The circular economy focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency through reuse, recycling, and sustainable design, while the green economy emphasizes reducing environmental risks and promoting sustainable development by integrating eco-friendly policies. Both models aim to foster economic growth that aligns with environmental preservation and social well-being. Explore more to understand how these economic frameworks can shape a sustainable future.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between circular economy and green economy is vital for implementing targeted sustainability strategies. Circular economy focuses on resource efficiency by designing out waste and promoting reuse and recycling in production and consumption. Green economy emphasizes reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities while promoting sustainable development and social well-being. Distinguishing these concepts helps policymakers and businesses allocate resources effectively to achieve economic growth with minimal environmental impact.
Comparison Table
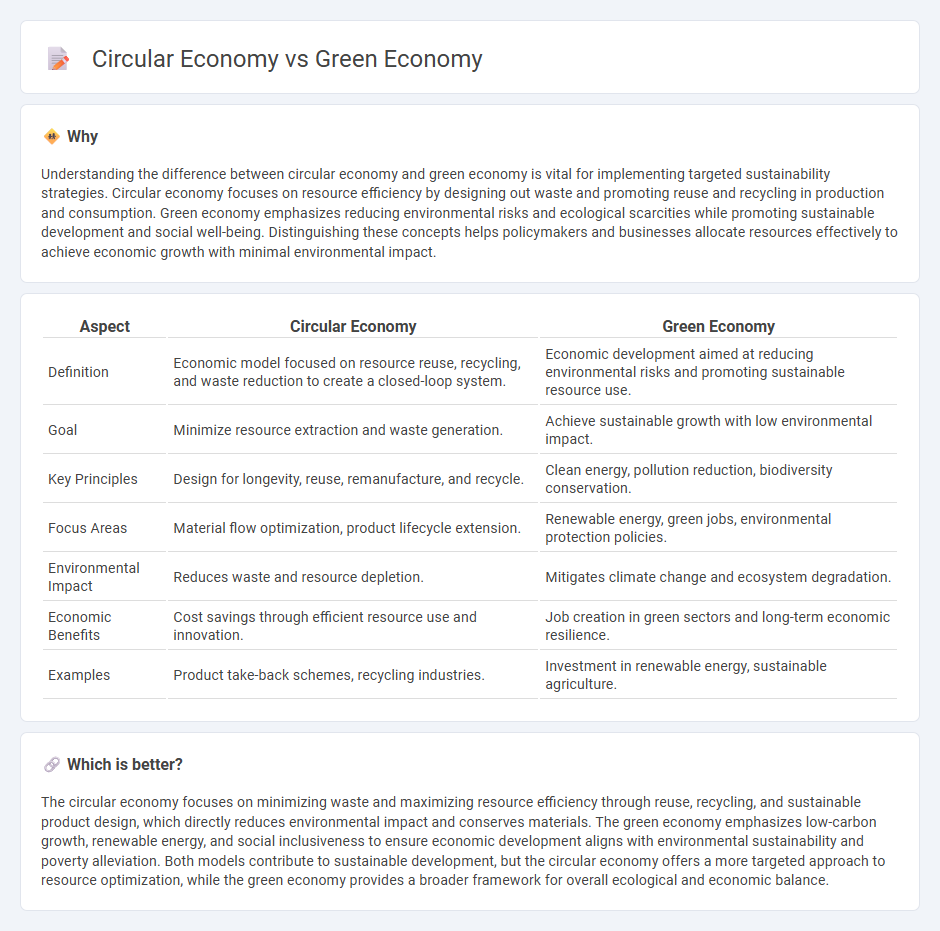
| Aspect | Circular Economy | Green Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic model focused on resource reuse, recycling, and waste reduction to create a closed-loop system. | Economic development aimed at reducing environmental risks and promoting sustainable resource use. |
| Goal | Minimize resource extraction and waste generation. | Achieve sustainable growth with low environmental impact. |
| Key Principles | Design for longevity, reuse, remanufacture, and recycle. | Clean energy, pollution reduction, biodiversity conservation. |
| Focus Areas | Material flow optimization, product lifecycle extension. | Renewable energy, green jobs, environmental protection policies. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste and resource depletion. | Mitigates climate change and ecosystem degradation. |
| Economic Benefits | Cost savings through efficient resource use and innovation. | Job creation in green sectors and long-term economic resilience. |
| Examples | Product take-back schemes, recycling industries. | Investment in renewable energy, sustainable agriculture. |
Which is better?
The circular economy focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency through reuse, recycling, and sustainable product design, which directly reduces environmental impact and conserves materials. The green economy emphasizes low-carbon growth, renewable energy, and social inclusiveness to ensure economic development aligns with environmental sustainability and poverty alleviation. Both models contribute to sustainable development, but the circular economy offers a more targeted approach to resource optimization, while the green economy provides a broader framework for overall ecological and economic balance.
Connection
Circular economy and green economy are interconnected through their shared goal of promoting sustainability by minimizing waste and conserving resources. Both models emphasize reducing environmental impact by encouraging recycling, reusing materials, and using renewable energy sources. Implementing circular economy principles supports green economy targets by fostering resource efficiency and driving low-carbon economic growth.
Key Terms
Sustainability
The green economy emphasizes reducing environmental risks and promoting sustainable development through low-carbon technologies and renewable energy use. In contrast, the circular economy focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency by designing products for reuse, recycling, and regeneration. Explore how these approaches drive sustainability and transform economic systems for a resilient future.
Resource Efficiency
Green economy emphasizes sustainable development by reducing environmental risks and promoting renewable resources, while circular economy prioritizes minimizing waste through reuse, recycling, and resource recovery. Resource efficiency in a green economy involves optimizing energy use and cutting emissions, whereas circular economy strategies focus on extending product lifecycles and maintaining materials within the production cycle. Explore how these approaches integrate to maximize sustainability and economic growth.
Waste Minimization
The green economy emphasizes reducing environmental impact through sustainable resource use and promoting renewable energy, while the circular economy specifically targets waste minimization by designing products for reuse, repair, and recycling to maintain material value. Circular economy strategies include closed-loop production systems aiming for zero waste, contrasting with the broader green economy's focus on overall ecological balance and economic growth. Explore more about how these concepts drive innovative waste management solutions and sustainable development.
Source and External Links
Green economy: definition, meaning and principles | Enel X - The green economy is a model that aims for sustainable development through both public and private investment to create infrastructure that supports social and environmental sustainability.
Green economy - Wikipedia - A green economy focuses on reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities by decoupling economic growth from resource use and adverse environmental impacts, with an emphasis on fostering jobs and growth in sustainable sectors.
The 5 Principles of Green Economy - An inclusive green economy is defined as low-carbon, resource-conserving, diverse, and circular, promoting both human well-being and ecological health.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com