highest value, and regenerating natural systems through design-driven approaches.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com