Circular economy focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency by recycling, reusing, and regenerating materials within closed-loop systems. Blue economy emphasizes sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and ecosystem health, integrating marine biodiversity conservation with innovation. Explore how these models transform sustainable development and drive economic resilience.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Circular Economy and Blue Economy is crucial for effective resource management and sustainable development. Circular Economy focuses on minimizing waste through recycling and reuse across all industries, while Blue Economy emphasizes the sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and ocean ecosystem health. Recognizing these differences helps policymakers and businesses implement targeted strategies that balance economic growth with environmental preservation. Knowledge of both models drives innovation in sustainability, reducing ecological footprints and promoting long-term economic resilience.
Comparison Table
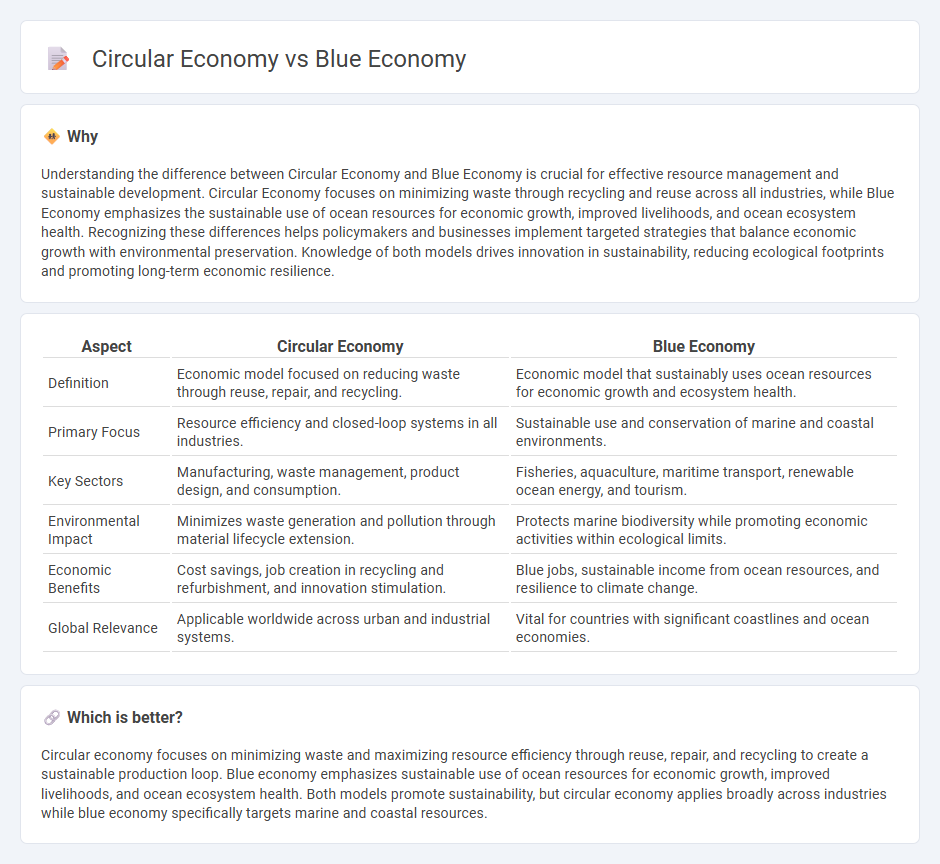
| Aspect | Circular Economy | Blue Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic model focused on reducing waste through reuse, repair, and recycling. | Economic model that sustainably uses ocean resources for economic growth and ecosystem health. |
| Primary Focus | Resource efficiency and closed-loop systems in all industries. | Sustainable use and conservation of marine and coastal environments. |
| Key Sectors | Manufacturing, waste management, product design, and consumption. | Fisheries, aquaculture, maritime transport, renewable ocean energy, and tourism. |
| Environmental Impact | Minimizes waste generation and pollution through material lifecycle extension. | Protects marine biodiversity while promoting economic activities within ecological limits. |
| Economic Benefits | Cost savings, job creation in recycling and refurbishment, and innovation stimulation. | Blue jobs, sustainable income from ocean resources, and resilience to climate change. |
| Global Relevance | Applicable worldwide across urban and industrial systems. | Vital for countries with significant coastlines and ocean economies. |
Which is better?
Circular economy focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency through reuse, repair, and recycling to create a sustainable production loop. Blue economy emphasizes sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and ocean ecosystem health. Both models promote sustainability, but circular economy applies broadly across industries while blue economy specifically targets marine and coastal resources.
Connection
Circular economy and Blue economy are connected through their shared emphasis on sustainability and resource efficiency, particularly in marine and coastal environments. Circular economy principles promote reducing waste and reusing materials, which supports the Blue economy's focus on sustainable use of ocean resources. Integrating these approaches enhances economic growth while protecting marine biodiversity and reducing environmental impact.
Key Terms
Sustainable ocean resources (Blue economy)
The blue economy emphasizes the sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and ocean ecosystem health, integrating fisheries, marine energy, and coastal tourism. Circular economy principles in ocean resource management prioritize waste reduction, recycling, and resource efficiency to minimize marine pollution and preserve biodiversity. Explore more about how blue and circular economies synergize to promote sustainable ocean resource management.
Resource efficiency (Circular economy)
Resource efficiency in the circular economy emphasizes minimizing waste through reuse, recycling, and sustainable design, effectively closing material loops to preserve finite resources. The blue economy, while also valuing resource efficiency, prioritizes sustainable use of ocean resources and marine ecosystems to support economic growth and environmental health. Explore the synergies and distinctions between these approaches to enhance sustainable development strategies.
Waste minimization
The blue economy emphasizes sustainable use of ocean resources to drive economic growth while minimizing marine waste, focusing on renewable energy, aquaculture, and waste reduction in maritime industries. Circular economy centers on designing out waste through recycling, reusing, and regenerating materials to create closed-loop systems in various sectors, including manufacturing and consumer products. Explore the distinct strategies and benefits these approaches offer to optimize waste minimization in environmental and economic contexts.
Source and External Links
Blue Economy Definitions - United Nations - The blue economy refers to the sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth, jobs, and livelihoods while ensuring the health of the ocean ecosystem.
What is the blue economy? - LSE Grantham Research Institute - The blue economy encompasses all economic activities related to oceans, seas, and coasts, aiming to use resources sustainably while protecting marine ecosystems.
Blue economy - Wikipedia - The blue economy involves the exploitation, preservation, and regeneration of marine environments, including traditional sectors like fisheries and tourism, as well as emerging industries such as renewable energy and aquaculture.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com