Price gouging involves sellers significantly increasing prices during high demand or shortages, exploiting consumers for maximum profit. Dumping occurs when producers export goods at below-market prices to eliminate competition and capture market share, potentially harming local industries. Explore the economic impacts and regulatory responses to price gouging and dumping for a deeper understanding.
Why it is important
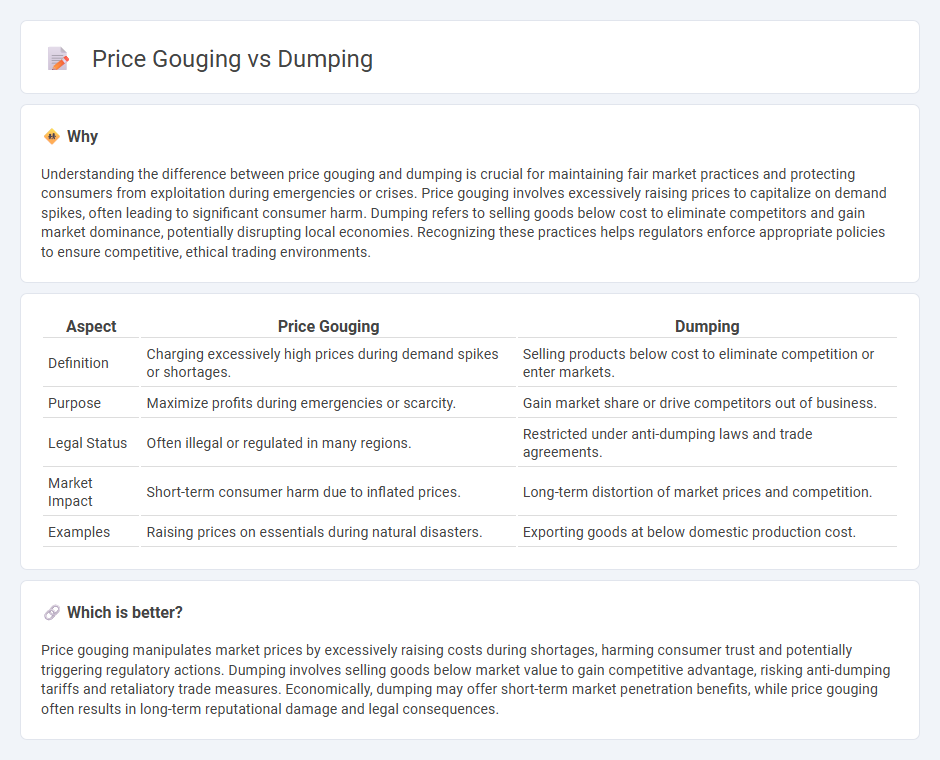
Understanding the difference between price gouging and dumping is crucial for maintaining fair market practices and protecting consumers from exploitation during emergencies or crises. Price gouging involves excessively raising prices to capitalize on demand spikes, often leading to significant consumer harm. Dumping refers to selling goods below cost to eliminate competitors and gain market dominance, potentially disrupting local economies. Recognizing these practices helps regulators enforce appropriate policies to ensure competitive, ethical trading environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Price Gouging | Dumping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Charging excessively high prices during demand spikes or shortages. | Selling products below cost to eliminate competition or enter markets. |
| Purpose | Maximize profits during emergencies or scarcity. | Gain market share or drive competitors out of business. |
| Legal Status | Often illegal or regulated in many regions. | Restricted under anti-dumping laws and trade agreements. |
| Market Impact | Short-term consumer harm due to inflated prices. | Long-term distortion of market prices and competition. |
| Examples | Raising prices on essentials during natural disasters. | Exporting goods at below domestic production cost. |
Which is better?
Price gouging manipulates market prices by excessively raising costs during shortages, harming consumer trust and potentially triggering regulatory actions. Dumping involves selling goods below market value to gain competitive advantage, risking anti-dumping tariffs and retaliatory trade measures. Economically, dumping may offer short-term market penetration benefits, while price gouging often results in long-term reputational damage and legal consequences.
Connection
Price gouging and dumping both disrupt market equilibrium by manipulating product prices to gain unfair advantage; price gouging inflates prices during high demand or scarcity, while dumping involves selling products below cost to outcompete rivals. These practices undermine fair competition, distort consumer trust, and can trigger regulatory scrutiny or trade disputes. Understanding their connection highlights vulnerabilities in economic markets and the importance of enforcement policies to maintain competitive integrity.
Key Terms
Market pricing
Dumping involves selling products in a foreign market at below cost to gain market share, distorting competitive pricing and undermining local businesses. Price gouging refers to excessively raising prices during demand surges or shortages, exploiting consumers and disrupting fair market pricing dynamics. Explore how regulatory frameworks address these practices to maintain balanced market pricing.
Anti-competitive practices
Dumping involves selling products in foreign markets at prices below production cost to undermine competitors, often triggering investigations under international trade laws such as the World Trade Organization's anti-dumping agreements. Price gouging refers to excessive price hikes during emergencies, exploiting consumers and violating domestic regulations designed to maintain fair market conditions. Explore in-depth analysis of anti-competitive practices, legal frameworks, and economic impacts to understand the distinctions and enforcement challenges.
Consumer protection
Dumping involves selling goods in a foreign market below fair value or production cost, often to undermine competitors, while price gouging refers to excessively raising prices during emergencies to exploit consumers. Consumer protection laws aim to prevent both practices by ensuring fair pricing, maintaining market competition, and protecting buyers from exploitation. Learn more about regulatory measures and enforcement strategies to safeguard consumer rights effectively.
Source and External Links
Dumping explained: definition and effects | Topics - Dumping is the practice where foreign firms sell products at artificially low prices, often due to subsidies or overproduction, posing unfair competition and threatening domestic industries, with the EU responding through anti-dumping duties to protect its market.
What is dumping, and why am I experiencing it? - Dumping syndrome is a medical condition where undigested food rapidly enters the small intestine, causing symptoms shortly after eating, often occurring after gastric surgery.
Dumping (pricing policy) - In economics, dumping is a predatory pricing strategy where exporters sell products below normal prices abroad to gain market share by driving out competition, potentially leading to monopolies and trade defenses like anti-dumping laws.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com