De-dollarisation refers to the process where countries reduce their reliance on the US dollar for international trade and reserves, aiming to decrease vulnerability to dollar fluctuations and US monetary policies. Reserve currency diversification involves expanding the portfolio of currencies held by central banks beyond the dollar, including euros, yuan, and gold, to enhance economic stability and geopolitical autonomy. Explore the implications of these strategies on global economic dynamics and currency markets.
Why it is important
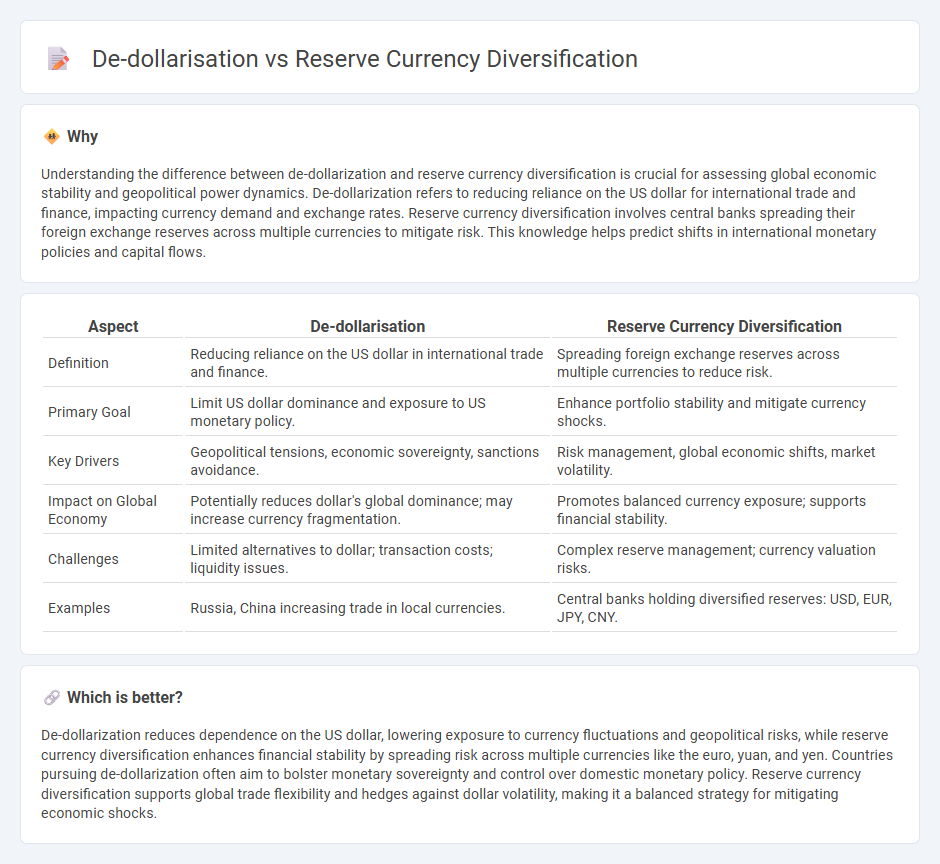
Understanding the difference between de-dollarization and reserve currency diversification is crucial for assessing global economic stability and geopolitical power dynamics. De-dollarization refers to reducing reliance on the US dollar for international trade and finance, impacting currency demand and exchange rates. Reserve currency diversification involves central banks spreading their foreign exchange reserves across multiple currencies to mitigate risk. This knowledge helps predict shifts in international monetary policies and capital flows.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | De-dollarisation | Reserve Currency Diversification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade and finance. | Spreading foreign exchange reserves across multiple currencies to reduce risk. |
| Primary Goal | Limit US dollar dominance and exposure to US monetary policy. | Enhance portfolio stability and mitigate currency shocks. |
| Key Drivers | Geopolitical tensions, economic sovereignty, sanctions avoidance. | Risk management, global economic shifts, market volatility. |
| Impact on Global Economy | Potentially reduces dollar's global dominance; may increase currency fragmentation. | Promotes balanced currency exposure; supports financial stability. |
| Challenges | Limited alternatives to dollar; transaction costs; liquidity issues. | Complex reserve management; currency valuation risks. |
| Examples | Russia, China increasing trade in local currencies. | Central banks holding diversified reserves: USD, EUR, JPY, CNY. |
Which is better?
De-dollarization reduces dependence on the US dollar, lowering exposure to currency fluctuations and geopolitical risks, while reserve currency diversification enhances financial stability by spreading risk across multiple currencies like the euro, yuan, and yen. Countries pursuing de-dollarization often aim to bolster monetary sovereignty and control over domestic monetary policy. Reserve currency diversification supports global trade flexibility and hedges against dollar volatility, making it a balanced strategy for mitigating economic shocks.
Connection
De-dollarisation reduces reliance on the US dollar by encouraging countries to use alternative currencies in international trade and reserves, directly promoting reserve currency diversification. This strategy mitigates geopolitical risks and currency exposure by spreading foreign exchange reserves across multiple stable currencies such as the euro, yuan, and gold. Expanding reserve currency options enhances global financial stability and cushions economies against dollar volatility and sanctions.
Key Terms
Foreign Exchange Reserves
Foreign Exchange Reserves management increasingly emphasizes reserve currency diversification to reduce dependency on the U.S. dollar and mitigate associated risks such as exchange rate volatility and geopolitical tensions. Central banks globally are reallocating a portion of their reserves into alternative assets including the euro, Chinese yuan, gold, and digital currencies as part of strategic de-dollarization efforts. Explore how these trends shape global financial stability and influence international monetary policy.
Currency Basket
Reserve currency diversification involves spreading foreign exchange reserves across multiple currencies to reduce reliance on the US dollar and mitigate risks associated with dollar fluctuations. De-dollarization refers to the process where countries actively reduce the use of the US dollar in trade, finance, and reserves to enhance monetary sovereignty and decrease exposure to US monetary policy. Explore how currency baskets play a pivotal role in balancing these strategies and promoting global financial stability.
Trade Settlement
Reserve currency diversification involves expanding the range of currencies used for international trade settlement to reduce reliance on the US dollar, enhancing financial stability and mitigating geopolitical risks. De-dollarisation specifically aims to replace the US dollar in trade transactions with alternative currencies, often driven by countries seeking to assert monetary sovereignty and reduce exposure to US-centric sanctions. Explore the evolving dynamics and strategic implications of trade settlement in a multipolar currency world.
Source and External Links
Reserve diversification and global foreign exchange markets - Emerging market central banks are considering diversifying reserves away from US dollar assets toward the euro, Australian and Canadian dollars, and potentially the Chinese renminbi, driven by factors like interest rates and confidence in currency stability, but dollar dominance has remained resilient post-crisis.
Dollar Dominance in the International Reserve System - Although the US dollar remains the dominant reserve currency, there is a gradual shift toward diversification with many countries increasing allocations to nontraditional reserve currencies and gold to mitigate geopolitical and sanctions risks.
Dollar Diversification: Why Now? - Investors are advised to diversify away from a 100% dollar portfolio to a mix including the euro, Japanese yen, and gold, potentially targeting around 30% non-dollar exposure to improve portfolio resilience amid geopolitical tensions and economic uncertainty.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com