Shrinkflation refers to the practice where products reduce in size or quantity while maintaining the same price, effectively increasing the unit price without immediate consumer awareness. Skimpflation occurs when businesses cut corners on quality or service, offering less value for the same cost, impacting customer satisfaction and perceived worth. Explore the differences between shrinkflation and skimpflation to understand their effects on consumer spending and the broader economy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between shrinkflation and skimpflation helps consumers identify deceptive cost-saving tactics affecting product quantity and quality. Shrinkflation involves reducing product size or quantity while maintaining price, whereas skimpflation refers to cutting services or quality to save costs. Accurate recognition enables better budgeting and purchasing decisions amidst inflation. Companies often use both strategies to mask price increases without alarming customers.
Comparison Table
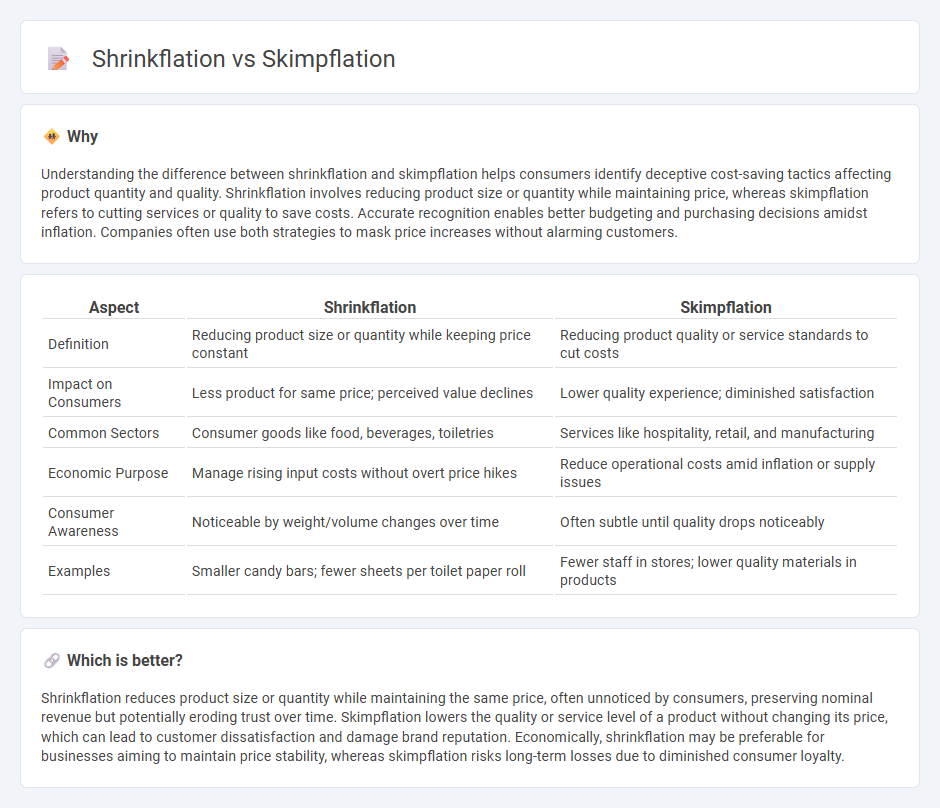
| Aspect | Shrinkflation | Skimpflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing product size or quantity while keeping price constant | Reducing product quality or service standards to cut costs |
| Impact on Consumers | Less product for same price; perceived value declines | Lower quality experience; diminished satisfaction |
| Common Sectors | Consumer goods like food, beverages, toiletries | Services like hospitality, retail, and manufacturing |
| Economic Purpose | Manage rising input costs without overt price hikes | Reduce operational costs amid inflation or supply issues |
| Consumer Awareness | Noticeable by weight/volume changes over time | Often subtle until quality drops noticeably |
| Examples | Smaller candy bars; fewer sheets per toilet paper roll | Fewer staff in stores; lower quality materials in products |
Which is better?
Shrinkflation reduces product size or quantity while maintaining the same price, often unnoticed by consumers, preserving nominal revenue but potentially eroding trust over time. Skimpflation lowers the quality or service level of a product without changing its price, which can lead to customer dissatisfaction and damage brand reputation. Economically, shrinkflation may be preferable for businesses aiming to maintain price stability, whereas skimpflation risks long-term losses due to diminished consumer loyalty.
Connection
Shrinkflation and skimpflation are both inflationary phenomena where businesses reduce product quantity or quality instead of raising prices to manage rising costs. Shrinkflation involves shrinking product sizes while maintaining price points, whereas skimpflation refers to cutting corners in service or product quality, impacting consumer experience. These strategies reflect companies' attempts to preserve profit margins amid inflation without overtly increasing prices.
Key Terms
Consumer Experience
Skimpflation impacts the consumer experience by reducing the quality or service level while maintaining the same price, leading to dissatisfaction despite stable costs. Shrinkflation involves decreasing product size or quantity without changing price, often causing consumers to feel they receive less value. Dive deeper to understand how these pricing strategies affect consumer perception and purchasing behavior.
Product Size
Skimpflation involves reducing the quality or quantity of accompanying items in a product package, while shrinkflation specifically refers to decreasing the physical size or weight of the primary product itself without a price change. In retail sectors, shrinkflation is more visible in packaged goods like snacks and beverages, impacting consumer perception of value directly through smaller portions. Explore more about how these strategies affect pricing and consumer trust.
Cost-Cutting
Skimpflation involves reducing the quality or quantity of services and products while maintaining the same price, directly affecting customer satisfaction. Shrinkflation occurs when companies reduce the size or volume of a product but keep the pricing constant, effectively increasing the cost per unit. Explore the detailed differences and implications of cost-cutting techniques in consumer markets to better understand their impact.
Source and External Links
We've Heard Of Shrinkflation, But What Is 'Skimpflation'? - Skimpflation describes the phenomenon where consumers pay the same price as before but receive a much lower quality product or service, such as reduced restaurant staff, slower service, or fewer hotel amenities, as companies cut costs without reducing prices.
Shrinkflation - Wikipedia - Skimpflation involves reducing the quality of a product or service as a way for companies to manage rising costs, distinguishing it from shrinkflation, which reduces the size or quantity while keeping prices stable.
Inflation, Shrinkflation, Skimpflation, and Excuseflation: What You Need to Know - Skimpflation is when companies decrease product quality but keep prices the same, often leading to consumer dissatisfaction and shifting customer demand toward competitors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com