Nearshoring involves relocating business operations closer to a company's home country, reducing transportation costs and improving communication, while outsourcing contracts services to third-party providers regardless of location. Companies increasingly favor nearshoring to mitigate supply chain risks and benefit from cultural and time zone similarities, enhancing efficiency compared to traditional outsourcing. Discover how these strategies impact global trade and business resilience by exploring key economic trends.
Why it is important
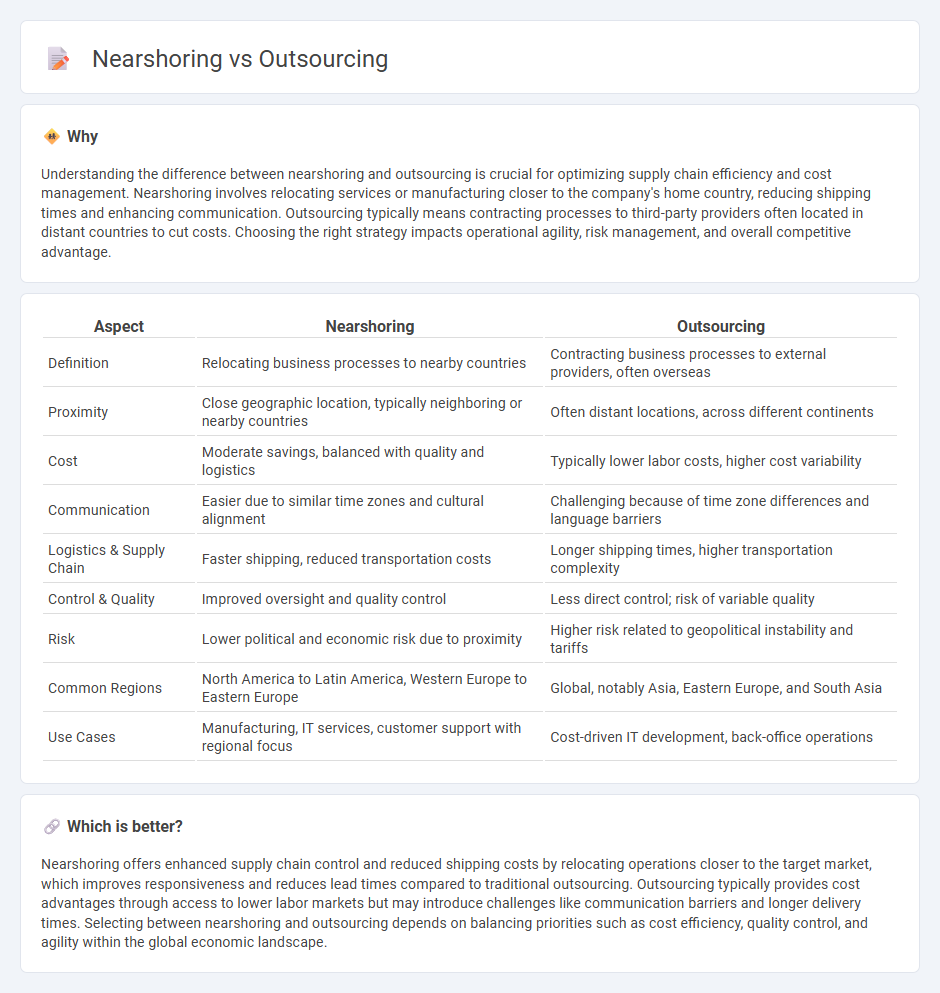
Understanding the difference between nearshoring and outsourcing is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and cost management. Nearshoring involves relocating services or manufacturing closer to the company's home country, reducing shipping times and enhancing communication. Outsourcing typically means contracting processes to third-party providers often located in distant countries to cut costs. Choosing the right strategy impacts operational agility, risk management, and overall competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Nearshoring | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relocating business processes to nearby countries | Contracting business processes to external providers, often overseas |
| Proximity | Close geographic location, typically neighboring or nearby countries | Often distant locations, across different continents |
| Cost | Moderate savings, balanced with quality and logistics | Typically lower labor costs, higher cost variability |
| Communication | Easier due to similar time zones and cultural alignment | Challenging because of time zone differences and language barriers |
| Logistics & Supply Chain | Faster shipping, reduced transportation costs | Longer shipping times, higher transportation complexity |
| Control & Quality | Improved oversight and quality control | Less direct control; risk of variable quality |
| Risk | Lower political and economic risk due to proximity | Higher risk related to geopolitical instability and tariffs |
| Common Regions | North America to Latin America, Western Europe to Eastern Europe | Global, notably Asia, Eastern Europe, and South Asia |
| Use Cases | Manufacturing, IT services, customer support with regional focus | Cost-driven IT development, back-office operations |
Which is better?
Nearshoring offers enhanced supply chain control and reduced shipping costs by relocating operations closer to the target market, which improves responsiveness and reduces lead times compared to traditional outsourcing. Outsourcing typically provides cost advantages through access to lower labor markets but may introduce challenges like communication barriers and longer delivery times. Selecting between nearshoring and outsourcing depends on balancing priorities such as cost efficiency, quality control, and agility within the global economic landscape.
Connection
Nearshoring and outsourcing are interconnected strategies used by companies to optimize operational efficiency and reduce costs by relocating business processes to external providers. Nearshoring specifically involves transferring operations to nearby countries with similar time zones and cultural affinities, while outsourcing broadly refers to contracting third-party firms regardless of location. Both approaches drive economic globalization, enhance supply chain resilience, and influence regional labor markets by shifting jobs across borders.
Key Terms
Cost Efficiency
Outsourcing often offers lower labor costs by leveraging global wage disparities, making it a cost-efficient solution for businesses seeking to reduce expenses. Nearshoring, while typically more expensive than traditional outsourcing, reduces costs related to transportation, tariffs, and time zone differences, enhancing overall operational savings. Explore the detailed cost efficiency comparison between outsourcing and nearshoring to optimize your business strategy.
Geographic Proximity
Nearshoring offers the advantage of geographic proximity, reducing time zone differences and enabling faster communication compared to traditional outsourcing. Companies benefit from closer cultural alignment and easier travel logistics when partnering with nearshore providers located in neighboring countries. Explore this strategic approach to optimize your global operations by learning more about geographic proximity in outsourcing decisions.
Labor Market
Outsourcing involves delegating tasks to external providers often located in distant countries with lower labor costs, while nearshoring transfers operations to nearby countries with similar time zones and cultural affinity, facilitating smoother communication and faster response times. The labor market in nearshore destinations, such as Mexico or Eastern Europe, typically offers a highly skilled workforce familiar with Western business practices, contrasting with traditional outsourcing hubs like India or the Philippines where cost efficiency is the primary advantage. Explore further to understand how labor market dynamics impact your strategic decision between outsourcing and nearshoring.
Source and External Links
What Is Outsourcing? (Including Types and Advantages) | Indeed.com - Outsourcing is the practice of hiring outside contractors or external companies to perform tasks or create goods, allowing companies to reduce costs, access specialized skills, and focus on core business activities.
What is Outsourcing and How Does it Work? - TechTarget - Outsourcing involves a company hiring a third party to handle specific tasks, operations, or services--such as IT, customer support, or payroll--often to improve efficiency and leverage external expertise.
What is Outsourcing? Definition, Advantages, and Examples - Outsourcing is contracting with a third-party provider to manage certain business functions, offering benefits like cost savings, access to specialized knowledge, and the ability to concentrate on primary business goals.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com