The eco-anxiety economy prioritizes sustainable practices and renewable resources to address environmental concerns, contrasting sharply with the linear economy's model of take-make-dispose that depletes natural resources and generates waste. By shifting consumer behavior and corporate strategies towards circularity and environmental responsibility, the eco-anxiety economy fosters resilience against climate change impacts and supports green innovation. Discover how this transformative economic approach is reshaping markets and influencing global sustainability efforts.
Why it is important
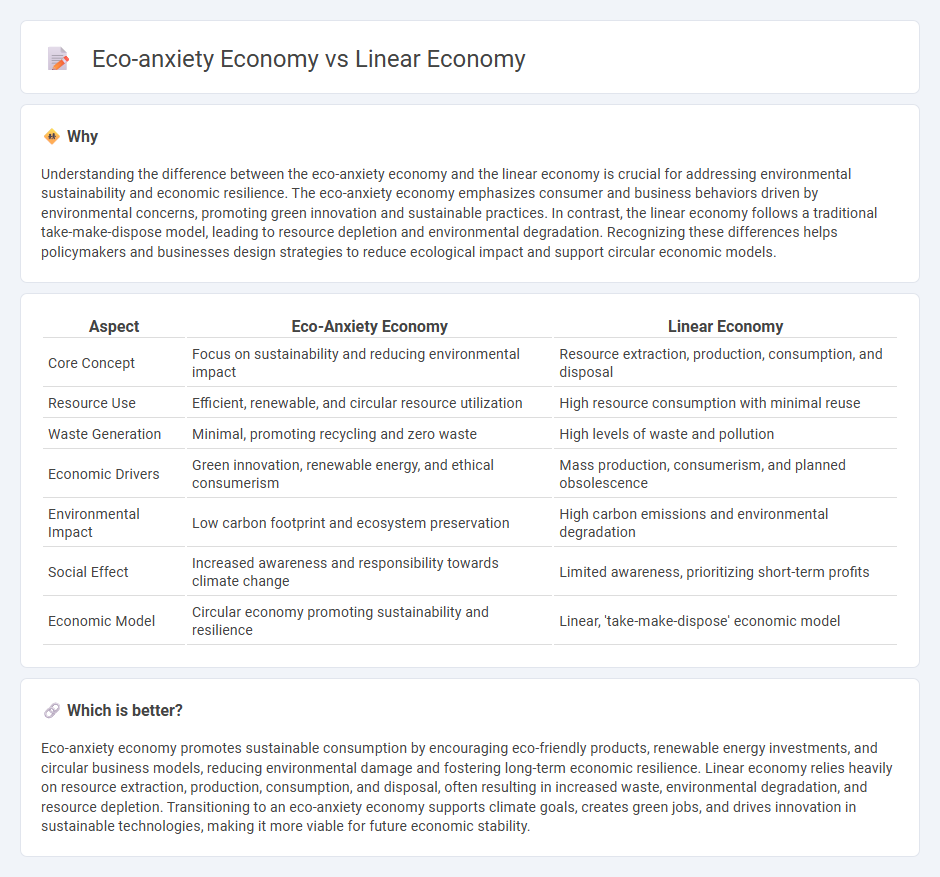
Understanding the difference between the eco-anxiety economy and the linear economy is crucial for addressing environmental sustainability and economic resilience. The eco-anxiety economy emphasizes consumer and business behaviors driven by environmental concerns, promoting green innovation and sustainable practices. In contrast, the linear economy follows a traditional take-make-dispose model, leading to resource depletion and environmental degradation. Recognizing these differences helps policymakers and businesses design strategies to reduce ecological impact and support circular economic models.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Eco-Anxiety Economy | Linear Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Core Concept | Focus on sustainability and reducing environmental impact | Resource extraction, production, consumption, and disposal |
| Resource Use | Efficient, renewable, and circular resource utilization | High resource consumption with minimal reuse |
| Waste Generation | Minimal, promoting recycling and zero waste | High levels of waste and pollution |
| Economic Drivers | Green innovation, renewable energy, and ethical consumerism | Mass production, consumerism, and planned obsolescence |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint and ecosystem preservation | High carbon emissions and environmental degradation |
| Social Effect | Increased awareness and responsibility towards climate change | Limited awareness, prioritizing short-term profits |
| Economic Model | Circular economy promoting sustainability and resilience | Linear, 'take-make-dispose' economic model |
Which is better?
Eco-anxiety economy promotes sustainable consumption by encouraging eco-friendly products, renewable energy investments, and circular business models, reducing environmental damage and fostering long-term economic resilience. Linear economy relies heavily on resource extraction, production, consumption, and disposal, often resulting in increased waste, environmental degradation, and resource depletion. Transitioning to an eco-anxiety economy supports climate goals, creates green jobs, and drives innovation in sustainable technologies, making it more viable for future economic stability.
Connection
Eco-anxiety drives consumer demand for sustainable products, challenging the traditional linear economy model that relies on extraction, production, and disposal. This psychological response encourages businesses to adopt circular economy practices to reduce environmental impact and manage resource scarcity effectively. Shifting from a linear to a circular economy addresses eco-anxiety by promoting waste reduction, recycling, and sustainable consumption patterns.
Key Terms
Resource Extraction
The linear economy relies heavily on extensive resource extraction, often leading to environmental degradation and depletion of finite materials. In contrast, the eco-anxiety economy emphasizes sustainable resource management, promoting circular models to reduce waste and lessen ecological impact. Explore how these economic models influence resource extraction and environmental outcomes for a deeper understanding.
Circularity
The linear economy follows a take-make-dispose model that depletes finite resources and generates significant waste, whereas the eco-anxiety economy emerges from increased awareness of environmental crises, driving demand for sustainable solutions such as circularity. Circular economy principles emphasize resource efficiency, recycling, and reuse to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation and reduce ecological footprints. Explore how adopting circular strategies can alleviate eco-anxiety while fostering resilient, sustainable economic models.
Psychological Well-being
The linear economy, driven by a take-make-dispose model, often leads to environmental degradation contributing to increased eco-anxiety, a growing psychological condition characterized by chronic fear of environmental doom. This eco-anxiety economy intensifies stress and emotional distress as individuals feel powerless against climate change impacts, highlighting the urgent need for sustainable economic practices that promote mental health resilience. Explore effective strategies to balance economic development with psychological well-being for a healthier planet and population.
Source and External Links
Linear Economy Explained - This webpage explains the linear economy model, characterized by the "Take-Make-Dispose" principle, highlighting its environmental impacts and unsustainable nature.
What is a Linear Economy? - This article discusses the traditional linear economy model and its environmental challenges, emphasizing the need for a more sustainable economic approach.
Linear Economy Definition - This page defines the linear economy as a "take-make-waste" model, highlighting its focus on high production and consumption rates without regard for waste and environmental degradation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com