Resilient supply chains emphasize flexibility, risk mitigation, and adaptability to disruptions, contrasting with globalized supply chains focused on cost efficiency and extensive sourcing networks. While globalized supply chains optimize for scale and international trade, resilient models prioritize local sourcing, diversification, and real-time responsiveness to maintain continuity. Explore the growing importance of resilient supply chains in today's dynamic economic landscape.
Why it is important
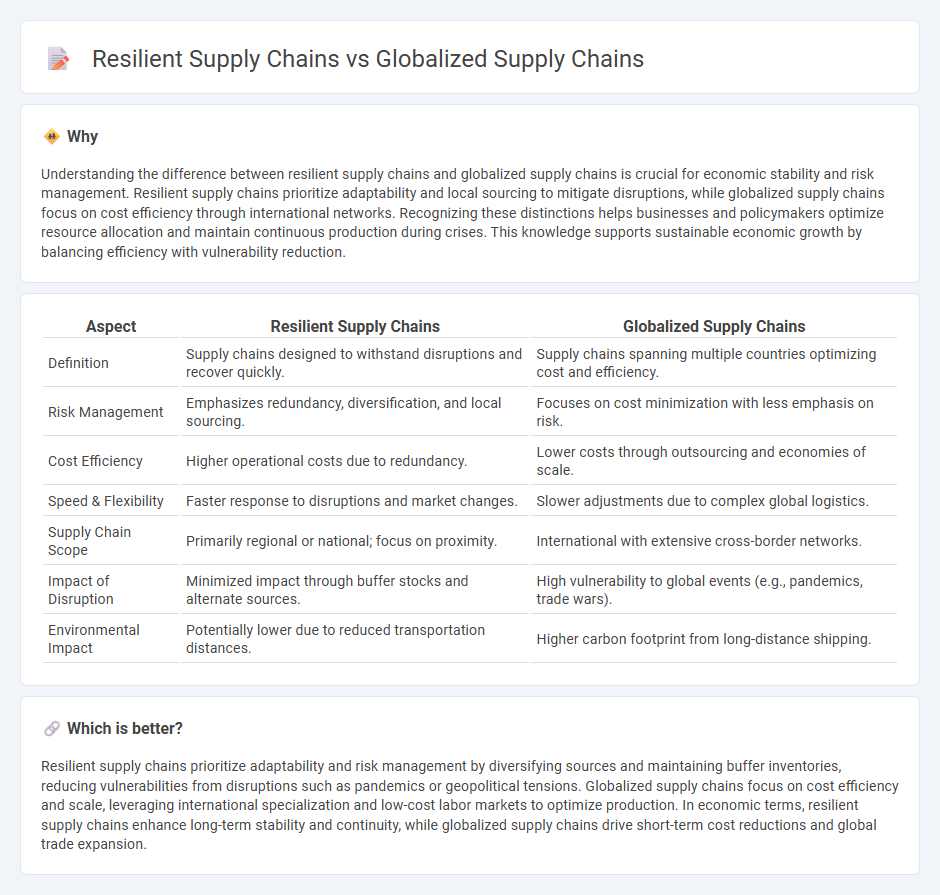
Understanding the difference between resilient supply chains and globalized supply chains is crucial for economic stability and risk management. Resilient supply chains prioritize adaptability and local sourcing to mitigate disruptions, while globalized supply chains focus on cost efficiency through international networks. Recognizing these distinctions helps businesses and policymakers optimize resource allocation and maintain continuous production during crises. This knowledge supports sustainable economic growth by balancing efficiency with vulnerability reduction.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Resilient Supply Chains | Globalized Supply Chains |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supply chains designed to withstand disruptions and recover quickly. | Supply chains spanning multiple countries optimizing cost and efficiency. |
| Risk Management | Emphasizes redundancy, diversification, and local sourcing. | Focuses on cost minimization with less emphasis on risk. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher operational costs due to redundancy. | Lower costs through outsourcing and economies of scale. |
| Speed & Flexibility | Faster response to disruptions and market changes. | Slower adjustments due to complex global logistics. |
| Supply Chain Scope | Primarily regional or national; focus on proximity. | International with extensive cross-border networks. |
| Impact of Disruption | Minimized impact through buffer stocks and alternate sources. | High vulnerability to global events (e.g., pandemics, trade wars). |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially lower due to reduced transportation distances. | Higher carbon footprint from long-distance shipping. |
Which is better?
Resilient supply chains prioritize adaptability and risk management by diversifying sources and maintaining buffer inventories, reducing vulnerabilities from disruptions such as pandemics or geopolitical tensions. Globalized supply chains focus on cost efficiency and scale, leveraging international specialization and low-cost labor markets to optimize production. In economic terms, resilient supply chains enhance long-term stability and continuity, while globalized supply chains drive short-term cost reductions and global trade expansion.
Connection
Resilient supply chains enhance the stability and efficiency of globalized supply chains by minimizing disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or pandemics. Incorporating adaptive strategies such as diversified sourcing, real-time data analytics, and flexible logistics strengthens global supply networks against volatile market conditions. This interdependence supports continuous trade flows and economic growth within the interconnected global economy.
Key Terms
Just-in-Time (JIT)
Globalized supply chains leverage Just-in-Time (JIT) methodologies to minimize inventory costs by synchronizing production with demand across international suppliers. Resilient supply chains, however, prioritize buffer stocks and diversified sourcing to mitigate disruptions despite increased carrying costs, challenging traditional JIT principles. Explore the evolving strategies balancing efficiency and robustness in modern supply chain management.
Nearshoring
Globalized supply chains often rely on extended networks spanning multiple continents, which can increase vulnerability to disruptions such as pandemics, geopolitical tensions, or shipping delays. Resilient supply chains emphasize Nearshoring, bringing production closer to end markets to reduce lead times, lower transportation costs, and enhance responsiveness to demand fluctuations. Explore the benefits and challenges of Nearshoring to understand its impact on supply chain resilience.
Risk Diversification
Globalized supply chains expand sourcing across multiple countries to reduce costs but often increase vulnerability to geopolitical risks and transportation disruptions. Resilient supply chains emphasize risk diversification by integrating local suppliers, multiple sourcing options, and advanced risk management technologies to maintain continuity during crises. Discover how businesses balance globalization with resilience to optimize risk diversification strategies.
Source and External Links
Global Supply Chain: What It Is, Importance, and Challenges - A global supply chain crosses international borders, linking manufacturers, suppliers, and customers in different countries, involving complex steps to move products from raw materials to finished goods while managing international regulations and freight costs.
Globalization And Supply Chain Management in 2025 - Globalization in supply chains enables sourcing, production, and distribution across borders with intricate coordination of factories, freight, customs, and technology, driven historically by innovations like containerization and the internet.
The Challenges and Opportunities of Globalization for Supply - Globalized supply chains offer opportunities such as cost reduction, access to new markets, innovation, efficiency, and risk diversification, while facing complexities from geographical, cultural, and regulatory factors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com