Slowbalisation marks a shift in global trade characterized by reduced growth rates and a focus on regional supply chains, challenging the decades-long trend of globalization. Reshoring intensifies this movement by encouraging companies to relocate manufacturing back to their home countries to enhance supply chain resilience and reduce dependency on distant markets. Discover more about how these trends are reshaping the global economic landscape.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between slowbalisation and reshoring is crucial for economic strategy as slowbalisation signals a gradual slowdown in global trade and interconnectedness, while reshoring involves bringing manufacturing and services back to the domestic economy. Companies can optimize supply chain resilience and cost efficiency by recognizing these trends. Policymakers rely on this knowledge to craft trade policies and labor market interventions that support sustainable economic growth. Accurate analysis of these phenomena helps anticipate shifts in employment, investment flows, and international competitiveness.
Comparison Table
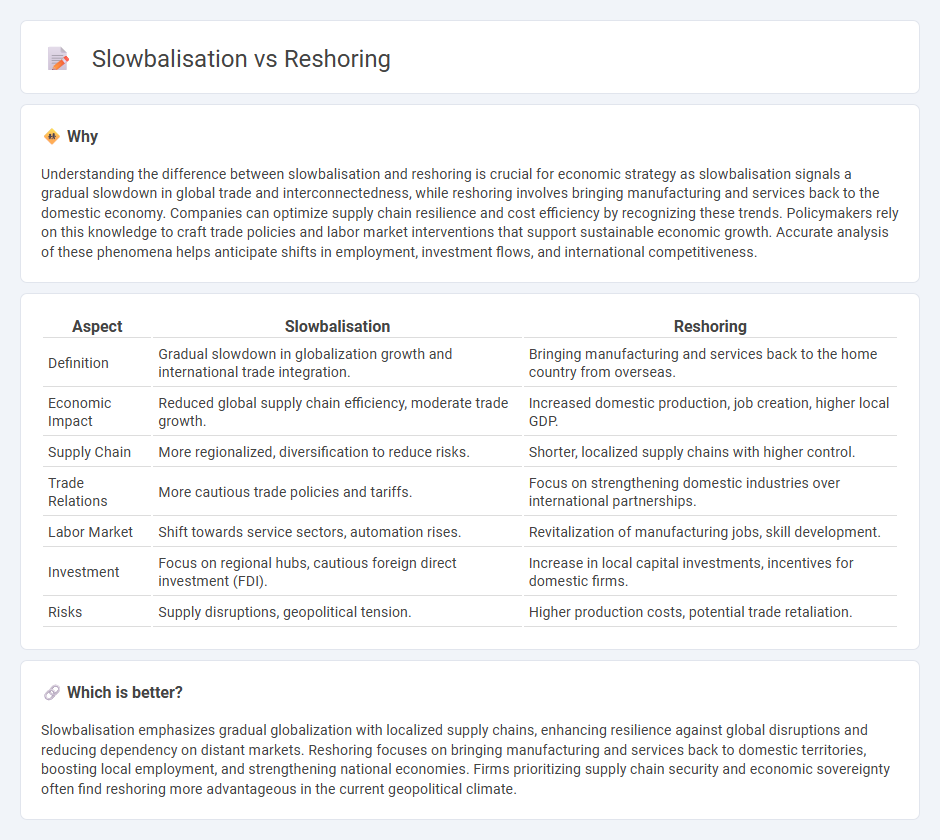
| Aspect | Slowbalisation | Reshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual slowdown in globalization growth and international trade integration. | Bringing manufacturing and services back to the home country from overseas. |
| Economic Impact | Reduced global supply chain efficiency, moderate trade growth. | Increased domestic production, job creation, higher local GDP. |
| Supply Chain | More regionalized, diversification to reduce risks. | Shorter, localized supply chains with higher control. |
| Trade Relations | More cautious trade policies and tariffs. | Focus on strengthening domestic industries over international partnerships. |
| Labor Market | Shift towards service sectors, automation rises. | Revitalization of manufacturing jobs, skill development. |
| Investment | Focus on regional hubs, cautious foreign direct investment (FDI). | Increase in local capital investments, incentives for domestic firms. |
| Risks | Supply disruptions, geopolitical tension. | Higher production costs, potential trade retaliation. |
Which is better?
Slowbalisation emphasizes gradual globalization with localized supply chains, enhancing resilience against global disruptions and reducing dependency on distant markets. Reshoring focuses on bringing manufacturing and services back to domestic territories, boosting local employment, and strengthening national economies. Firms prioritizing supply chain security and economic sovereignty often find reshoring more advantageous in the current geopolitical climate.
Connection
Slowbalisation refers to the deceleration of global economic integration, leading to a shift away from hyper-globalized supply chains. Reshoring involves relocating production and manufacturing activities back to a company's home country, often driven by the need to reduce dependency on distant suppliers and mitigate geopolitical risks. Together, slowbalisation and reshoring reflect a strategic realignment in the global economy, emphasizing local resilience and sustainability over expansive international networks.
Key Terms
Supply Chain
Reshoring involves relocating supply chain operations closer to a company's home country to enhance control and reduce risks associated with long-distance logistics. Slowbalisation reflects a gradual reduction in globalization intensity, leading companies to prioritize regional supply chains for improved resilience and sustainability. Explore more about how these trends reshape supply chain strategies and impact global trade dynamics.
Trade Balance
Reshoring involves bringing manufacturing and services back to the home country, aiming to improve the trade balance by reducing imports and boosting domestic exports. Slowbalisation refers to the deceleration of global supply chain expansion, leading to more regionalized trade networks and impacting trade balances by shifting import-export dynamics. Explore how these trends reshape global trade balances in detail.
Manufacturing
Reshoring in manufacturing involves relocating production back to a company's home country to enhance supply chain resilience, reduce transportation costs, and increase control over quality. Slowbalisation reflects the gradual slowdown of global supply chain expansion, emphasizing nearshoring, regional manufacturing hubs, and diversified sourcing to mitigate geopolitical risks and trade uncertainties. Explore the evolving manufacturing strategies and their impact on global trade dynamics for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
Reshoring - SCRG - Reshoring is the process of bringing manufacturing operations back from a foreign country to a business's home country, aiming to regain control over quality, lead time, and supply chain risks.
What is Reshoring? Understanding Manufacturing Location Terms - Reshoring refers specifically to returning production from overseas back to the domestic country where the company is headquartered or sells products, contrasting with offshoring or insourcing based on location and ownership.
What is Reshoring? - Reshoring strengthens the economy by creating well-paying manufacturing jobs domestically and lowering total product costs while improving innovation and reducing unemployment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com