Price gouging involves raising prices excessively during high demand or emergencies, exploiting consumers, while loss leader pricing sets products below cost to attract customers and boost overall sales. Both strategies impact market behavior differently and reflect varied business ethics and regulatory responses. Explore these pricing tactics to understand their effects on consumer welfare and competition.
Why it is important
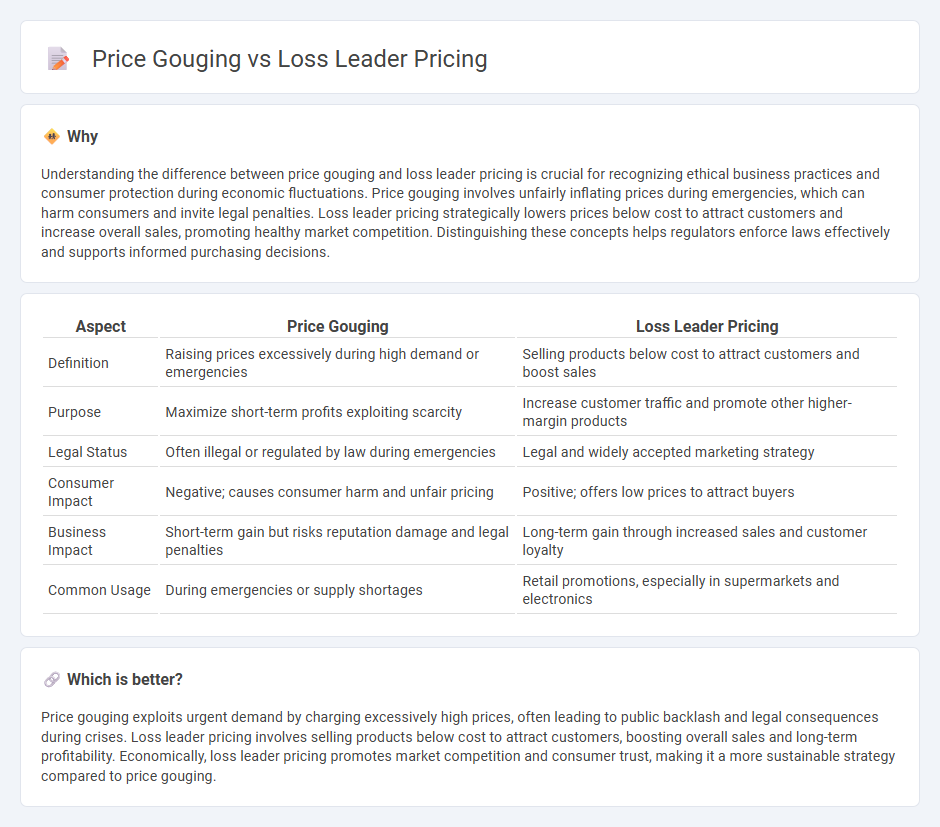
Understanding the difference between price gouging and loss leader pricing is crucial for recognizing ethical business practices and consumer protection during economic fluctuations. Price gouging involves unfairly inflating prices during emergencies, which can harm consumers and invite legal penalties. Loss leader pricing strategically lowers prices below cost to attract customers and increase overall sales, promoting healthy market competition. Distinguishing these concepts helps regulators enforce laws effectively and supports informed purchasing decisions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Price Gouging | Loss Leader Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raising prices excessively during high demand or emergencies | Selling products below cost to attract customers and boost sales |
| Purpose | Maximize short-term profits exploiting scarcity | Increase customer traffic and promote other higher-margin products |
| Legal Status | Often illegal or regulated by law during emergencies | Legal and widely accepted marketing strategy |
| Consumer Impact | Negative; causes consumer harm and unfair pricing | Positive; offers low prices to attract buyers |
| Business Impact | Short-term gain but risks reputation damage and legal penalties | Long-term gain through increased sales and customer loyalty |
| Common Usage | During emergencies or supply shortages | Retail promotions, especially in supermarkets and electronics |
Which is better?
Price gouging exploits urgent demand by charging excessively high prices, often leading to public backlash and legal consequences during crises. Loss leader pricing involves selling products below cost to attract customers, boosting overall sales and long-term profitability. Economically, loss leader pricing promotes market competition and consumer trust, making it a more sustainable strategy compared to price gouging.
Connection
Price gouging and loss leader pricing both influence consumer behavior by manipulating price points to affect demand, yet they operate in fundamentally opposite ways. Price gouging exploits supply constraints to dramatically increase prices during emergencies, whereas loss leader pricing deliberately sets prices below cost to attract customers and stimulate sales. These contrasting pricing strategies highlight different economic approaches to market control and consumer influence.
Key Terms
Predatory Pricing
Loss leader pricing involves setting prices below cost to attract customers, often used strategically to increase market share or drive competitors out. Predatory pricing, a form of price gouging, aggressively undercuts rivals with the intent to eliminate competition and later raise prices. Explore more about how predatory pricing impacts market dynamics and legal boundaries.
Market Power
Loss leader pricing strategically sets products below cost to attract customers and increase market share, leveraging market power to boost sales volume and encourage repeat purchases. Price gouging exploits market power during shortages or emergencies by charging excessively high prices, often triggering legal and ethical concerns. Explore the nuances between loss leader pricing and price gouging to better understand their impact on competitive dynamics and consumer protection.
Consumer Protection
Loss leader pricing strategically sets products below cost to attract consumers and increase overall sales volume, benefiting both buyers and sellers. Price gouging exploits emergencies by excessively inflating prices, often leading to consumer harm and legal penalties under Consumer Protection laws. Explore how regulations differentiate these practices to safeguard consumers effectively.
Source and External Links
Loss leader - Wikipedia - Loss leader pricing is a strategy where a product is sold below market cost to attract customers, who are then expected to buy other higher-margin products, generating overall profit for the vendor.
What is a Loss Leader? - DealHub - Loss leader pricing involves selling a product at a loss to draw customers in, with the goal that they will purchase additional profitable items or become long-term customers.
What is Loss Leader Pricing? A Guide To How It Works - Shopify - Loss leader pricing is a legal marketing tactic to attract customers with low-priced popular products to boost overall sales, distinct from predatory pricing, which is designed to push competitors out of the market.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com