Micro-mobility solutions, including e-scooters and shared bicycles, offer cost-effective, environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional ride-hailing services, reducing urban congestion and emissions. Ride-hailing platforms provide convenience and accessibility but often contribute to increased traffic and higher operational costs. Explore the economic impacts and future trends of micro-mobility versus ride-hailing to understand their roles in modern urban transportation.
Why it is important
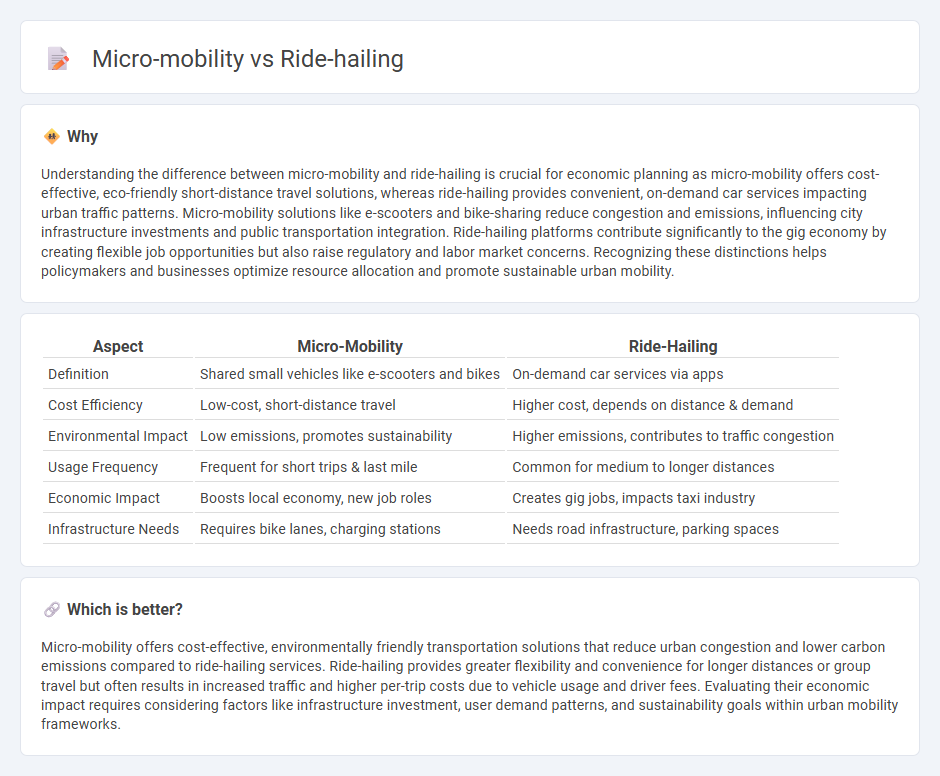
Understanding the difference between micro-mobility and ride-hailing is crucial for economic planning as micro-mobility offers cost-effective, eco-friendly short-distance travel solutions, whereas ride-hailing provides convenient, on-demand car services impacting urban traffic patterns. Micro-mobility solutions like e-scooters and bike-sharing reduce congestion and emissions, influencing city infrastructure investments and public transportation integration. Ride-hailing platforms contribute significantly to the gig economy by creating flexible job opportunities but also raise regulatory and labor market concerns. Recognizing these distinctions helps policymakers and businesses optimize resource allocation and promote sustainable urban mobility.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Micro-Mobility | Ride-Hailing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared small vehicles like e-scooters and bikes | On-demand car services via apps |
| Cost Efficiency | Low-cost, short-distance travel | Higher cost, depends on distance & demand |
| Environmental Impact | Low emissions, promotes sustainability | Higher emissions, contributes to traffic congestion |
| Usage Frequency | Frequent for short trips & last mile | Common for medium to longer distances |
| Economic Impact | Boosts local economy, new job roles | Creates gig jobs, impacts taxi industry |
| Infrastructure Needs | Requires bike lanes, charging stations | Needs road infrastructure, parking spaces |
Which is better?
Micro-mobility offers cost-effective, environmentally friendly transportation solutions that reduce urban congestion and lower carbon emissions compared to ride-hailing services. Ride-hailing provides greater flexibility and convenience for longer distances or group travel but often results in increased traffic and higher per-trip costs due to vehicle usage and driver fees. Evaluating their economic impact requires considering factors like infrastructure investment, user demand patterns, and sustainability goals within urban mobility frameworks.
Connection
Micro-mobility and ride-hailing services are interconnected through their shared goal of providing efficient, last-mile transportation solutions in urban economies. Both sectors contribute to reducing traffic congestion, lowering carbon emissions, and creating new economic opportunities by integrating digital platforms with urban mobility infrastructure. Their symbiotic relationship drives innovation and expands consumer choices, reshaping urban transport ecosystems and supporting sustainable economic growth.
Key Terms
Market Segmentation
Ride-hailing services primarily target urban commuters seeking convenience and speed, catering to individuals without personal vehicles or those avoiding public transit during peak hours. Micro-mobility options, including e-scooters and bike-sharing, appeal to environmentally conscious users and short-distance travelers aiming to reduce carbon footprints and enhance last-mile connectivity. Explore detailed insights on market segmentation and consumer behaviors to optimize transportation solutions effectively.
Pricing Model
Ride-hailing services typically employ dynamic pricing models that adjust fares based on demand, distance, and time, while micro-mobility providers often offer flat rates or subscription plans for short trips, emphasizing affordability and accessibility. Surge pricing in ride-hailing can lead to higher costs during peak hours, contrasting with the predictable pricing of micro-mobility options like e-scooters and bike shares. Explore the evolving pricing strategies shaping urban transportation and how they impact consumer choices.
Last-Mile Connectivity
Ride-hailing services offer convenient door-to-door transportation, often addressing longer last-mile distances with flexible routing and on-demand availability. Micro-mobility options, such as e-scooters and bike-sharing, provide eco-friendly, cost-effective solutions for shorter last-mile trips, particularly in dense urban areas. Explore how integrating ride-hailing and micro-mobility can optimize last-mile connectivity and transform urban transportation.
Source and External Links
Ride-hailing - What it is and how it works? - Car Rental Glossary - Ride-hailing lets customers order personalized rides via a smartphone app, with payment handled automatically and no stops made for other passengers.
Ride-hailing vs ride-sharing - what's the difference? - ATOM Mobility - Ride-hailing is the on-demand hiring of a driver through an app, mainly for taxi-like services but also covering other personalized transport needs.
Ride-Hailing vs. Ride-Sharing: The Key Difference - Ecolane - In ride-hailing, a rider hires a personal driver for a direct trip without sharing the vehicle or making additional stops for other passengers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com