Rising government debt and increasing inflation rates highlight the growing tension between doom spending and consumer restraint in today's economy. While panic-driven purchases temporarily boost retail activity, long-term consumer confidence declines as households prioritize saving over spending. Explore the complex economic impacts of these contrasting behaviors.
Why it is important
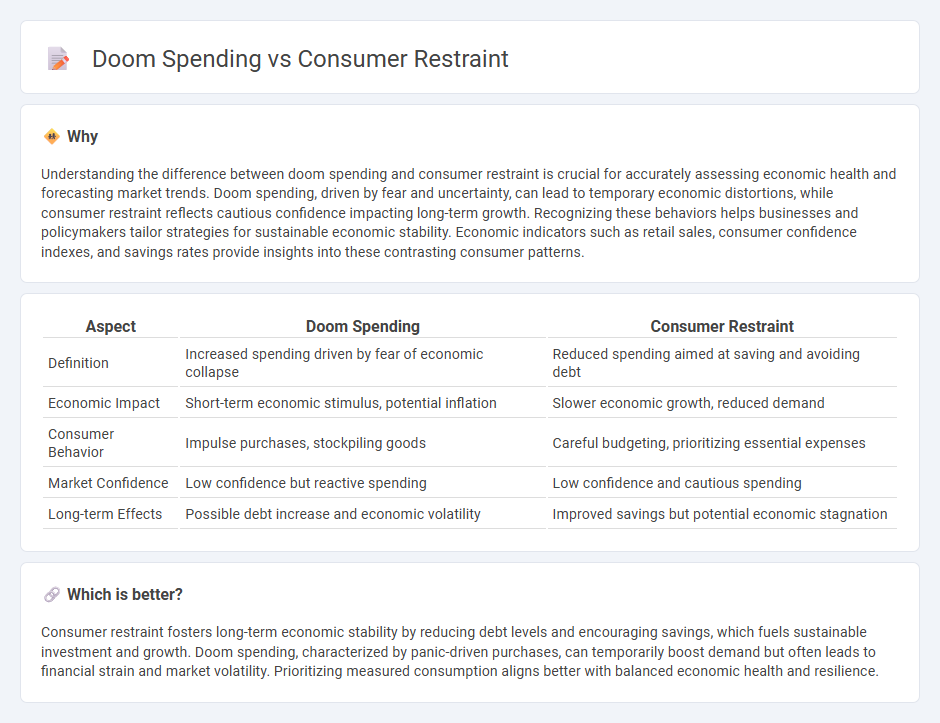
Understanding the difference between doom spending and consumer restraint is crucial for accurately assessing economic health and forecasting market trends. Doom spending, driven by fear and uncertainty, can lead to temporary economic distortions, while consumer restraint reflects cautious confidence impacting long-term growth. Recognizing these behaviors helps businesses and policymakers tailor strategies for sustainable economic stability. Economic indicators such as retail sales, consumer confidence indexes, and savings rates provide insights into these contrasting consumer patterns.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Doom Spending | Consumer Restraint |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increased spending driven by fear of economic collapse | Reduced spending aimed at saving and avoiding debt |
| Economic Impact | Short-term economic stimulus, potential inflation | Slower economic growth, reduced demand |
| Consumer Behavior | Impulse purchases, stockpiling goods | Careful budgeting, prioritizing essential expenses |
| Market Confidence | Low confidence but reactive spending | Low confidence and cautious spending |
| Long-term Effects | Possible debt increase and economic volatility | Improved savings but potential economic stagnation |
Which is better?
Consumer restraint fosters long-term economic stability by reducing debt levels and encouraging savings, which fuels sustainable investment and growth. Doom spending, characterized by panic-driven purchases, can temporarily boost demand but often leads to financial strain and market volatility. Prioritizing measured consumption aligns better with balanced economic health and resilience.
Connection
Doom spending refers to increased consumer purchases driven by fear of future shortages, often seen during economic uncertainty or crises. Consumer restraint occurs when shoppers limit their spending due to concerns about economic stability, inflation, or job security. These opposing behaviors highlight how fear and uncertainty can simultaneously push consumers toward either stockpiling goods or tightening their budgets, impacting overall economic demand patterns.
Key Terms
Discretionary Income
Consumer restraint often occurs when individuals prioritize saving or essential expenses, limiting discretionary income use. Doom spending, conversely, drives increased purchases of non-essentials as a coping mechanism during economic uncertainty, tapping deeply into discretionary income. Explore how these contrasting behaviors impact financial stability and market trends.
Behavioral Economics
Consumer restraint reflects a deliberate reduction in spending driven by economic uncertainty, risk aversion, or shifts in preferences, highlighting the role of loss aversion and future discounting in behavioral economics. Doom spending, conversely, embodies impulsive, anxiety-driven expenditures aimed at instant gratification or emotional relief during crises, influenced by heuristic biases and affective forecasting errors. Explore the psychological mechanisms behind these contrasting behaviors to better understand their impact on economic cycles.
Consumption Smoothing
Consumer restraint involves reducing spending to manage limited resources, while doom spending refers to excessive purchases driven by anxiety about the future. Both behaviors relate to consumption smoothing, where individuals adjust their spending over time to maintain stable living standards despite economic uncertainty. Explore the nuances of consumption smoothing to understand how these opposing behaviors impact financial planning.
Source and External Links
Investigating Consumer Restraint - This study examines motivations and human values behind everyday consumers' participation in Buy Nothing Day, using a hybrid content analysis of Twitter data.
Restraint That Blinds - This research explores how the numerosity of cost information influences self-control among restrained consumers, finding that they are more reliant on numerosity cues.
Investigating Consumer Restraint Using Hybrid Content Analysis - The study investigates consumer motivations and values for participating in Buy Nothing Day, highlighting consumerism and personal welfare as primary factors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com