Gigification transforms traditional work by creating flexible, short-term job opportunities through digital platforms, empowering workers to engage in various projects without long-term commitments. Self-employment offers individuals autonomy and full control over their business operations but often involves higher financial risks and responsibilities. Explore the key differences and benefits of gigification versus self-employment to understand which model suits your career goals best.
Why it is important
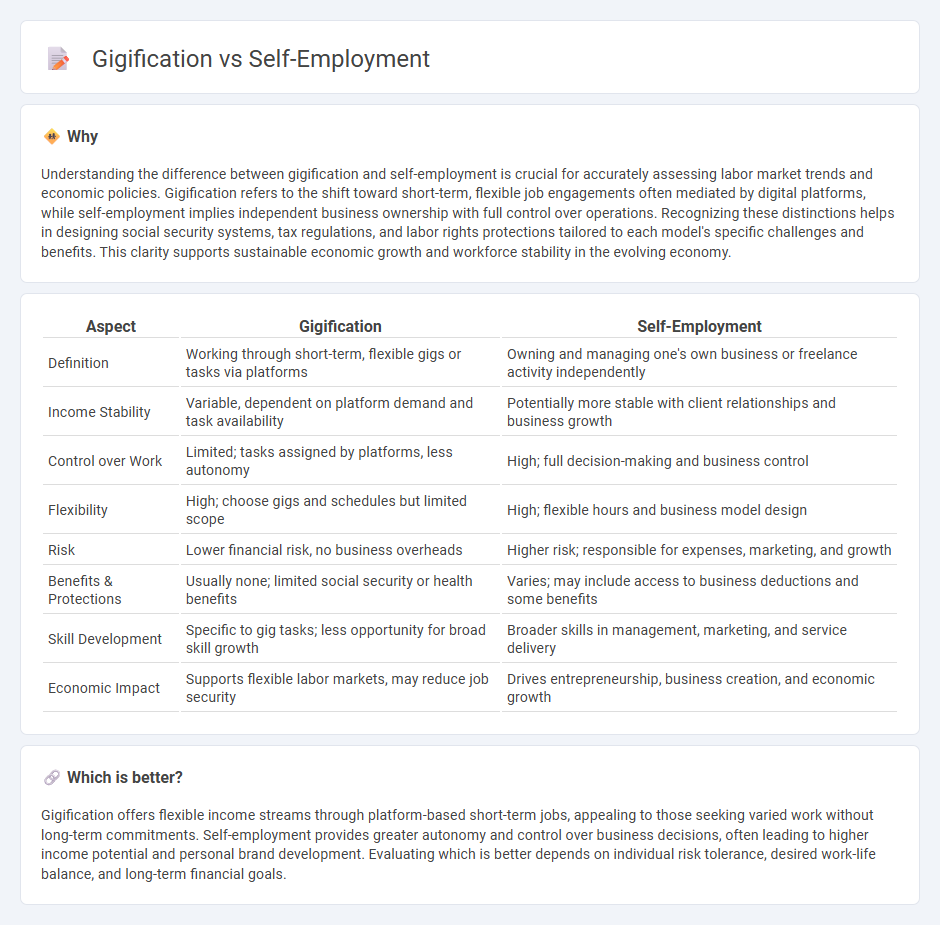
Understanding the difference between gigification and self-employment is crucial for accurately assessing labor market trends and economic policies. Gigification refers to the shift toward short-term, flexible job engagements often mediated by digital platforms, while self-employment implies independent business ownership with full control over operations. Recognizing these distinctions helps in designing social security systems, tax regulations, and labor rights protections tailored to each model's specific challenges and benefits. This clarity supports sustainable economic growth and workforce stability in the evolving economy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gigification | Self-Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Working through short-term, flexible gigs or tasks via platforms | Owning and managing one's own business or freelance activity independently |
| Income Stability | Variable, dependent on platform demand and task availability | Potentially more stable with client relationships and business growth |
| Control over Work | Limited; tasks assigned by platforms, less autonomy | High; full decision-making and business control |
| Flexibility | High; choose gigs and schedules but limited scope | High; flexible hours and business model design |
| Risk | Lower financial risk, no business overheads | Higher risk; responsible for expenses, marketing, and growth |
| Benefits & Protections | Usually none; limited social security or health benefits | Varies; may include access to business deductions and some benefits |
| Skill Development | Specific to gig tasks; less opportunity for broad skill growth | Broader skills in management, marketing, and service delivery |
| Economic Impact | Supports flexible labor markets, may reduce job security | Drives entrepreneurship, business creation, and economic growth |
Which is better?
Gigification offers flexible income streams through platform-based short-term jobs, appealing to those seeking varied work without long-term commitments. Self-employment provides greater autonomy and control over business decisions, often leading to higher income potential and personal brand development. Evaluating which is better depends on individual risk tolerance, desired work-life balance, and long-term financial goals.
Connection
Gigification drives the rise of self-employment by enabling workers to engage in flexible, short-term contracts through digital platforms such as Uber, Upwork, and Fiverr. This shift fosters economic decentralization, allowing individuals to monetize diverse skills independently while reducing reliance on traditional full-time employment. Data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics shows a consistent increase in gig workers, reflecting a significant transformation in labor market dynamics influenced by technological advances.
Key Terms
Flexibility
Self-employment offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing individuals to set their own schedules and choose projects aligned with their skills and interests. Gigification, characterized by short-term, task-based engagements, provides even greater adaptability with opportunities to work across multiple platforms and industries simultaneously. Explore the nuances between these work models to determine which flexibility benefits your career goals the most.
Income Stability
Self-employment offers greater income stability through consistent client relationships and predictable projects, whereas gigification often results in fluctuating earnings due to short-term contracts and variable demand. The gig economy emphasizes flexibility but can lead to income unpredictability lacking traditional employment benefits such as insurance and retirement plans. Explore more insights to understand how income stability varies between self-employment and gig work.
Autonomy
Self-employment offers individuals full autonomy over business decisions, work schedules, and client selection, fostering a stronger sense of control and entrepreneurial freedom. Gigification, while providing flexibility, often involves platform-imposed constraints like algorithm-driven task assignments and standardized service terms, which can limit true autonomy. Explore how these dynamics shape the future of work and personal independence.
Source and External Links
Self-employment - Wikipedia - Self-employment refers to working for oneself rather than for an employer, with rising levels in the U.S. linked to positive impacts on income growth, job creation, and poverty reduction, especially in non-metropolitan areas.
Self-employment | Explore Careers - Self-employment offers opportunities across many fields, including gig work, freelancing, and starting a business, and provides benefits like flexible schedules but also requires strong self-motivation and awareness of its challenges.
Self-employment tax (Social Security and Medicare taxes) - IRS - Self-employed individuals must pay self-employment tax, covering both Social Security and Medicare contributions, calculated on net earnings and often paid quarterly as estimated taxes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com