A soft landing occurs when economic growth slows to a sustainable rate without triggering a recession, maintaining steady employment and controlled inflation. Stagflation combines stagnant economic growth with high inflation and rising unemployment, posing significant challenges for policymakers. Explore the key differences and implications of soft landing versus stagflation to better understand economic cycles.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between soft landing and stagflation is crucial for making informed economic decisions and policy responses. A soft landing refers to a scenario where economic growth slows down without triggering a recession or high inflation, maintaining stable employment levels. Stagflation describes a period of stagnant economic growth combined with high inflation and unemployment, severely impacting purchasing power and market stability. Knowing these distinctions helps investors, policymakers, and businesses anticipate risks and adjust strategies accordingly.
Comparison Table
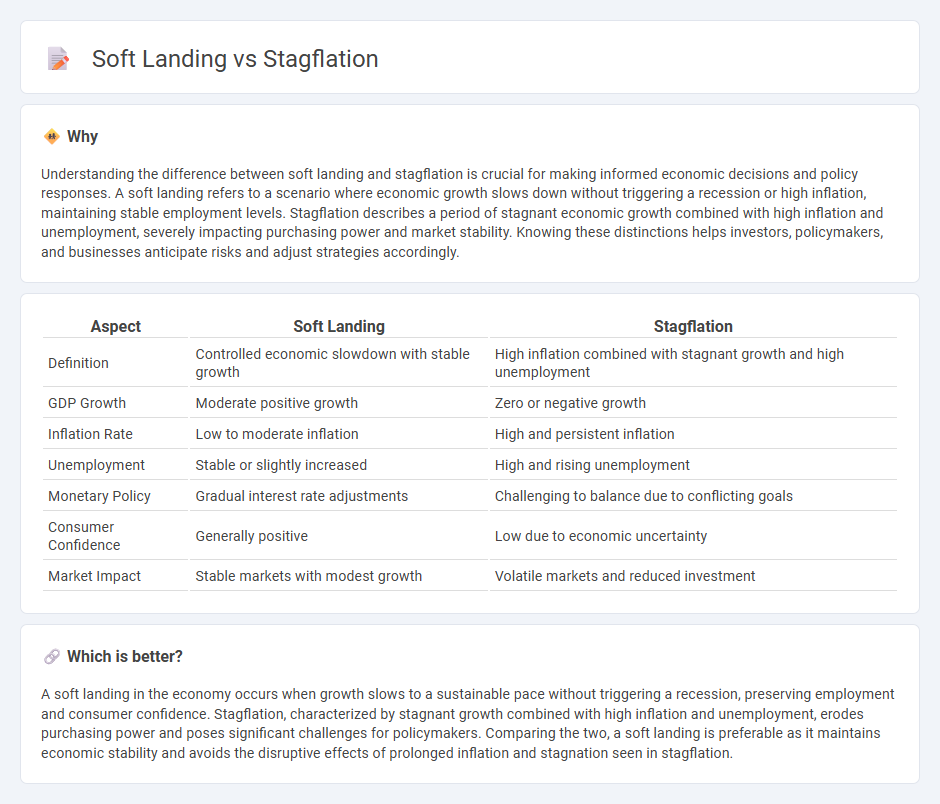
| Aspect | Soft Landing | Stagflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Controlled economic slowdown with stable growth | High inflation combined with stagnant growth and high unemployment |
| GDP Growth | Moderate positive growth | Zero or negative growth |
| Inflation Rate | Low to moderate inflation | High and persistent inflation |
| Unemployment | Stable or slightly increased | High and rising unemployment |
| Monetary Policy | Gradual interest rate adjustments | Challenging to balance due to conflicting goals |
| Consumer Confidence | Generally positive | Low due to economic uncertainty |
| Market Impact | Stable markets with modest growth | Volatile markets and reduced investment |
Which is better?
A soft landing in the economy occurs when growth slows to a sustainable pace without triggering a recession, preserving employment and consumer confidence. Stagflation, characterized by stagnant growth combined with high inflation and unemployment, erodes purchasing power and poses significant challenges for policymakers. Comparing the two, a soft landing is preferable as it maintains economic stability and avoids the disruptive effects of prolonged inflation and stagnation seen in stagflation.
Connection
A soft landing in the economy occurs when growth slows down just enough to avoid recession, maintaining stable inflation and employment levels. Stagflation, characterized by stagnant growth combined with high inflation and unemployment, represents a failure to achieve a soft landing. The connection lies in central banks' attempts to cool inflation without triggering economic stagnation, a delicate balance often challenging to maintain.
Key Terms
Inflation
Stagflation occurs when inflation remains high despite stagnant economic growth and rising unemployment, creating a challenging environment for policymakers. In contrast, a soft landing aims to reduce inflation gradually without triggering a recession, maintaining moderate growth and stable employment levels. Explore further to understand strategies for managing inflation in diverse economic scenarios.
Unemployment
Stagflation presents a challenging economic scenario characterized by high inflation, stagnant growth, and rising unemployment, creating a difficult environment for labor markets. In contrast, a soft landing aims to reduce inflation with minimal impact on employment, maintaining stable job creation and controlled unemployment rates. Explore further to understand how these economic conditions affect workforce dynamics and policy decisions.
Monetary policy
Monetary policy plays a critical role in managing stagflation and achieving a soft landing in economic cycles. During stagflation, central banks face the challenge of tightening monetary policy to control inflation while avoiding exacerbating unemployment, often leading to higher interest rates and reduced money supply. In contrast, a soft landing strategy involves carefully calibrated monetary interventions to moderate inflation and sustain growth without triggering a recession; explore advanced monetary policy frameworks to understand these complex dynamics in depth.
Source and External Links
Overview, Examples, Why Stagflation is Feared - Stagflation is an economic condition marked by high inflation, slow economic growth, and persistently high unemployment, creating a policy dilemma for governments since actions to curb inflation may raise unemployment, and vice versa.
Stagflation - Wikipedia - Stagflation refers to the simultaneous occurrence of high inflation, stagnant economic growth, and elevated unemployment, challenging traditional economic theories that inflation and unemployment are inversely related.
What Is Stagflation (and Why Should You Care)? - Fordham Now - Stagflation occurs when prices keep rising (inflation) while it becomes harder to find jobs due to a slowing economy (stagnation), combining the worst aspects of both inflation and economic slowdown.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com