Nearshoring entails relocating business operations to nearby countries, reducing shipping costs and improving supply chain efficiency, while insourcing focuses on utilizing internal resources to manage production and services within the company. Both strategies aim to optimize operational costs and enhance control over quality and delivery times. Explore deeper insights into how nearshoring and insourcing impact global economic trends and competitive advantage.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between nearshoring and insourcing is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and cost management. Nearshoring involves relocating production to nearby countries to reduce transportation time and costs, while insourcing means bringing processes in-house to enhance control and quality. Identifying the right strategy impacts risk mitigation, operational agility, and competitive advantage in a global market. Businesses leverage these distinctions to balance investment, labor markets, and geopolitical factors effectively.
Comparison Table
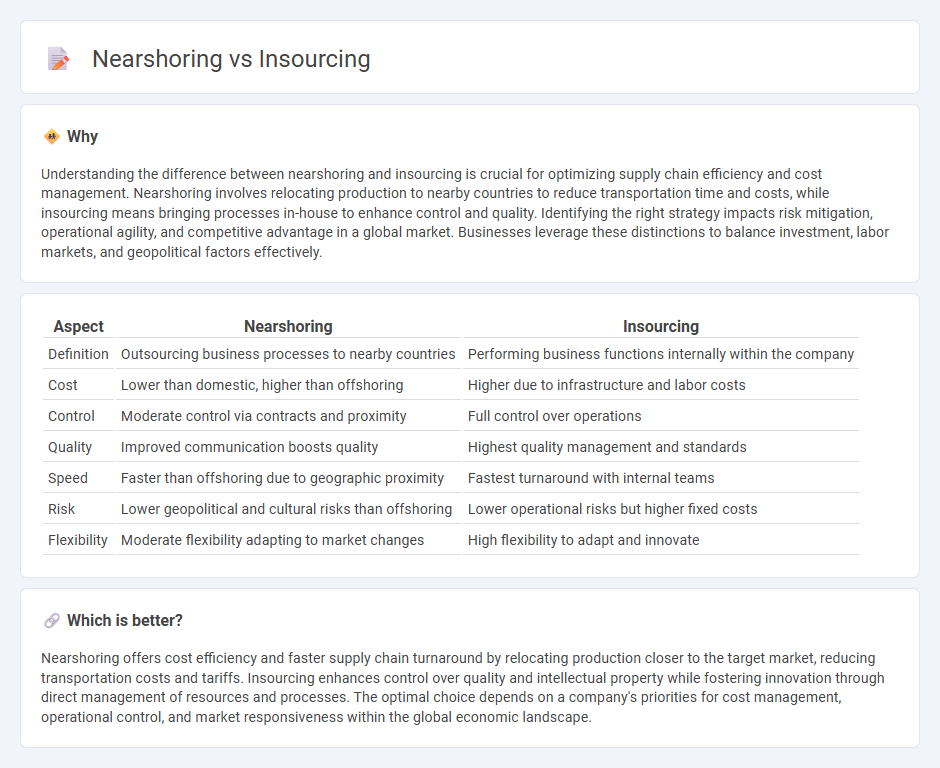
| Aspect | Nearshoring | Insourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outsourcing business processes to nearby countries | Performing business functions internally within the company |
| Cost | Lower than domestic, higher than offshoring | Higher due to infrastructure and labor costs |
| Control | Moderate control via contracts and proximity | Full control over operations |
| Quality | Improved communication boosts quality | Highest quality management and standards |
| Speed | Faster than offshoring due to geographic proximity | Fastest turnaround with internal teams |
| Risk | Lower geopolitical and cultural risks than offshoring | Lower operational risks but higher fixed costs |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility adapting to market changes | High flexibility to adapt and innovate |
Which is better?
Nearshoring offers cost efficiency and faster supply chain turnaround by relocating production closer to the target market, reducing transportation costs and tariffs. Insourcing enhances control over quality and intellectual property while fostering innovation through direct management of resources and processes. The optimal choice depends on a company's priorities for cost management, operational control, and market responsiveness within the global economic landscape.
Connection
Nearshoring and insourcing are interconnected strategies that enhance supply chain resilience and reduce operational costs by relocating production closer to the company's home country. Nearshoring minimizes logistical delays and tariffs by shifting manufacturing to nearby regions, while insourcing brings critical processes in-house to improve quality control and innovation. Together, these approaches optimize resource allocation, boost local economies, and strengthen competitive advantage in a global marketplace.
Key Terms
Labor Costs
Insourcing minimizes labor costs by utilizing existing in-house teams, eliminating outsourcing fees and allowing greater control over employee productivity and quality. Nearshoring reduces expenses through geographic proximity, lower wages than onshore labor, and reduced shipping costs compared to offshore alternatives. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which labor cost strategy aligns best with your business goals.
Supply Chain
Insourcing in supply chain management involves bringing production or logistics processes back in-house to increase control and reduce dependency on external vendors, while nearshoring relocates these operations closer to the company's primary market, often within neighboring countries. Nearshoring offers benefits such as reduced transportation costs and shorter lead times compared to offshore outsourcing, whereas insourcing enhances flexibility and quality control within the supply chain. Explore more about how insourcing and nearshoring strategies can optimize your supply chain efficiency and resilience.
Operational Control
Insourcing enhances operational control by consolidating processes within the company's infrastructure, allowing for direct management and rapid response to issues. Nearshoring offers improved control compared to offshoring by situating operations closer geographically, reducing communication delays and enabling smoother collaboration. Explore in-depth comparisons to determine the best strategy for maximizing your operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
What Is Insourcing and How It Works (With Examples) - Insourcing is the process of bringing staff or expertise from outside the company or within the organization to complete tasks, offering greater efficiency, quality control, and direct management compared to outsourcing.
What Is Insourcing? Definition, Benefits, And Examples - Insourcing means assigning tasks or projects to internal departments or teams rather than seeking external contractors, leveraging in-house expertise and resources for cost savings and enhanced operational flexibility.
Insourcing: Definition, Examples, vs. Outsourcing - Insourcing involves reassigning business operations or projects to internal staff and resources, sometimes building cross-functional teams within the company for improved outcomes and alignment with business strategies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com